一、环境:
操作系统:Debian GNU/Linux 10
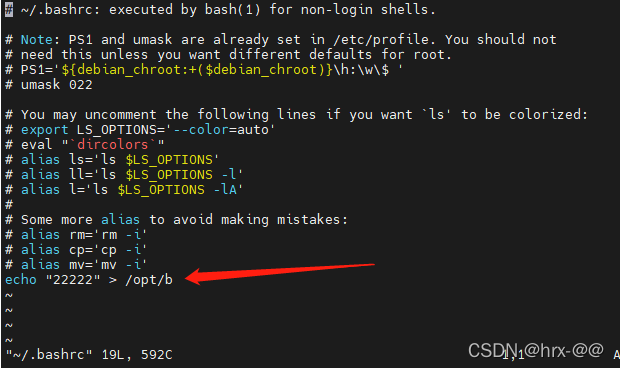
二、方法1:~/.bashrc
可以添加脚本在 ~/.bashrc末尾执行。
三、方法2:/etc/profile
可以添加脚本在 /etc/profile末尾执行。

四、方法3:rc.local
1、查看一下rc-local.service文件是不是存在
路径:/lib/systemd/system/rc-local.service
内容:
# SPDX-License-Identifier: LGPL-2.1+
#
# This file is part of systemd.
#
# systemd is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it
# under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by
# the Free Software Foundation; either version 2.1 of the License, or
# (at your option) any later version.
# This unit gets pulled automatically into multi-user.target by
# systemd-rc-local-generator if /etc/rc.local is executable.
[Unit]
Description=/etc/rc.local Compatibility
Documentation=man:systemd-rc-local-generator(8)
ConditionFileIsExecutable=/etc/rc.local
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=forking
ExecStart=/etc/rc.local start
TimeoutSec=0
RemainAfterExit=yes
GuessMainPID=no
注:这里面就指出了可执行文件是 /etc/rc.local 。
2、默认的状态
root@npi:/lib/systemd/system# systemctl status rc-local.service
● rc-local.service - /etc/rc.local Compatibility
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/rc-local.service; static; vendor preset:
Drop-In: /lib/systemd/system/rc-local.service.d
└─debian.conf
Active: inactive (dead)
Docs: man:systemd-rc-local-generator(8)
注:因为没有 /etc/rc.local 这个文件,或者这个文件没有权限。
3、创建 /etc/rc.local
(1)写入内容
#!/bin/sh -e
#
# rc.local
#
# This script is executed at the end of each multiuser runlevel.
# Make sure that the script will "exit 0" on success or any other
# value on error.
#
# In order to enable or disable this script just change the execution
# bits.
#
# By default this script does nothing.
exit 0
注:如果有什么要开启启动的脚本可以插入在 exit 0 之前。
(2)赋予可执行权限
chmod +x /etc/rc.local
3、启动rc.local服务
systemctl start rc.local
注:重启后服务会自动启动
4、重启后查询状态
root@npi:~# systemctl status rc.local
● rc-local.service - /etc/rc.local Compatibility
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/rc-local.service; enabled-runtime; vendor
Drop-In: /lib/systemd/system/rc-local.service.d
└─debian.conf
Active: active (exited) since Tue 2022-01-04 16:06:09 CST; 3min 51s ago
Docs: man:systemd-rc-local-generator(8)
Process: 367 ExecStart=/etc/rc.local start (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Jan 04 16:06:09 npi systemd[1]: Starting /etc/rc.local Compatibility...
Jan 04 16:06:09 npi systemd[1]: Started /etc/rc.local Compatibility.
注:验证确实有执行rc.local内的内容







 文章介绍了在DebianGNU/Linux10系统中,通过修改~/.bashrc、/etc/profile和启用rc.local服务来添加启动脚本的方法。rc.local的设置包括创建文件、赋予执行权限以及启动和检查服务状态。
文章介绍了在DebianGNU/Linux10系统中,通过修改~/.bashrc、/etc/profile和启用rc.local服务来添加启动脚本的方法。rc.local的设置包括创建文件、赋予执行权限以及启动和检查服务状态。
















 935
935

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








