总述
上一篇 【网络编程】IO 多路复用 select 讲了 IO 多路复用和 select 的使用方法,这一篇尝试对 epoll 进行使用。
在实现机制上,epoll 对象有 eventpoll 事件池(红黑树)和 rdlist 就绪列表(双向链表)两个核心的数据结构。在使用上,epoll 对外提供了 epoll_create、epoll_ctl、epoll_wait 三个接口:
epoll_create 用来创建一个 epoll 对象;
epoll_ctl 用来向事件池增删事件、修改事件池中已有的事件;
epoll_wait 用来检查就绪列表,获取就绪的 IO 事件;

接口 epoll_create
int epoll_create(int size);epoll_create 只有一个参数 size,本意是用来告知内核想要向 epoll 对象添加的文件描述符的个数,实际到了 linux 2.6.8 版本之后,这个参数不再被内核需要,传参会被忽略,但是为了向后兼容,传参还是应该大于 0。man epoll_create:

如果创建 epoll 对象失败,epoll_create 返回 -1;如果创建成功,epoll_create 返回 epoll 对象的句柄(也是文件描述符,使用完毕后应该 close 掉,否则会导致句柄泄漏)。
接口 epoll_ctl
int epoll_ctl(int epfd, int op, int fd, struct epoll_event *event);epoll_ctl 的 第 1 个参数 是 epoll_create 返回的 epoll 对象的句柄(每个 epoll 对象都有一个独立的事件池,要对事件池进行操作,就要指明具体是哪一个 epoll 对象的事件池)。
第 2 个参数 是要对事件池进行操作的类型,EPOLL_CTL_ADD、EPOLL_CTL_MOD、EPOLL_CTL_DEL 分别对应向事件池增加事件、删除事件、修改已有事件。
第 3 个参数 传入要监听的句柄。
第 4 个参数 传入要监听的事件,类型是指向 epoll_event 结构体的指针。
如果函数执行成功,返回 0;执行失败则返回 -1。
epoll_event
epoll_event 结构体在 epoll_ctl 和 epoll_event 两个接口里都有用到,被用于注册所感兴趣的事件和回传所发生的待处理的事件,epoll_event 结构体包含 events 和 data 两个成员:
struct epoll_event {
__uint32_t events; // 感兴趣的事件和 epoll 的工作模式
epoll_data_t data; // User data variable
};events 是向 epoll 对象注册的事件(感兴趣的要监听的事件)以及 epoll 的工作模式,都有对应的枚举值表示:EPOLLIN 表示感兴趣的事件是第 3 个参数传入的文件描述符可读、EPOLLOUT 表示感兴趣的事件是第 3 个参数传入的文件描述符可写 ···,EPOLLET 指定事件为边缘触发模式。实际传参时,把几个枚举值进行 位或 以后传给 events 成员,eg.
// 向 epoll 对象注册事件,关注句柄是否可读,同时设定 epoll 的工作模式为边缘触发
stEpEvent.events= EPOLLIN | EPOLLET;
stEpEvent.data.fd = iLsnFd_5197;
epoll_ctl(iEpObj, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, iLsnFd_5197, &stEpEvent);data 是一个联合体,其中的 fd 起到了传递 socket 句柄的作用 —— 注册事件时告知 epoll 我们关注的句柄;等到事件就绪时,根据 fd 得知是哪一个句柄上有就绪事件。
typedef union epoll_data {
void *ptr;
int fd;
__uint32_t u32;
__uint64_t u64;
} epoll_data_t;工作模式
epoll 的工作模式有水平触发、边缘触发两种,水平触发、边缘触发指的是 epoll 对于就绪事件的两种提醒方式:
水平触发(Level Trigger,LT)是 epoll 默认的工作模式,只要文件描述符上有就绪事件,每次调用 epoll_wait 就都会返回。带来的不好的影响是,如果有大量的不需要读写的就绪文件描述符,每次调用 epoll_wait 都会返回就绪事件,影响应用程序查找、处理自己感兴趣的文件描述符。
边缘触发(Edge Trigger,ET)是“高速模式”,只有当 socket 的状态发生变化的时候(接收缓冲区从没有数据到有数据,发送缓冲区从满变成不满)才会通知。也就是在 ET 模式下,就绪事件只会被通知一次。也就意味着,在 ET 模式下,必须要“一次性把事情做完”—— 把所有可读数据读完、把所有数据发完 —— 不然下次调用 epoll_wait 也不会有提醒。
接口 epoll_wait
int epoll_wait(int epfd, struct epoll_event * events, int maxevents, int timeout);epoll_wait 的 第 1 个参数 是 epoll_create 返回的 epoll 对象的句柄;
第 2 个参数 是用于回传待处理事件的数组,类型是指向 epoll_event 结构体的指针;
第 3 个参数 传入每次能处理的事件数,也就是告诉内核本次返回的最大的文件描述符数量;
第 4 个参数 传入等待 I/O 事件发生的超时时间,单位是毫秒,传 0 指示立即返回,传 -1 指示永久阻塞;
当事件就绪后,就被加入到 rdlist(就绪链表)中。epoll_wait 检查是否有事件发生时,仅仅需要检查 rdlist 中是否有数据即可。如果 rdlist 中有数据(有事件就绪),就返回就绪事件数;如果 rdlist 中没有数据就阻塞住应用程序,持续等待;如果等待到超时时间都没有事件就绪,就返回 0;如果接口执行过程中出错,则返回 -1。
epoll_wait 函数只能获取是否有注册事件发生,但是事件到底是什么、是哪个 socket 上的事件都是不知道的。这就要到用上面提到的 epoll_event 结构体里的 data.fd,判断是否是关注的 socket(注册到 epoll 的 socket 和感兴趣的事件可能会很多,但不一定所有注册的 socket 的就绪事件都是当下关注的),再用 fd 对数据进行读写。
主体流程结构
epoll 不仅可以监测连接句柄是否可读、可写,还可以监测监听句柄上是否有可以 accept 的连接。所以,在【网络编程】IO 多路复用 select 实验的基础上,让服务端多监听一个端口 5198,把客户端的数量增加到 4 个,让 2 个客户端 connect 5197 端口、2 个客户端 connect 5198 端口,在服务端监听线程里创建一个 epoll 对象,同时监测 5197 和 5198 两个端口,检查是否有可用连接。在服务端工作线程里,创建另一个 epoll 对象, 监测已建立的连接上是否有数据可读。监听线程 accept 一个连接后,就把连接句柄加入到工作线程创建的 epoll 对象的事件池中。主体的流程结构如下:

实验结果
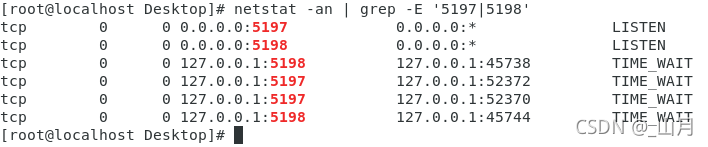
服务端的监听线程分两次检测到可用连接,工作线程一次性检测到四个可接收的事件:

完整代码实现
头文件
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h>宏定义
#define LOCAL_IP_ADDR "127.0.0.1"
#define SERVER_LISTEN_PORT_5197 5197
#define SERVER_LISTEN_PORT_5198 5198
#define MAX_LISTEN_EVENTS 16
#define NET_MSG_BUF_LEN 128
#define CLINET_SEND_MSG "Hello Server~"
#define SERVER_SEND_MSG "Hello Client~"功能函数获取线程 ID
pid_t gettid(void) {
return syscall(SYS_gettid);
}客户端线程入口函数
void* client(void* param) {
int iRes = 0;
int iConnFd = 0;
int iNetMsgLen = 0;
int servLsnPort = *(int *)param;
pthread_t thdId = gettid();
char szNetMsg[NET_MSG_BUF_LEN] = {0};
struct sockaddr_in stServAddr;
iConnFd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (-1 == iConnFd) {
printf("Client[%u] failed to create socket, err[%s]\n",
thdId, strerror(errno));
return NULL;
}
// 填充目标地址结构体,指定协议族、目标端口、目标主机 IP 地址
stServAddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
stServAddr.sin_port = htons(servLsnPort);
stServAddr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(LOCAL_IP_ADDR);
// 1 参传套接字句柄,2 参传准备连接的目标地址结构体指针,3 参传地址结构体大小
while (1) {
iRes = connect(iConnFd, (struct sockaddr *)&stServAddr,
sizeof(stServAddr));
if (0 != iRes) {
printf("Client[%u] failed to connect to[%s:%u], err[%s]\n",
thdId, LOCAL_IP_ADDR, servLsnPort, strerror(errno));
sleep(2);
continue;
} else {
printf("Client[%u] succeeded to connect to[%s:%u]\n",
thdId, LOCAL_IP_ADDR, servLsnPort);
break;
}
}
iNetMsgLen = send(iConnFd, CLINET_SEND_MSG,
strlen(CLINET_SEND_MSG), 0);
if (iNetMsgLen < 0) {
printf("Client[%u] failed to send msg to server, err[%s]\n",
thdId, strerror(errno));
close(iConnFd);
return NULL;
}
iNetMsgLen = recv(iConnFd, szNetMsg, sizeof(szNetMsg), 0);
if (iNetMsgLen < 0) {
printf("Client[%u] failed to read from network, err[%s]\n",
thdId, strerror(errno));
} else {
printf("Client[%u] recv reply[%s]\n", thdId, szNetMsg);
}
close(iConnFd);
return NULL;
}
功能函数处理可读事件
int recvEventProc(int iEventNum, struct epoll_event *pastEvents) {
int iRes = 0, iIndex = 0, iNetMsgLen = 0, iConnFd = 0;
char szNetMsg[NET_MSG_BUF_LEN] = {0};
for (iIndex = 0; iIndex < iEventNum; iIndex++) {
// 用临时变量简化代码
iConnFd = pastEvents[iIndex].data.fd;
// 接收 client 消息
iNetMsgLen = recv(iConnFd, szNetMsg, sizeof(szNetMsg), 0);
if (iNetMsgLen < 0) {
printf("Server work failed to recv from network, err[%s]\n",
strerror(errno));
break;
}
printf("Server work recv msg[%s]\n", szNetMsg);
// 答复 client
iNetMsgLen = send(iConnFd, SERVER_SEND_MSG,
strlen(SERVER_SEND_MSG), 0);
if (iNetMsgLen < 0) {
printf("Server work failed to reply client, err[%s]\n",
strerror(errno));
break;
}
close(iConnFd);
}
// 出现异常,提前退出 for 循环的情况
if (iIndex < iEventNum) {
close(iConnFd);
iRes = -1;
}
return iRes;
}
服务端工作线程入口函数
void* serverWork(void* param) {
int iRes = 0, iEventNum = 0;
struct epoll_event astEvents[MAX_LISTEN_EVENTS] = {0};
int *piEpConnFd = (int *)param;
*piEpConnFd = epoll_create(MAX_LISTEN_EVENTS);
if (-1 == *piEpConnFd) {
printf("Server work failed to create epoll obj, err[%s]\n",
strerror(errno));
return NULL;
}
while (1) {
printf("Server work start wait recv event.\n");
// -1 指示无限期阻塞
iEventNum = epoll_wait(*piEpConnFd, astEvents,
MAX_LISTEN_EVENTS, -1);
if (-1 == iEventNum) {
printf("Server work failed to get recv event, err[%s]\n",
strerror(errno));
break;
}
printf("Server work get [%u] recv event\n", iEventNum);
iRes = recvEventProc(iEventNum, astEvents);
if (-1 == iRes) {
printf("Server work failed to proc recv event\n");
break;
}
}
return NULL;
}
功能函数处理可用连接
int connEventProc(int iEventNum, struct epoll_event *pastEvents, int iEpConnFd) {
int iRes = 0, iIndex = 0, iConnFd = 0;
socklen_t iSockAddrLen = 0;
struct sockaddr_in stCliAddr = {0};
struct epoll_event stEpConnEvent = {0};
for (iIndex = 0; iIndex < iEventNum; iIndex++) {
// 每次 accept 之前,iSockAddrLen 都需要被恢复,否则报错参数非法
iSockAddrLen = sizeof(stCliAddr);
// 1 参传入监听句柄,2 传入地址结构体指针接收客户端地
// 3 参传入地址结构体大小
iConnFd = accept(pastEvents[iIndex].data.fd,
(struct sockaddr*)&stCliAddr, &iSockAddrLen);
if (-1 == iConnFd) {
printf("Server lsn failed to accept conn request, err[%s]\n",
strerror(errno));
iRes = -1;
break;
}
printf("Server lsn accept connect request from[%s:%u]\n",
inet_ntoa(stCliAddr.sin_addr), ntohs(stCliAddr.sin_port));
// 注册事件
stEpConnEvent.events= EPOLLIN;
stEpConnEvent.data.fd = iConnFd;
iRes = epoll_ctl(iEpConnFd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, iConnFd,
&stEpConnEvent);
if (-1 == iRes) {
printf("Server lsn failed to add epoll event, err[%s]\n",
strerror(errno));
break;
}
}
return iRes;
}
功能函数启动端口监听
int serverStartLsn(int iLsnPort, int *piLsnFd) {
int iRes = 0, iReusePort = 0;
struct sockaddr_in stLsnAddr;
// 创建 socket
*piLsnFd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (-1 == *piLsnFd) {
printf("Server lsn failed to create socket, err[%s]\n",
strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
// 设置端口复用
iReusePort = 1;
iRes = setsockopt(*piLsnFd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEPORT, &iReusePort,
sizeof (iReusePort));
if (-1 == iRes) {
printf("Server lsn failed set reuse attr, err[%s]\n",
strerror(errno));
close(*piLsnFd);
return -1;
}
stLsnAddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
stLsnAddr.sin_port = htons(iLsnPort);
stLsnAddr.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY;
// 绑定端口
iRes = bind(*piLsnFd, (struct sockaddr*)&stLsnAddr,
sizeof(stLsnAddr));
if (-1 == iRes) {
printf("Server lsn failed to bind port[%u], err[%s]\n",
iLsnPort, strerror(errno));
close(*piLsnFd);
return -1;
} else {
printf("Server lsn succeeded to bind port[%u], start listen.\n",
iLsnPort);
}
iRes = listen(*piLsnFd, MAX_LISTEN_EVENTS);
if (-1 == iRes) {
printf("Server lsn failed to listen port[%u], err[%s]\n",
iLsnPort, strerror(errno));
close(*piLsnFd);
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
服务端监听线程入口函数
void* serverLsn(void* param) {
int iRes = 0;
int iLsnFd_5197 = 0, iLsnFd_5198 = 0;
int iEpObj = 0, iEventNum = 0;
int *piEpConnFd = (int *)param;
struct epoll_event stEpEvent;
struct epoll_event astEvents[MAX_LISTEN_EVENTS] = {0};
// 保证 work 线程的 epoll 对象有效
if (NULL == piEpConnFd || -1 == *piEpConnFd) {
printf("Server lsn get invalid ep conn fd\n");
return NULL;
}
while (0 == *piEpConnFd) {
sleep(1);
continue;
}
iRes = serverStartLsn(SERVER_LISTEN_PORT_5197, &iLsnFd_5197);
if (-1 == iRes) {
printf("Server lsn failed to start lsn port[%u]\n",
SERVER_LISTEN_PORT_5197);
return NULL;
}
iRes = serverStartLsn(SERVER_LISTEN_PORT_5198, &iLsnFd_5198);
if (-1 == iRes) {
printf("Server lsn failed to start lsn port[%u]\n\n",
SERVER_LISTEN_PORT_5198);
close(iLsnFd_5197);
return NULL;
}
// 创建 epoll 对象用于监听
iEpObj = epoll_create(MAX_LISTEN_EVENTS);
if (-1 == iEpObj) {
printf("Server lsn failed to create lsn epoll obj, err[%s]\n",
strerror(errno));
close(iLsnFd_5197);
close(iLsnFd_5198);
return NULL;
}
// 向 epoll 对象注册事件
memset(&stEpEvent, 0, sizeof(stEpEvent));
stEpEvent.events= EPOLLIN;
stEpEvent.data.fd = iLsnFd_5197;
epoll_ctl(iEpObj, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, iLsnFd_5197, &stEpEvent);
// 向 epoll 对象注册事件
memset(&stEpEvent, 0, sizeof(stEpEvent));
stEpEvent.events= EPOLLIN;
stEpEvent.data.fd = iLsnFd_5198;
epoll_ctl(iEpObj, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, iLsnFd_5198, &stEpEvent);
// 监听
while (1) {
printf("Server lsn start wait conn event.\n");
memset(astEvents, 0, sizeof(astEvents));
iEventNum = epoll_wait(iEpObj, astEvents, MAX_LISTEN_EVENTS, -1);
if (-1 == iEventNum) {
printf("Server lsn failed to wait conn event, err[%s].\n",
strerror(errno));
break;
}
printf("Server lsn get [%u] conn event\n", iEventNum);
iRes = connEventProc(iEventNum, astEvents, *piEpConnFd);
if (0 != iRes) {
printf("Server lsn failed to proc conn event.\n");
close(iLsnFd_5197);
close(iLsnFd_5198);
return NULL;
}
}
close(iLsnFd_5197);
close(iLsnFd_5198);
return NULL;
}
主函数
int main() {
// 线程 ID,实质是 unsigned long 类型整数
pthread_t thdServerWork = 101;
pthread_t thdServerLsn = 102;
pthread_t thdClient1 = 1;
pthread_t thdClient2 = 2;
pthread_t thdClient3 = 3;
pthread_t thdClient4 = 4;
// 用于监测 socket 是否可读的 epoll 对象句柄
int iEpConnFd = 0;
// 连接端口
int serverPort_5197 = 5197;
int serverPort_5198 = 5198;
// 1 参传线程 ID,2 参传线程属性,
// 3 参指定线程入口函数,4 参指定传给入口函数的参数
pthread_create(&thdServerWork, NULL, serverWork, &iEpConnFd);
pthread_create(&thdServerLsn, NULL, serverLsn, &iEpConnFd);
pthread_create(&thdClient1, NULL, client, &serverPort_5197);
pthread_create(&thdClient2, NULL, client, &serverPort_5197);
pthread_create(&thdClient3, NULL, client, &serverPort_5198);
pthread_create(&thdClient4, NULL, client, &serverPort_5198);
// 1 参传入线程 ID,2 参用于接收线程入口函数的返回值,不需要返回值则置 NULL
pthread_join(thdServerWork, NULL);
pthread_join(thdServerLsn, NULL);
pthread_join(thdClient1, NULL);
pthread_join(thdClient2, NULL);
pthread_join(thdClient3, NULL);
pthread_join(thdClient4, NULL);
return 0;
}







 本文详细介绍了Linux下epoll的使用,包括epoll_create、epoll_ctl、epoll_wait三个主要接口的功能和用法,并探讨了epoll的工作模式——水平触发和边缘触发。通过一个实验展示了epoll如何在服务端同时监听多个端口,并处理来自不同客户端的连接和数据。epoll_event结构体在注册事件和处理就绪事件中的作用也得到了阐述。
本文详细介绍了Linux下epoll的使用,包括epoll_create、epoll_ctl、epoll_wait三个主要接口的功能和用法,并探讨了epoll的工作模式——水平触发和边缘触发。通过一个实验展示了epoll如何在服务端同时监听多个端口,并处理来自不同客户端的连接和数据。epoll_event结构体在注册事件和处理就绪事件中的作用也得到了阐述。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








