Spring
Spring是什么


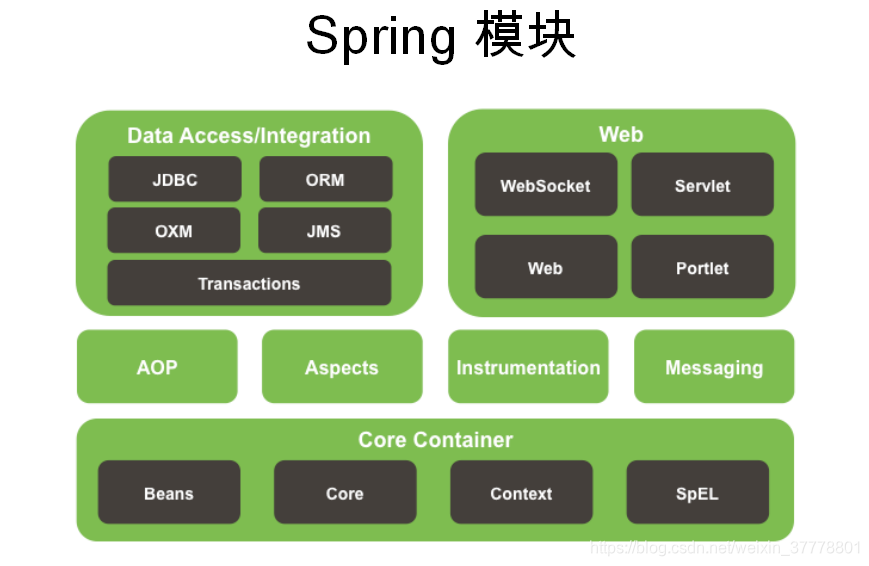
Spring有哪些模块:
我们在用Eclipse来进行开发的时候,可以安装一个插件:

搭建 Spring 开发环境

新建Spring项目:

有一个 HelloWorld 类:
public class HelloWorld {
private String user;
public HelloWorld() {
System.out.println("HelloWorld's constructor...");
}
public void setUser(String user) {
this.user = user;
}
public HelloWorld(String user) {
this.user = user;
}
public void hello(){
}
}
在没有Spring的时候,我们创建一个对象就是这样来创建的:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HelloWorld helloWorld = new HelloWorld();
helloWorld.setUser("Tom");
helloWorld.hello();
}
}
现在,当我们用了Spring的时候,就是可以这样来进行创建对象了:
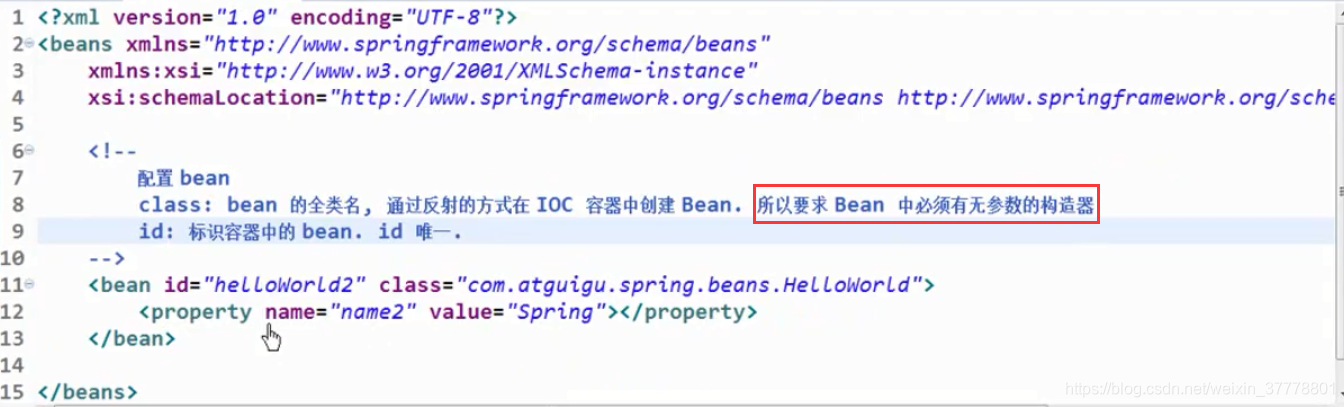
首先,我们创建一个Spring的配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-4.0.xsd">
<!-- 配置一个 bean -->
<bean id="helloWorld" class="com.atguigu.spring.helloworld.HelloWorld">
<!-- 为属性赋值 -->
<property name="user" value="Jerry"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
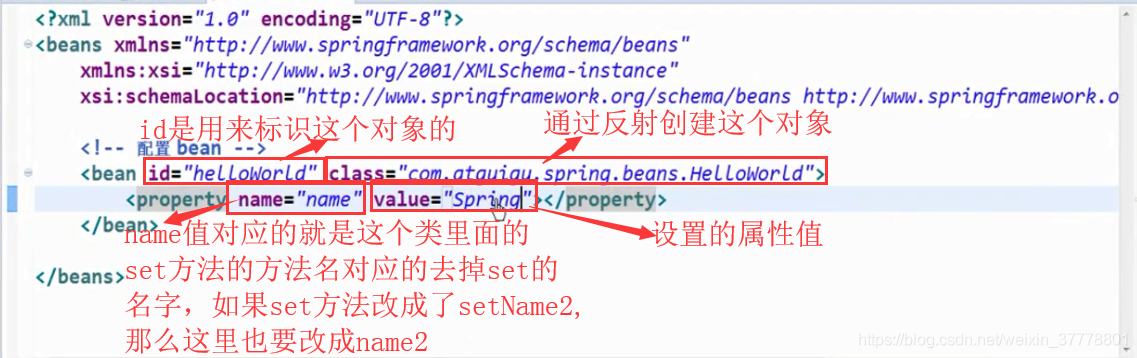
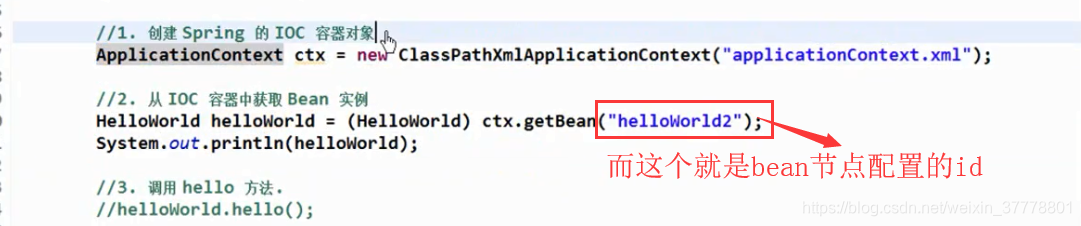
这个时候,就是可以这样来获取bean的实例:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 创建 Spring 的 IOC 容器
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
//2. 从 IOC 容器中获取 bean 的实例
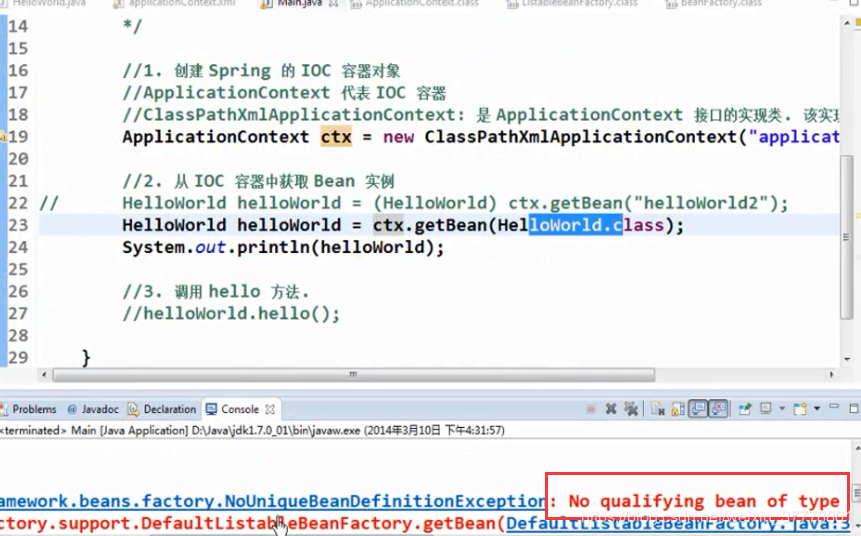
HelloWorld helloWorld = (HelloWorld) ctx.getBean("helloWorld3");
//根据类型来获取 bean 的实例: 要求在 IOC 容器中只有一个与之类型匹配的 bean, 若有多个则会抛出异常.
//一般情况下, 该方法可用, 因为一般情况下, 在一个 IOC 容器中一个类型对应的 bean 也只有一个.
//HelloWorld helloWorld1 = ctx.getBean(HelloWorld.class);
//3. 使用 bean
helloWorld.hello();
}
}
如果我们只创建了ioc容器,不进行调用getBean方法来获取对象实例,那么这个时候,ioc会为我们做什么事呢 ?为了清楚的看到效果,我们给HelloWorld这个类里面的无参构造器和set方法各打印一句话,让我们看看运行之后,控制台是如何打印的:
public class HelloWorld {
private String user;
public HelloWorld() {
System.out.println("HelloWorld's constructor...");
}
public void setUser(String user) {
System.out.println("setUser:" + user);
this.user = user;
}
public HelloWorld(String user) {
this.user = user;
}
public void hello(){
System.out.println("Hello: " + user);
}
}

Spring 中的 Bean 配置

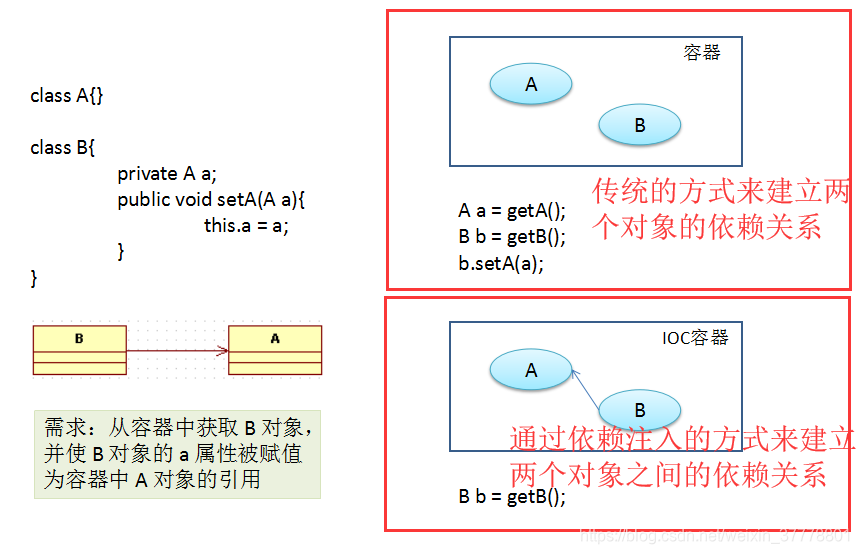
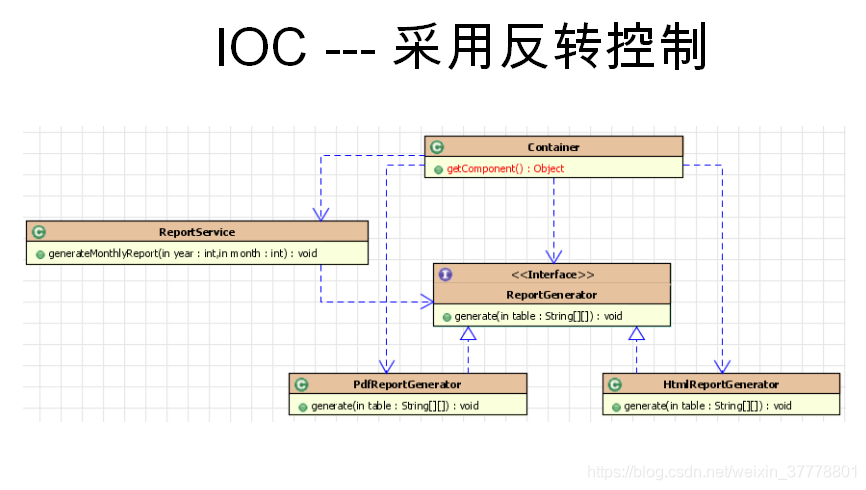
控制反转和依赖注入:

- 在传统的方式,如果一个对象要和另外一个对象之间有依赖关系,我们可以通过把一个对象作为另外一个对象的成员属性,然后通过set方法的方式来进行关联;
A a = new A();
B b = new B();
b.setA(a);
- 现在,有了Spring的依赖注入就可以自动的建立依赖关系;
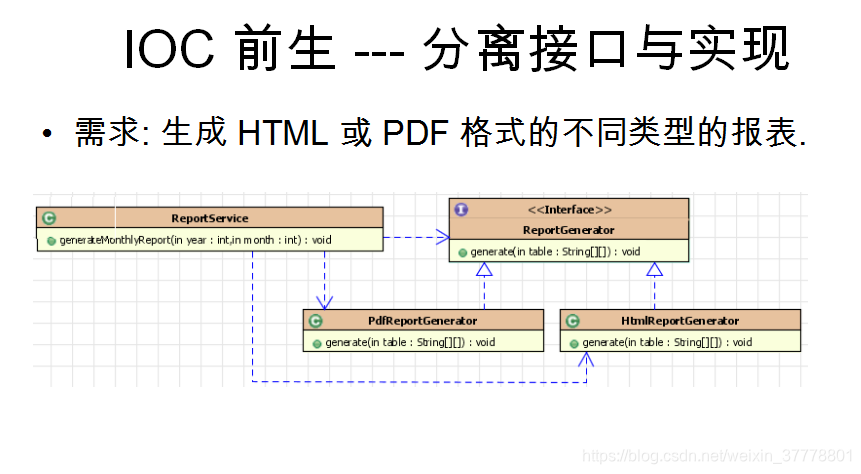
IOC的前生:
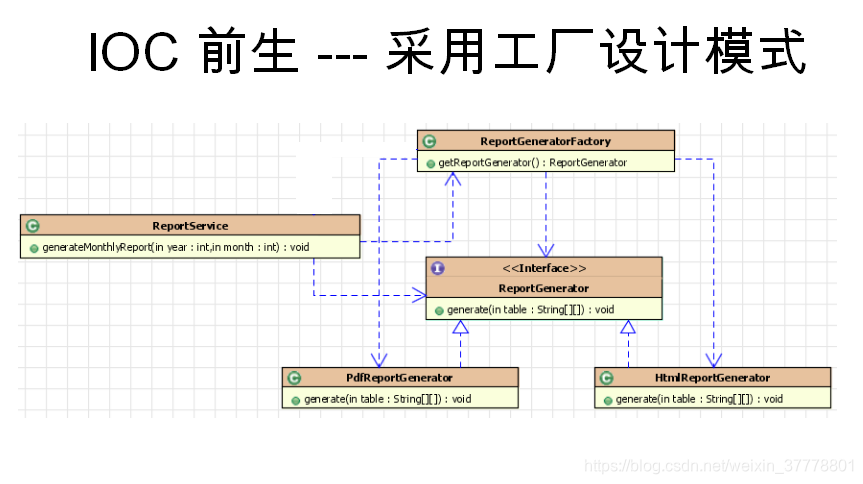
配置Bean:基于xml文件配置的方式

在 Spring 的 IOC 容器里配置 Bean

Spring IOC容器

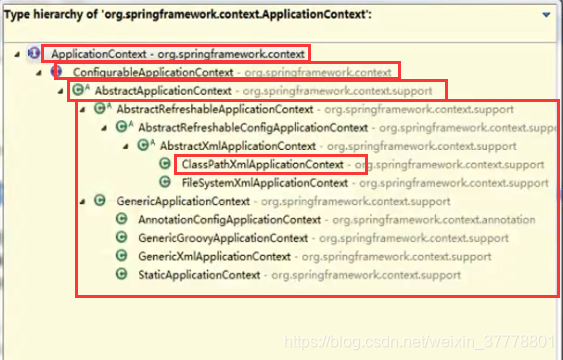
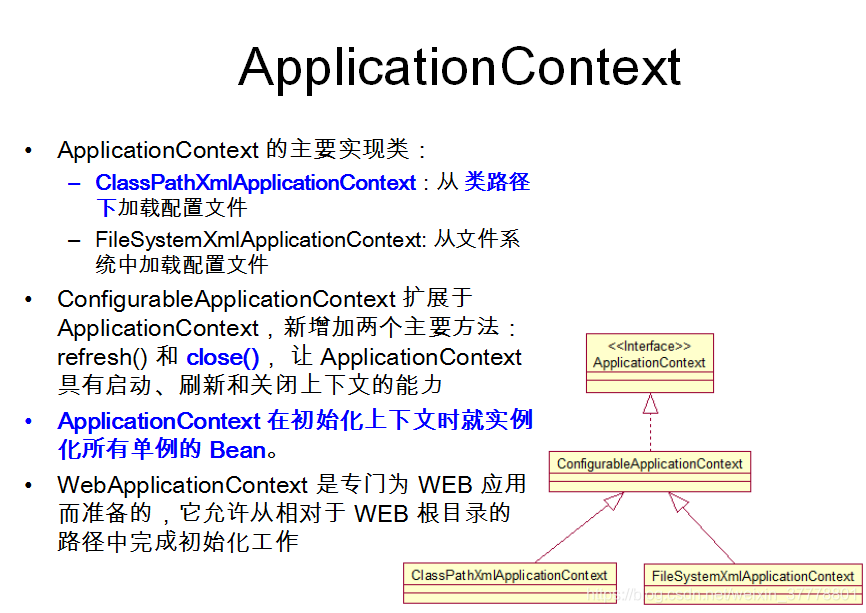
ApplicationContext:
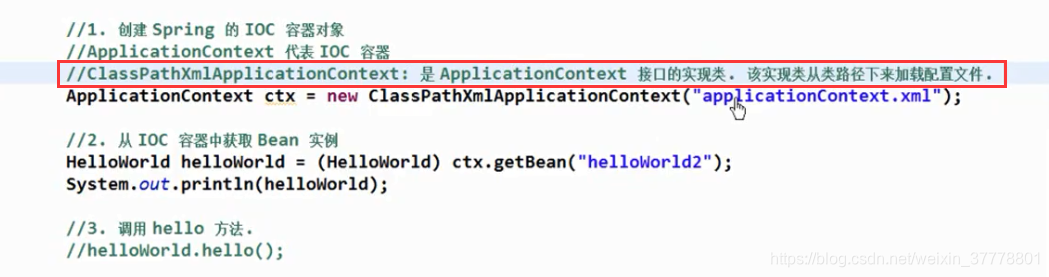
从IOC容器中获取Bean的方法

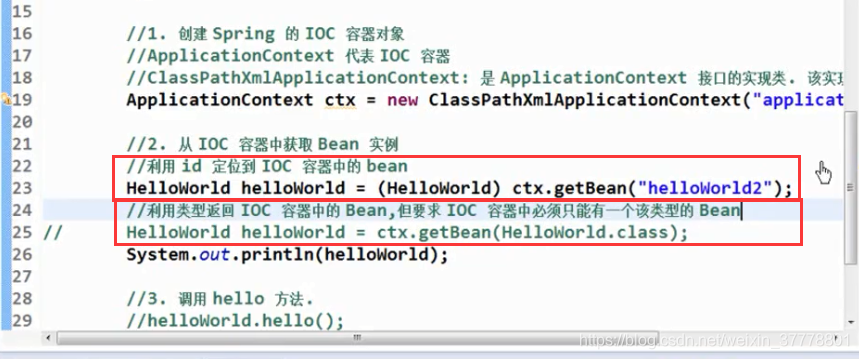
我们还可以用类型来进行获取 Bean 的实例对象,这个时候,就是不用进行强转:
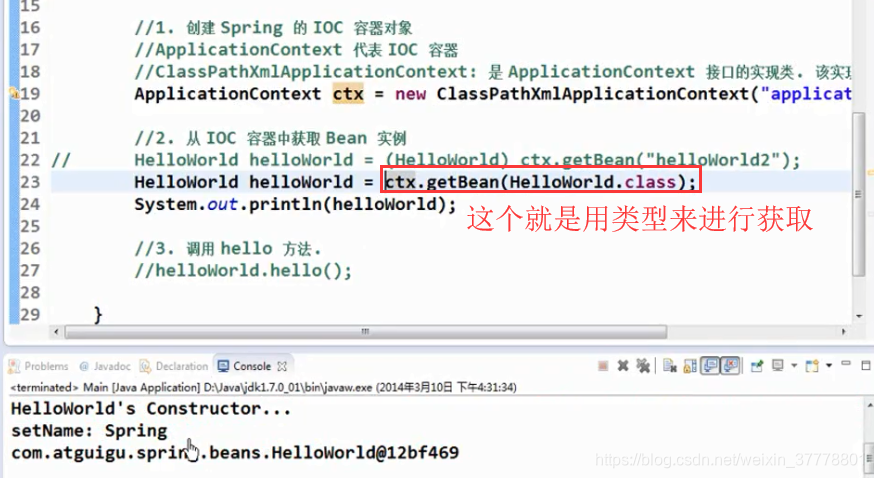
通过类型来进行获取要求这个类型的 Bean 在 IOC 容器里面是唯一的,通过 id 来进行获取就不会有这样的问题,因为我明确指名了是哪一个 Bean 的实例:
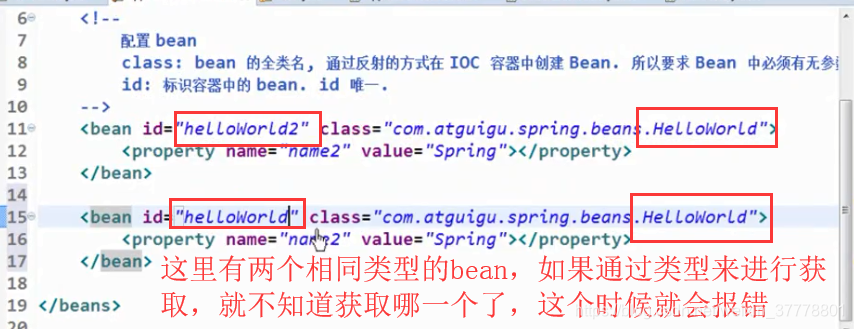
这个时候,IOC容器就不知道要返回哪一个了:
属性的注入方式

属性注入(set方法注入)

构造方法注入

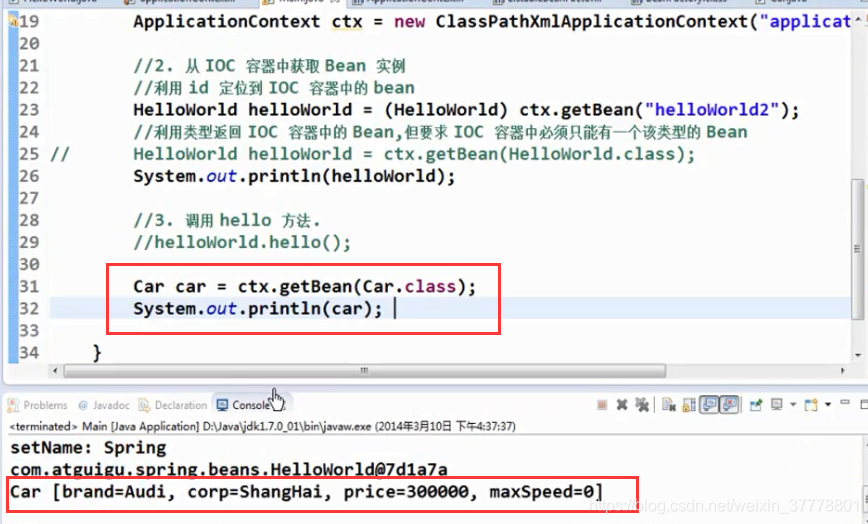
有一个Car类:
public class Car {
private String company;
private String brand;
private int maxSpeed;
private float price;
public Car(String company, String brand, float price) {
super();
this.company = company;
this.brand = brand;
this.price = price;
}
public Car(String company, String brand, int maxSpeed) {
super();
this.company = company;
this.brand = brand;
this.maxSpeed = maxSpeed;
}
public Car(String company, String brand, int maxSpeed, float price) {
super();
this.company = company;
this.brand = brand;
this.maxSpeed = maxSpeed;
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Car [company=" + company + ", brand=" + brand + ", maxSpeed="
+ maxSpeed + ", price=" + price + "]";
}
}
我们可以这样来设置属性:
这个是按照构造器里面的参数顺序来配的:

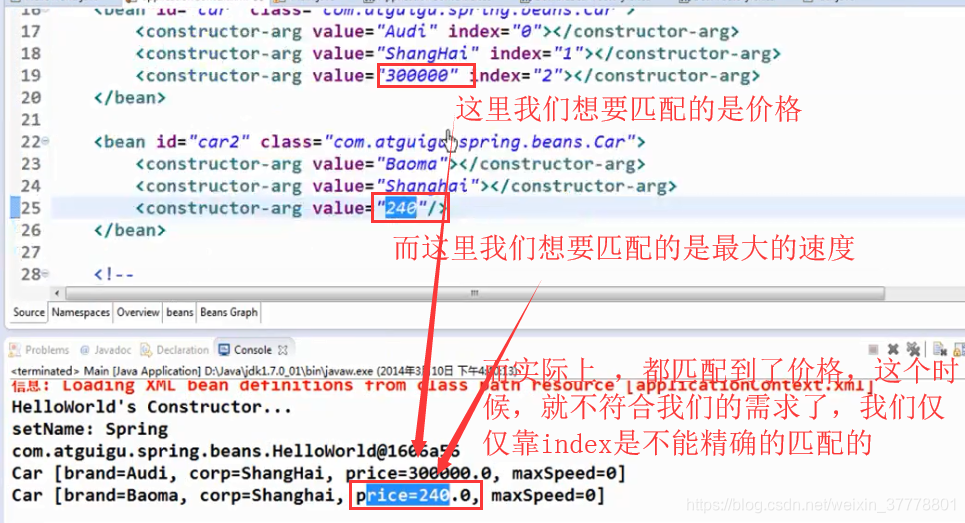
实际上,我们也可以用index来指明参数的顺序:

现在有一个问题,有两个参数个数相同的构造器:
public Car(String company, String brand, float price) {
super();
this.company = company;
this.brand = brand;
this.price = price;
}
public Car(String company, String brand, int maxSpeed) {
super();
this.company = company;
this.brand = brand;
this.maxSpeed = maxSpeed;
}
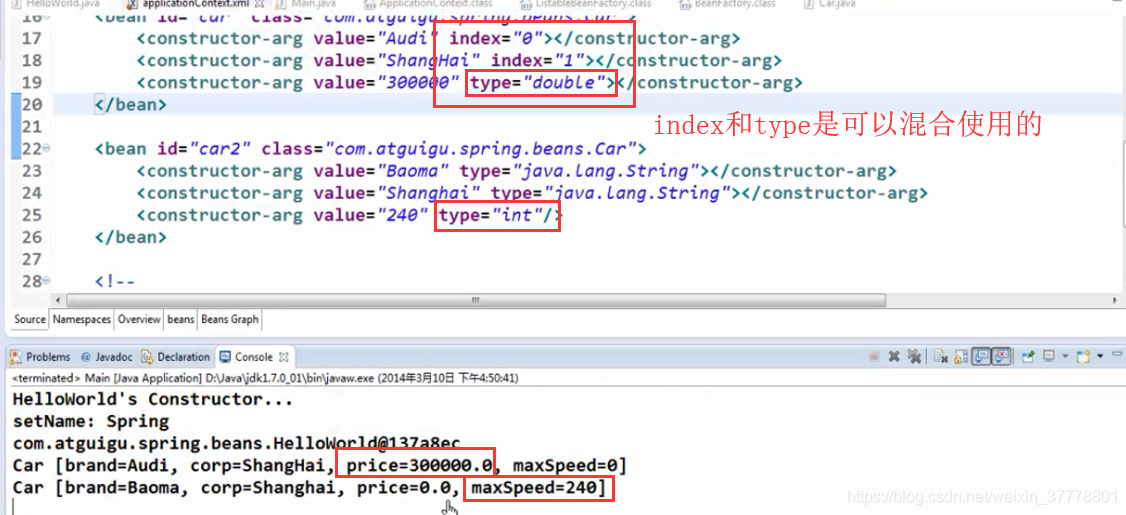
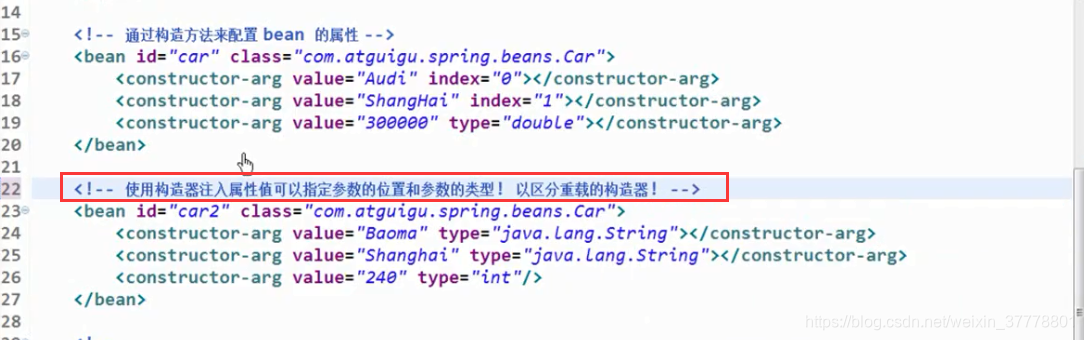
index和type是可以混合使用的,这个时候,就是可以精确的匹配了:
注入属性值的细节

value属性:

子节点:

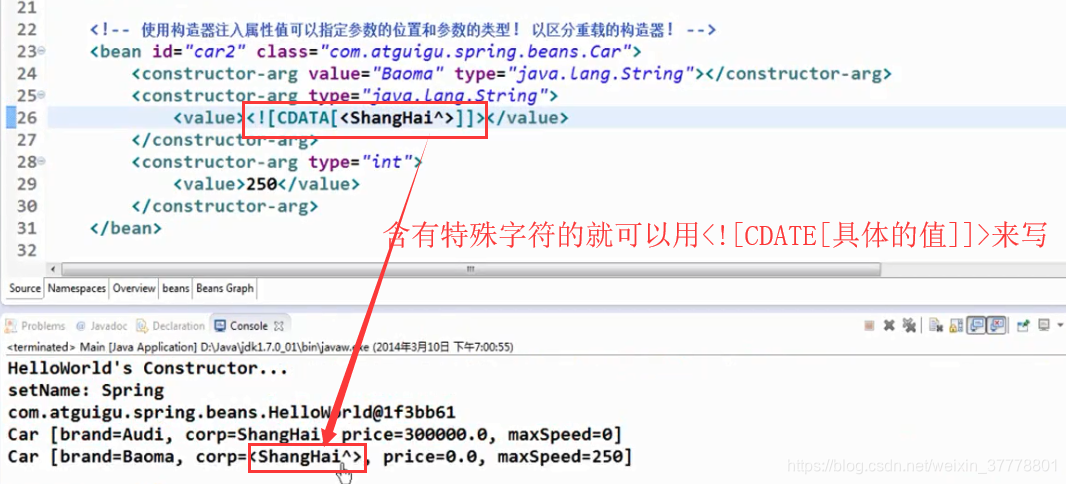
含有特殊字符的就可以这样来写:
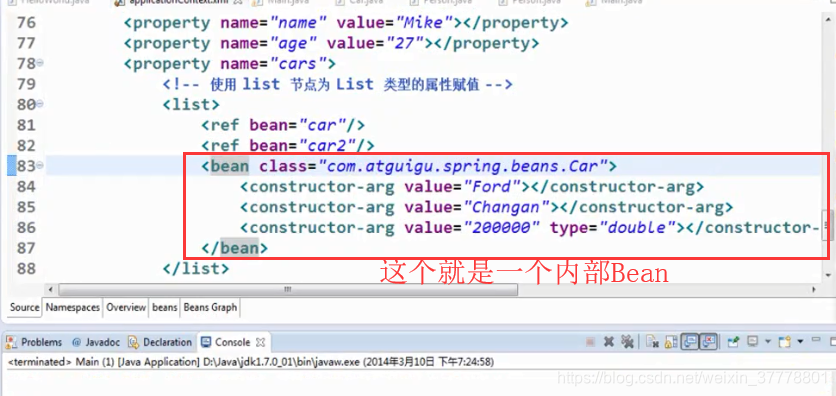
引用其他的Bean



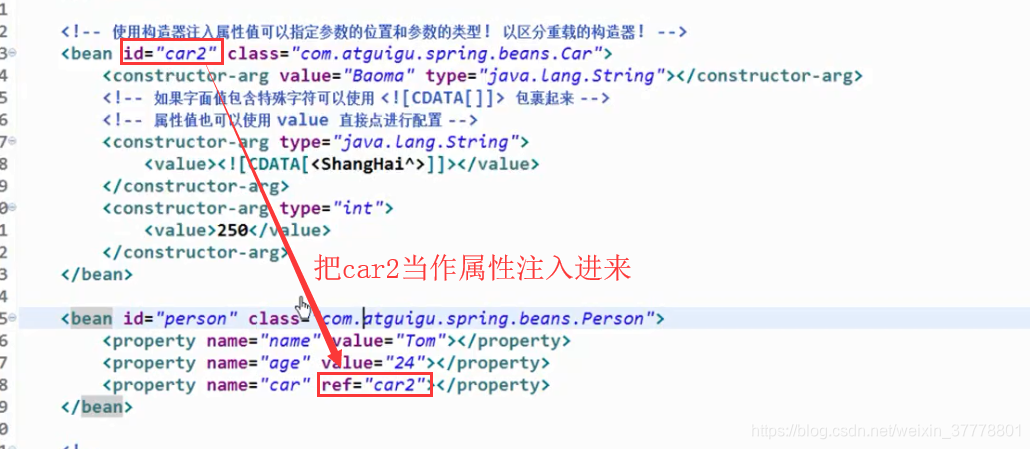
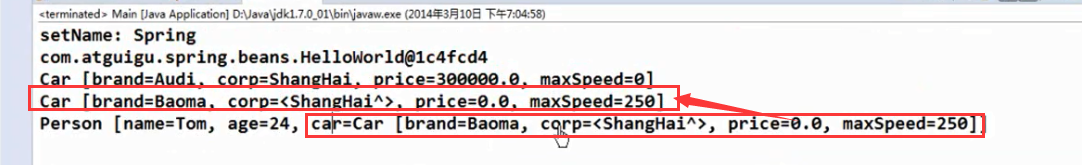
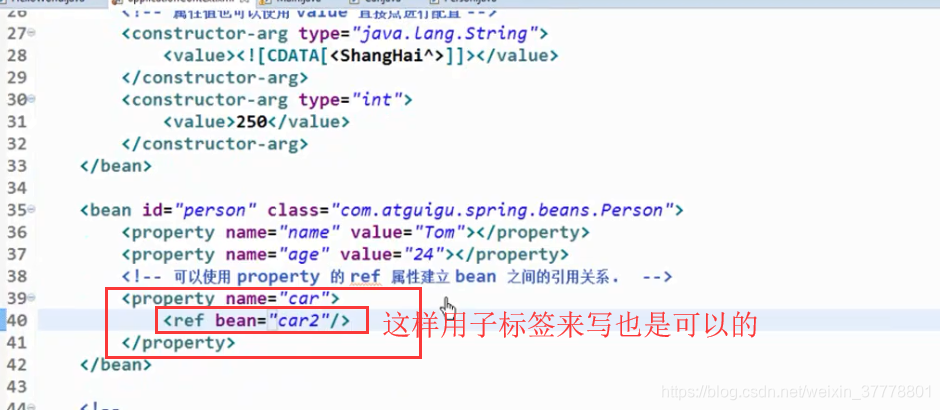
这样配的话,就是一个内部Bean,内部Bean不用写id,在类的内部声明的一个Bean,在外部是不能够被引用的:
<!-- 声明使用内部 bean -->
<bean id="service2" class="com.atguigu.spring.ref.Service">
<property name="dao">
<!-- 内部 bean, 类似于匿名内部类对象. 不能被外部的 bean 来引用, 也没有必要设置 id 属性 -->
<bean class="com.atguigu.spring.ref.Dao">
<property name="dataSource" value="c3p0"></property>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
用构造器配置的方式也是一样的:

null值和级联属性

设置null值:
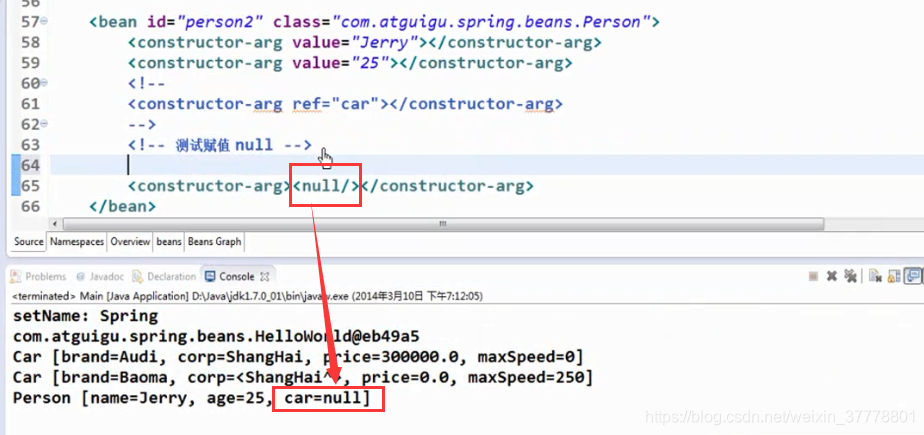
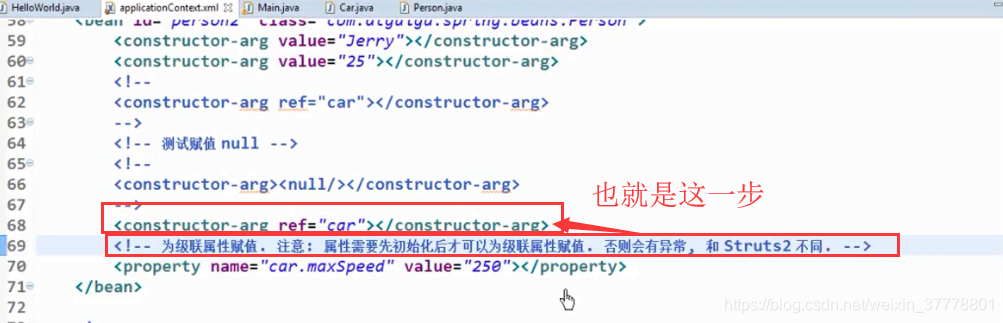
设置级联属性:在设置级联属性的时候,对象一定要先进行赋值,不然的话,对象就会为null值,也就对里面的属性赋不了值:
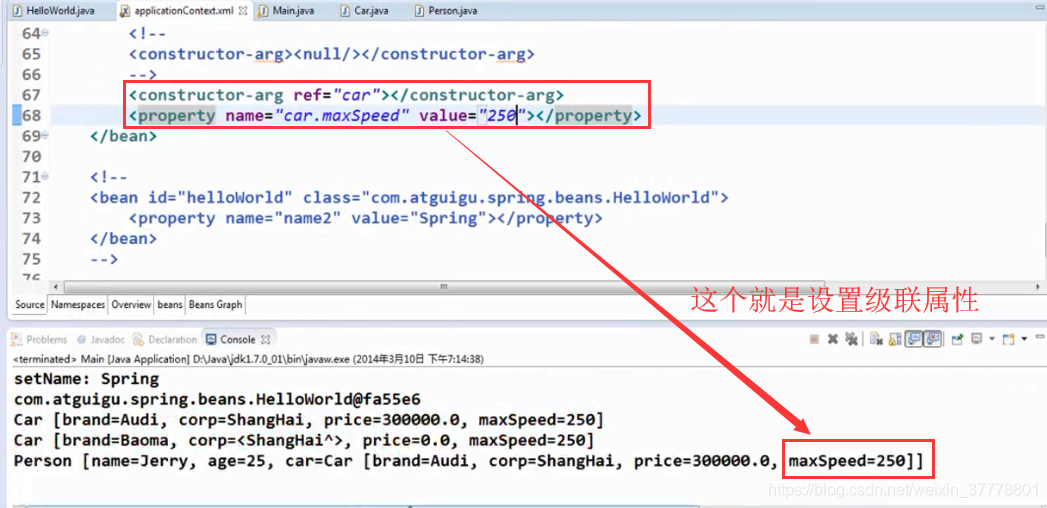
需要注意的地方:
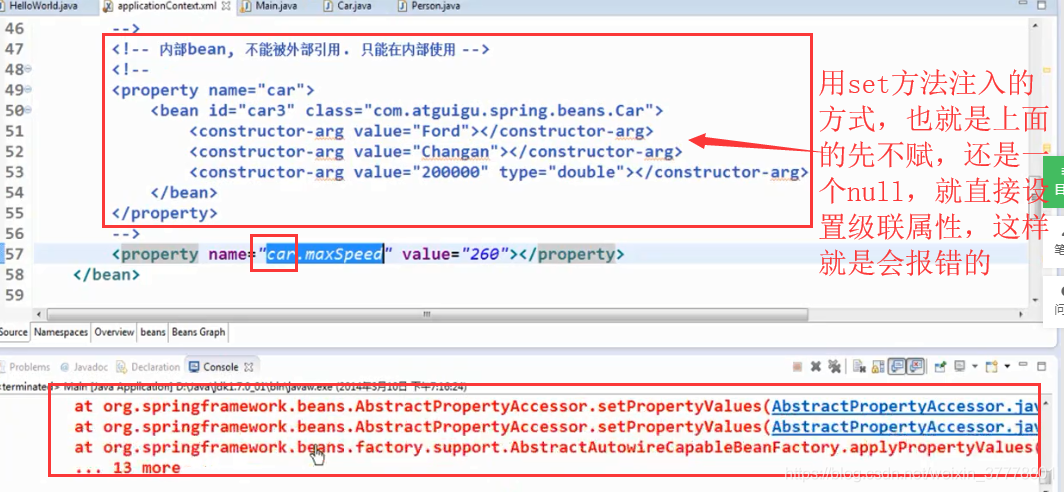
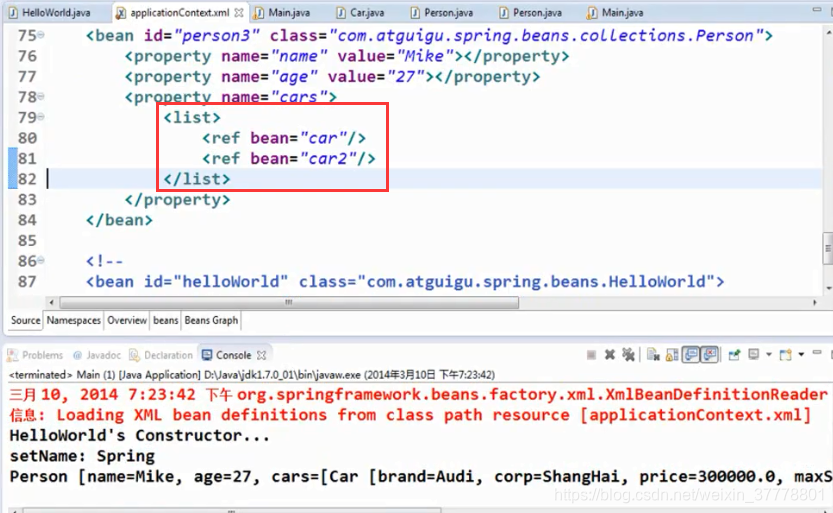
集合属性
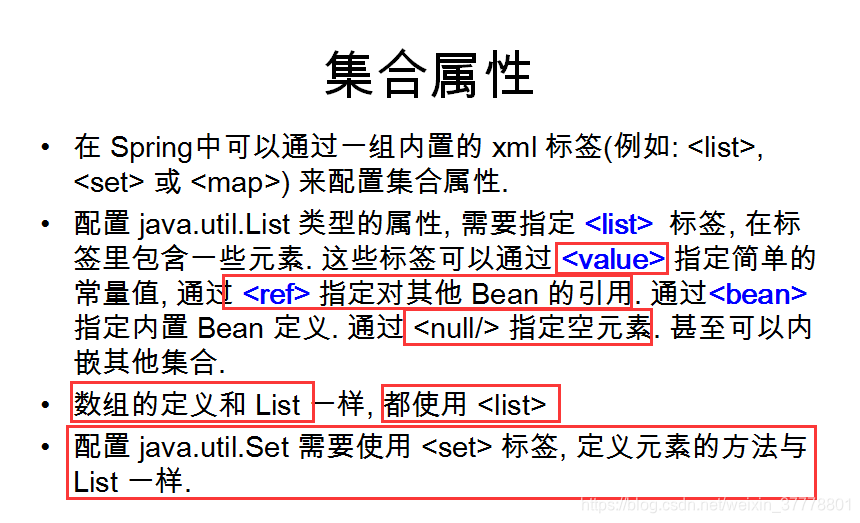
List:
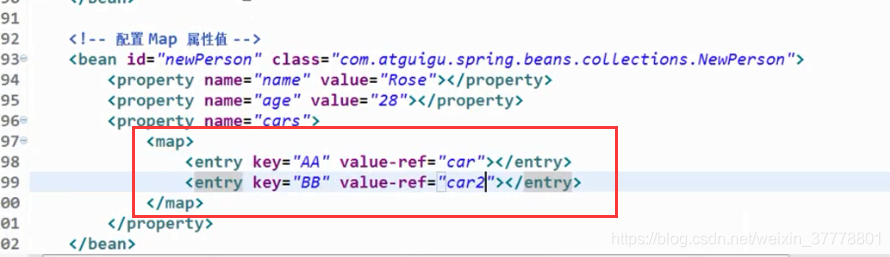
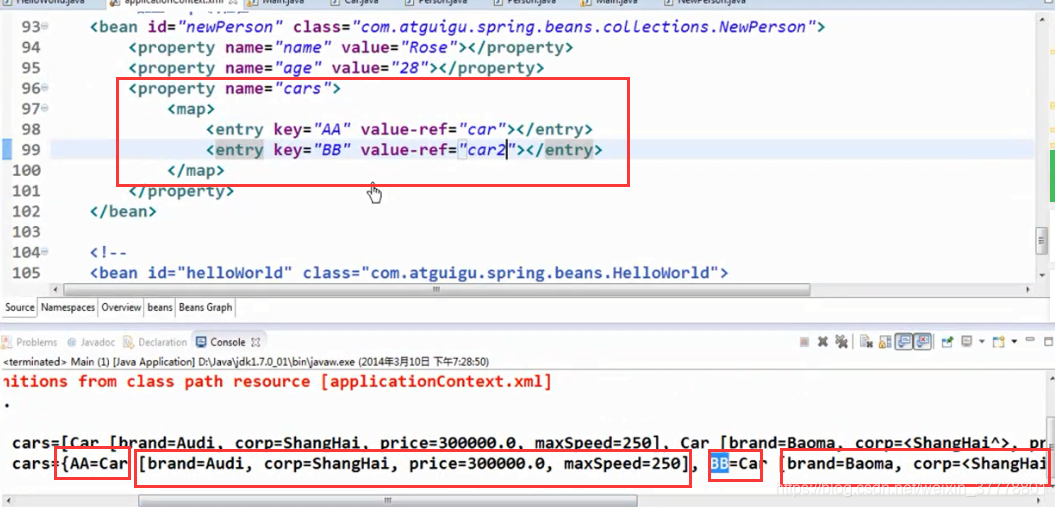
Map:

properties:

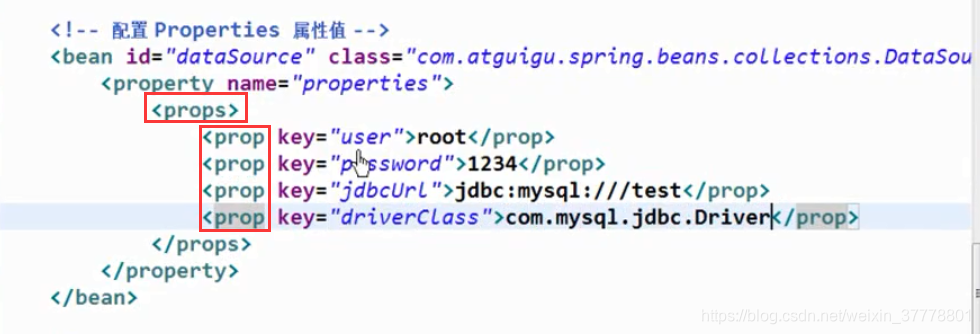
我们可以把集合拿出来定义,以达到共享的目的:


P命名空间























 173万+
173万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








