Table of Contents
1. python的数据类型
Python 中数据类型可以分为 数字型 和 非数字型
-
数字型
-
整型 (
int) -
浮点型(
float) -
布尔型(
bool)-
真
True非 0 数—— 非零即真 -
假
False0
-
-
复数型 (
complex)-
主要用于科学计算,例如:平面场问题、波动问题、电感电容等问题
-
-
-
非数字型
-
字符串
-
列表
-
元组
-
字典
-
-
在
Python中,所有 非数字型变量 都支持以下特点:-
都是一个 序列
sequence,也可以理解为 容器 -
取值
[] -
遍历
for in -
计算长度、最大/最小值、比较、删除
-
链接
+和 重复* -
切片
-
2. 列表的基本使用
-
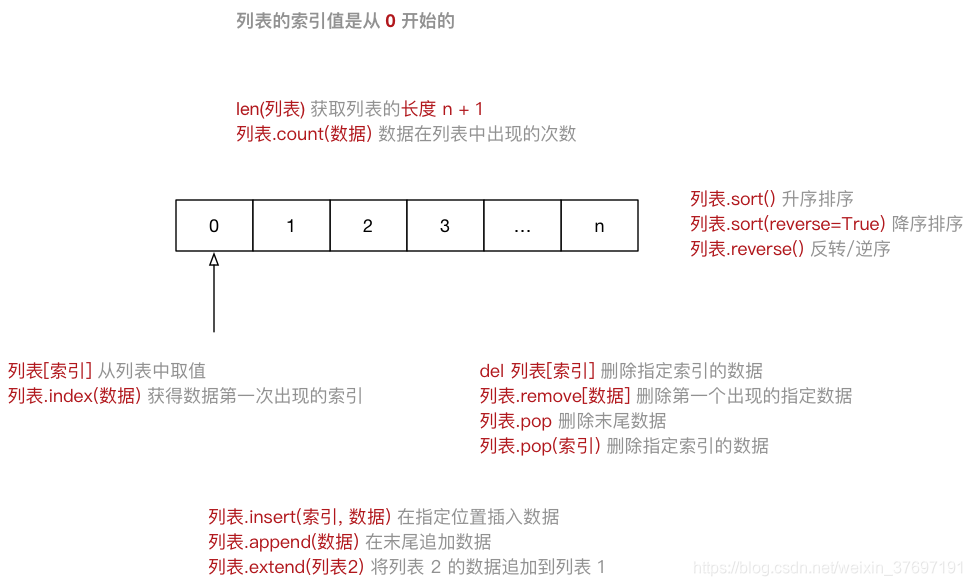
List(列表) 是Python中使用 最频繁 的数据类型,在其他语言中通常叫做 数组
-
在
ipython3中定义一个 列表,例如:name_list = [] -
输入
name_list.按下TAB键,ipython会提示 列表 能够使用的 方法 如下:
In [1]: name_list. name_list.append name_list.count name_list.insert name_list.reverse name_list.clear name_list.extend name_list.pop name_list.sort name_list.copy name_list.index name_list.remove
| 序号 | 分类 | 关键字 / 函数 / 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 增加 | 列表.insert(索引, 数据) | 在指定位置插入数据 |
| 列表.append(数据) | 在末尾追加数据 | ||
| 列表.extend(列表2) | 将列表2 的数据追加到列表 | ||
| 2 | 修改 | 列表[索引] = 数据 | 修改指定索引的数据 |
| 3 | 删除 | del 列表[索引] | 删除指定索引的数据 |
| 列表.remove[数据] | 删除第一个出现的指定数据 | ||
| 列表.pop | 删除末尾数据 | ||
| 列表.pop(索引) | 删除指定索引数据 | ||
| 列表.clear | 清空列表 | ||
| 4 | 统计 | len(列表) | 列表长度 |
| 列表.count(数据) | 数据在列表中出现的次数 | ||
| 5 | 排序 | 列表.sort() | 升序排序 |
| 列表.sort(reverse=True) | 降序排序 | ||
| 列表.reverse() | 逆序、反转 |
3. 元组的基本使用
-
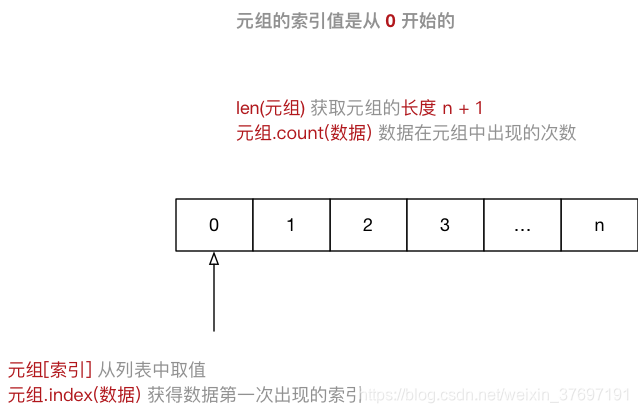
Tuple(元组)与列表类似,不同之处在于元组的 元素不能修改-
元组 表示多个元素组成的序列
-
元组 在
Python开发中,有特定的应用场景
-
info_tuple = ("zhangsan", 18, 1.75)
创建空元组
info_tuple = ()
元组中 只包含一个元素 时,需要 在元素后面添加逗号
info_tuple = (50, )
-
在
ipython3中定义一个 元组,例如:info = () -
输入
info.按下TAB键,ipython会提示 元组 能够使用的函数如下:
info.count info.index
4. 字典的基本使用
-
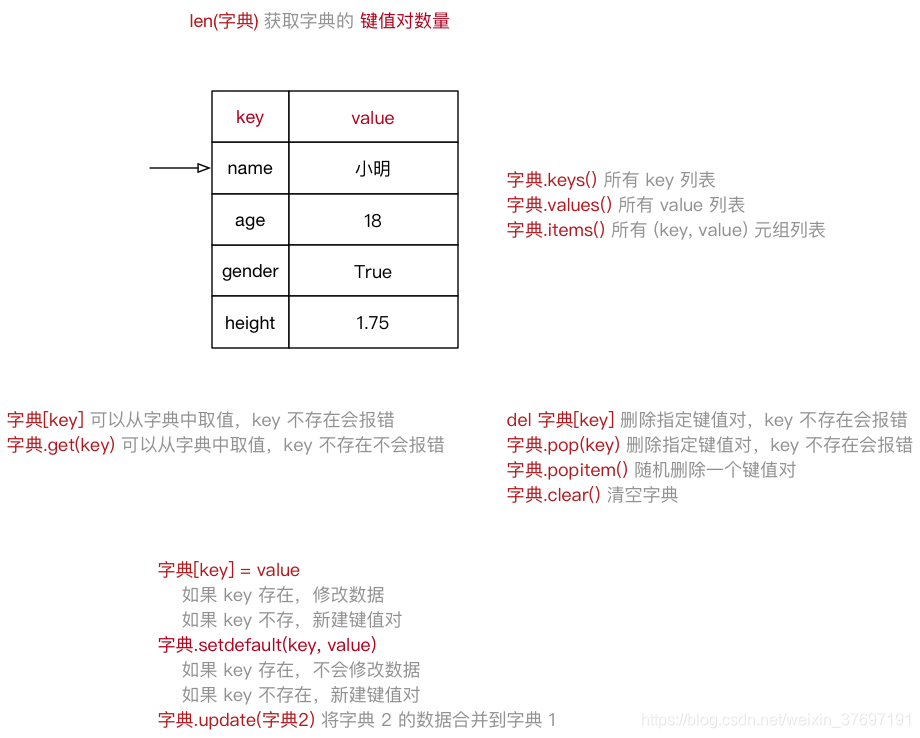
dictionary(字典) 是 除列表以外Python之中 最灵活 的数据类型 -
字典同样可以用来 存储多个数据
-
通常用于存储 描述一个
物体的相关信息
-
-
字典使用 键值对 存储数据,键值对之间使用
,分隔-
键
key是索引 -
值
value是数据 -
键 和 值 之间使用
:分隔 -
键必须是唯一的
-
值 可以取任何数据类型,但 键 只能使用 字符串、数字或 元组
-
xiaoming = {"name": "小明", "age": 18, "gender": True, "height": 1.75}
-
在
ipython3中定义一个 字典,例如:xiaoming = {} -
输入
xiaoming.按下TAB键,ipython会提示 字典 能够使用的函数如下:
In [1]: xiaoming. xiaoming.clear xiaoming.items xiaoming.setdefault xiaoming.copy xiaoming.keys xiaoming.update xiaoming.fromkeys xiaoming.pop xiaoming.values xiaoming.get xiaoming.popitem
5. 字符串的基本使用
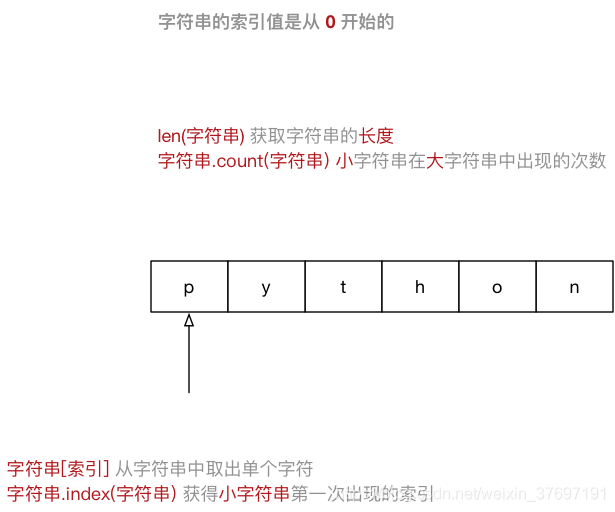
string = "Hello Python"
for c in string:
print(c)
-
在
ipython3中定义一个 字符串,例如:hello_str = "" -
输入
hello_str.按下TAB键,ipython会提示 字符串 能够使用的 方法 如下:
In [1]: hello_str. hello_str.capitalize hello_str.isidentifier hello_str.rindex hello_str.casefold hello_str.islower hello_str.rjust hello_str.center hello_str.isnumeric hello_str.rpartition hello_str.count hello_str.isprintable hello_str.rsplit hello_str.encode hello_str.isspace hello_str.rstrip hello_str.endswith hello_str.istitle hello_str.split hello_str.expandtabs hello_str.isupper hello_str.splitlines hello_str.find hello_str.join hello_str.startswith hello_str.format hello_str.ljust hello_str.strip hello_str.format_map hello_str.lower hello_str.swapcase hello_str.index hello_str.lstrip hello_str.title hello_str.isalnum hello_str.maketrans hello_str.translate hello_str.isalpha hello_str.partition hello_str.upper hello_str.isdecimal hello_str.replace hello_str.zfill hello_str.isdigit hello_str.rfind
提示:正是因为 python 内置提供的方法足够多,才使得在开发时,能够针对字符串进行更加灵活的操作!应对更多的开发需求!
1) 判断类型 - 9
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| string.isspace() | 如果 string 中只包含空格,则返回 True |
| string.isalnum() | 如果 string 至少有一个字符并且所有字符都是字母或数字则返回 True |
| string.isalpha() | 如果 string 至少有一个字符并且所有字符都是字母则返回 True |
| string.isdecimal() | 如果 string 只包含数字则返回 True,全角数字 |
| string.isdigit() | 如果 string 只包含数字则返回 True,全角数字、⑴、\u00b2 |
| string.isnumeric() | 如果 string 只包含数字则返回 True,全角数字,汉字数字 |
| string.istitle() | 如果 string 是标题化的(每个单词的首字母大写)则返回 True |
| string.islower() | 如果 string 中包含至少一个区分大小写的字符,并且所有这些(区分大小写的)字符都是小写,则返回 True |
| string.isupper() | 如果 string 中包含至少一个区分大小写的字符,并且所有这些(区分大小写的)字符都是大写,则返回 True |
2) 查找和替换 - 7
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| string.startswith(str) | 检查字符串是否是以 str 开头,是则返回 True |
| string.endswith(str) | 检查字符串是否是以 str 结束,是则返回 True |
| string.find(str, start=0, end=len(string)) | 检测 str 是否包含在 string 中,如果 start 和 end 指定范围,则检查是否包含在指定范围内,如果是返回开始的索引值,否则返回 -1 |
| string.rfind(str, start=0, end=len(string)) | 类似于 find(),不过是从右边开始查找 |
| string.index(str, start=0, end=len(string)) | 跟 find() 方法类似,不过如果 str 不在 string 会报错 |
| string.rindex(str, start=0, end=len(string)) | 类似于 index(),不过是从右边开始 |
| string.replace(old_str, new_str, num=string.count(old)) | 把 string 中的 old_str 替换成 new_str,如果 num 指定,则替换不超过 num 次 |
3) 大小写转换 - 5
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| string.capitalize() | 把字符串的第一个字符大写 |
| string.title() | 把字符串的每个单词首字母大写 |
| string.lower() | 转换 string 中所有大写字符为小写 |
| string.upper() | 转换 string 中的小写字母为大写 |
| string.swapcase() | 翻转 string 中的大小写 |
4) 文本对齐 - 3
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| string.ljust(width) | 返回一个原字符串左对齐,并使用空格填充至长度 width 的新字符串 |
| string.rjust(width) | 返回一个原字符串右对齐,并使用空格填充至长度 width 的新字符串 |
| string.center(width) | 返回一个原字符串居中,并使用空格填充至长度 width 的新字符串 |
5) 去除空白字符 - 3
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| string.lstrip() | 截掉 string 左边(开始)的空白字符 |
| string.rstrip() | 截掉 string 右边(末尾)的空白字符 |
| string.strip() | 截掉 string 左右两边的空白字符 |
6) 拆分和连接 - 5
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| string.partition(str) | 把字符串 string 分成一个 3 元素的元组 (str前面, str, str后面) |
| string.rpartition(str) | 类似于 partition() 方法,不过是从右边开始查找 |
| string.split(str="", num) | 以 str 为分隔符拆分 string,如果 num 有指定值,则仅分隔 num + 1 个子字符串,str 默认包含 '\r', '\t', '\n' 和空格 |
| string.splitlines() | 按照行('\r', '\n', '\r\n')分隔,返回一个包含各行作为元素的列表 |
| string.join(seq) | 以 string 作为分隔符,将 seq 中所有的元素(的字符串表示)合并为一个新的字符串 |
字符串的切片
-
切片 方法适用于 字符串、列表、元组
-
切片 使用 索引值 来限定范围,从一个大的 字符串 中 切出 小的 字符串
-
列表 和 元组 都是 有序 的集合,都能够 通过索引值 获取到对应的数据
-
字典 是一个 无序 的集合,是使用 键值对 保存数据
-
num_str = "0123456789"
# 1. 截取从 2 ~ 5 位置 的字符串
print(num_str[2:6])
# 2. 截取从 2 ~ `末尾` 的字符串
print(num_str[2:])
# 3. 截取从 `开始` ~ 5 位置 的字符串
print(num_str[:6])
# 4. 截取完整的字符串
print(num_str[:])
# 5. 从开始位置,每隔一个字符截取字符串
print(num_str[::2])
# 6. 从索引 1 开始,每隔一个取一个
print(num_str[1::2])
# 倒序切片
# -1 表示倒数第一个字符
print(num_str[-1])
# 7. 截取从 2 ~ `末尾 - 1` 的字符串
print(num_str[2:-1])
# 8. 截取字符串末尾两个字符
print(num_str[-2:])
# 9. 字符串的逆序(面试题)
print(num_str[::-1])6. 公共方法
6.1 Python 内置函数
Python 包含了以下内置函数:
| 函数 | 描述 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| len(item) | 计算容器中元素个数 | |
| del(item) | 删除变量 | del 有两种方式 |
| max(item) | 返回容器中元素最大值 | 如果是字典,只针对 key 比较 |
| min(item) | 返回容器中元素最小值 | 如果是字典,只针对 key 比较 |
| cmp(item1, item2) | 比较两个值,-1 小于/0 相等/1 大于 | Python 3.x 取消了 cmp 函数 |
注意
-
字符串 比较符合以下规则: "0" < "A" < "a"
6.2 切片
| 描述 | Python 表达式 | 结果 | 支持的数据类型 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 切片 | "0123456789"[::-2] | "97531" | 字符串、列表、元组 |
-
切片 使用 索引值 来限定范围,从一个大的 字符串 中 切出 小的 字符串
-
列表 和 元组 都是 有序 的集合,都能够 通过索引值 获取到对应的数据
-
字典 是一个 无序 的集合,是使用 键值对 保存数据
6.3 运算符
| 运算符 | Python 表达式 | 结果 | 描述 | 支持的数据类型 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| + | [1, 2] + [3, 4] | [1, 2, 3, 4] | 合并 | 字符串、列表、元组 |
| * | ["Hi!"] * 4 | ['Hi!', 'Hi!', 'Hi!', 'Hi!'] | 重复 | 字符串、列表、元组 |
| in | 3 in (1, 2, 3) | True | 元素是否存在 | 字符串、列表、元组、字典 |
| not in | 4 not in (1, 2, 3) | True | 元素是否不存在 | 字符串、列表、元组、字典 |
| > >= == < <= | (1, 2, 3) < (2, 2, 3) | True | 元素比较 | 字符串、列表、元组 |
注意
-
in在对 字典 操作时,判断的是 字典的键 -
in和not in被称为 成员运算符
成员运算符
成员运算符用于 测试 序列中是否包含指定的 成员
| 运算符 | 描述 | 实例 |
|---|---|---|
| in | 如果在指定的序列中找到值返回 True,否则返回 False | 3 in (1, 2, 3) 返回 True |
| not in | 如果在指定的序列中没有找到值返回 True,否则返回 False | 3 not in (1, 2, 3) 返回 False |
注意:在对 字典 操作时,判断的是 字典的键





















 407
407

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








