1、货物出货与进货
#if 0
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
/*
某商店经销一种货物。货物购进和卖出时以箱为单位。各箱
的重量不一样,因此商店需要记录目前库存的总重量,现在用
C++模拟商店货物购进和卖出的情况
*/
class Goods {
public:
Goods() {
weight = 0;
next = NULL;
cout << "创建了一个重量为:" << weight << "的货物" << endl;
}
Goods(int w) {
//需要创建一个w的货物,并且仓库加这个重量
weight = w;
next = NULL;
total_weight += w;
cout << "创建了一个重量为:" << weight << "的货物" << endl;
}
static int get_total_wight() {
return total_weight;
}
~Goods() {
//需要删除一个w的货物,并且仓库减这个重量
cout << "删除了一个重量为:" << weight << "的货物" << endl;
total_weight -= weight;
}
public:
Goods *next;
private:
int weight;
static int total_weight;
};
int Goods::total_weight = 0;
void buy(Goods *&head, int w) {
//创建一个货物 重量为w
Goods *new_goods = new Goods(w);
if (head == NULL)
head = new_goods;
else {
new_goods->next = head; //头结点插入
head = new_goods;
}
}
void sale(Goods * &head) {
if (head == NULL) {
cout << "仓库为空" << endl;
return;
}
Goods *temp = head;
head = head->next;
delete temp;
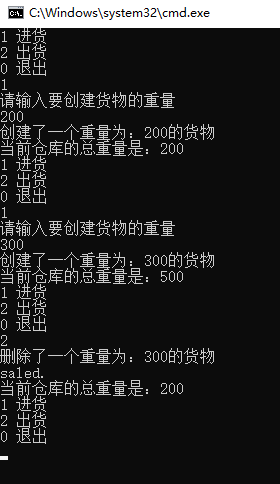
cout << "saled." << endl;
}
int main(void) {
int choice = 0;
int w;
Goods *head = NULL; //利用链表管理 无头指针
do
{
cout << "1 进货" << endl;
cout << "2 出货" << endl;
cout << "0 退出" << endl;
cin >> choice;
switch (choice)
{
case 1:
cout << "请输入要创建货物的重量" << endl;
cin >> w;
buy(head, w);
break;
case 2:
sale(head);
break;
case 0:
return 0;
break;
default:
break;
}
cout << "当前仓库的总重量是:" <<Goods::get_total_wight()<< endl;
} while (1);
}
#endif
我的思路:
#if 0
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
/*
某商店经销一种货物。货物购进和卖出时以箱为单位。各箱
的重量不一样,因此商店需要记录目前库存的总重量,现在用
C++模拟商店货物购进和卖出的情况
*/
class Goods {
public:
Goods(int num, int weight) {
m_num = num;
m_weight = weight;
}
void get_in_good() {
m_sum_weight += m_num*m_weight;
}
void get_out_good(int num, int weight) {
m_sum_weight -= num*weight;
}
static int get_m_sum_weight(){
return m_sum_weight;
}
private:
int m_num;
int m_weight;
static int m_sum_weight;
};
int Goods::m_sum_weight = 0;
int main() {
Goods g1(1, 20);
Goods g2(2, 30);
Goods g3(3, 50);
g1.get_in_good();
g2.get_in_good();
g3.get_in_good();
g2.get_out_good(1, 30);
cout << Goods::get_m_sum_weight() << endl;
return 0;
}
#endif
2、数组类的封装
MyArray.h
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class MyArray
{
public:
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const MyArray &obj);
friend istream& operator>>(istream& os, MyArray &obj);
friend bool operator==(const MyArray &a1, const MyArray& a2); //全局函数
bool operator!=(const MyArray& another); //成员函数
MyArray();
MyArray(int length);
MyArray(const MyArray &obj);
MyArray& operator=(const MyArray &obi);
int& operator[](int index) const;
void setData(int index, int value);
int getData(int index);
int getLength() const;
~MyArray();
private:
int m_length;
int *m_space; //指向堆上空间 数组首地址
};
MyArray.cpp
#include "MyArray.h"
MyArray::MyArray() {
cout << "MyArray()" << endl;
m_length = 0;
m_space = NULL;
}
MyArray::MyArray(int length){
/*if (length < 0)
{
m_length = 0;
m_space = new int[length];
}
else {
m_length = length;
m_space = new int[length];
}*/
//等价于
if (length < 0)
{
length = 0;
}
m_length = length;
m_space = new int[length];
}
MyArray::MyArray(const MyArray &obj) {
if (obj.m_length>=0)
{
if (m_space != NULL) {
delete[] m_space;
m_space = NULL;
}
this->m_length = obj.m_length;
this->m_space = new int[this->m_length];
for (int i = 0; i < m_length; i++) //数据元素深拷贝
{
this->m_space[i] = obj.m_space[i];
}
}
}
MyArray::~MyArray() {
if (m_space != NULL) {
delete[] m_space;
m_space = NULL;
}
}
MyArray& MyArray::operator=(const MyArray &another) {
if (this == &another)
{
return *this;
}
if (this->m_space != NULL) {
delete this->m_space;
this->m_space = NULL;
this->m_length = 0;
}
if (another.m_length >= 0)
{
this->m_length = another.m_length;
this->m_space = new int[this->m_length];
for (int i = 0; i < m_length; i++) //数据元素深拷贝
{
this->m_space[i] = another.m_space[i];
}
}
return *this;
}
int& MyArray::operator[](int index) const{
return this->m_space[index];
}
void MyArray::setData(int index, int value) {
if (m_space != NULL) {
//a1.setData(i, i);
m_space[index] = value;
}
}
int MyArray::getData(int index) {
return m_space[index];
}
int MyArray::getLength() const {
return m_length;
}
bool MyArray::operator!=(const MyArray& another) {
/*if (this->getLength() != another.getLength()) {
return true;
}
for (int i = 0; i < this->getLength(); i++) {
if (this->m_space[i] != another.m_space[i])
return true;
}
return false;*/
//等价于
return !(*this == another);
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const MyArray &obj) { //防止被修改添加const后报错
//原因分析:在调用getLengt()传入的是&obj,并不是const类型
//安全性高的转换为安全性低的会报错
//下面的operator[](&obj)传入的是&obj,并不是const类型 所以报错
//修改方法就是加上在getLength() 函数后添加const
//修改方法就是加上在operator[](int index)函数后添加const
os << "遍历整个数组" << endl;
//for (int i = 0; i <obj.m_length; i++) 无法修改
for (int i = 0; i <obj.getLength(); i++)
{
//os << obj.m_space[i] << " ";
//等价于
os << obj[i] << " ";
}
return os;
}
//istream& operator >> (istream& is,MyArray &obj) {
// cout << "请输入数组元素个数:";
// cin >> obj.m_length;
// obj.m_space = new int[obj.m_length];
// for (int i = 0; i < obj.m_length; i++)
// {
// int j;
// cin >> j;
// obj.m_space[i] = j;
// }
// return is;
//
//}
istream& operator>>(istream& is, MyArray &array) {
cout << "请输入:" << array.getLength() << "个数" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < array.getLength(); i++)
{
cin >> array[i];
}
return is;
}
bool operator==(const MyArray &a1, const MyArray& a2) {
if (a1.getLength() != a2.getLength()) {
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < a1.getLength(); i++)
{
if (a1.m_space[i] != a2.m_space[i])
return false;
}
return true;
}
main.cpp
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include"MyArray.h"
int main() {
MyArray a1(10);
for (int i = 0; i < a1.getLength(); i++)
{
//a1.setData(i, i);
a1[i] = i + 10; //space[i]=i+10
}
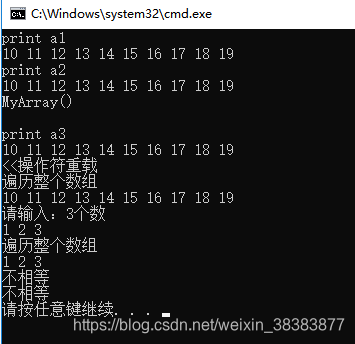
cout << "print a1" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < a1.getLength(); i++)
{
//cout<<a1.getData(i)<<" ";
cout << a1[i] << " " ;
}
MyArray a2 = a1;
cout << endl<<"print a2" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < a2.getLength(); i++)
{
//cout<<a1.getData(i)<<" ";
cout << a2[i] << " " ;
}
cout << endl;
MyArray a3;
a3 = a1;
cout << endl << "print a3" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < a3.getLength(); i++)
{
//cout << a3.getData(i) << " ";
cout << a3[i] << " " ;
}
cout <<endl<< "<<操作符重载" << endl;
cout << a3 << endl;
MyArray array1(3);
cin >> array1;
cout << array1 << endl;
if (array1 == a1) {
cout << "相等" << endl;
}
else
cout << "不相等" << endl;
if (array1 != a1) {
cout << "不相等" << endl;
}
else
cout << "相等" << endl;
}








 本文通过C++实现了一个模拟商店货物进出的系统,包括货物的重量记录和库存管理。此外,还详细介绍了如何封装一个数组类,包括构造、析构、赋值、重载运算符等功能。
本文通过C++实现了一个模拟商店货物进出的系统,包括货物的重量记录和库存管理。此外,还详细介绍了如何封装一个数组类,包括构造、析构、赋值、重载运算符等功能。

















 436
436

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










