Spring注解-IOC
组件注册
@Configuration&@Bean
@Configuration:声明一个配置类
@Bean:向容器中注册bean,bean的类型为方法返回值类型,ID默认就是方法名。可以通过修改@Bean注解的value属性或者方法名来修改beanID
//配置类=配置文件
@Configuration
public class MainConfig {
//向容器中注册bean,类型为返回值类型,ID默认就是方法名
@Bean("person")
public Person person01(){
return new Person("zhangsan",23);
}
}
public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig.class);
Person person = applicationContext.getBean(Person.class);
System.out.println(person);
String[] beanNamesForType = applicationContext.getBeanNamesForType(Person.class);
for (int i = 0; i < beanNamesForType.length; i++) {
System.out.println(beanNamesForType[i]);
}
}
}

-
使用Spring提供的FactoryBean:默认获取到的是FactoryBean调用getObject返回的对象,想要获取FactoryBean本身,需要在bean id前加“&”
@Configuration @Import({MyImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar.class}) public class MainConfig3 { @Bean public MyFactoryBean myFactoryBean() { return new MyFactoryBean(); } }public class MyFactoryBean implements FactoryBean<Product> { @Override public Product getObject() throws Exception { return new Product(); } @Override public Class<?> getObjectType() { return Product.class; } @Override public boolean isSingleton() { return true; } }@Test public void mainConfig3Test() { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig3.class); Object bean = context.getBean("myFactoryBean"); System.out.println("bean的类型:"+bean.getClass()); }
@Test public void mainConfig3Test() { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig3.class); Object bean = context.getBean("&myFactoryBean"); System.out.println("bean的类型:"+bean.getClass()); }
@ComponentScan
@ComponentScan:指定包扫描的路径。可以把指定路径下标注了@Controller、@Repository、@Service、@Component注解的类加到容器中。可以通过includeFilters和excludeFilters来指定添加和剔除哪些组件。
//配置类=配置文件
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(value = "com.hjw", excludeFilters = {
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION, classes = {Controller.class}),
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE, classes = {Dao.class})
})
//FilterType.ANNOTATION:按注解过滤
//FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE:按类型过滤
//FilterType.CUSTOM:自定义规则
public class MainConfig {
//向容器中注册bean,类型为返回值类型,ID默认就是方法名
@Bean("person")
public Person person01(){
return new Person("zhangsan",23);
}
}
public class IOCTest {
@Test
public void test1(){
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig.class);
String[] names = context.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (int i = 0; i < names.length; i++) {
System.out.println(names[i]);
}
}
}
@org.springframework.stereotype.Controller
public class Controller {
}
@org.springframework.stereotype.Service
public class Service {
}
@Repository
public class Dao {
}

自定义FilterType
public enum FilterType {
/**
* Filter candidates marked with a given annotation.
* @see org.springframework.core.type.filter.AnnotationTypeFilter
*/
ANNOTATION,
/**
* Filter candidates assignable to a given type.
* @see org.springframework.core.type.filter.AssignableTypeFilter
*/
ASSIGNABLE_TYPE,
/**
* Filter candidates matching a given AspectJ type pattern expression.
* @see org.springframework.core.type.filter.AspectJTypeFilter
*/
ASPECTJ,
/**
* Filter candidates matching a given regex pattern.
* @see org.springframework.core.type.filter.RegexPatternTypeFilter
*/
REGEX,
/** Filter candidates using a given custom
* {@link org.springframework.core.type.filter.TypeFilter} implementation.
*/
CUSTOM
}
通过实现org.springframework.core.type.filter.TypeFilter来自定义过滤器
public class MyFilter implements TypeFilter {
/**
*
* @param metadataReader 当前正在扫描的类信息
* @param metadataReaderFactory 可以获取到其他类信息
* @return
* @throws IOException
*/
@Override
public boolean match(MetadataReader metadataReader, MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory) throws IOException {
// 当前类的注解信息
AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata = metadataReader.getAnnotationMetadata();
// 当前类信息
ClassMetadata classMetadata = metadataReader.getClassMetadata();
String className = classMetadata.getClassName();
System.out.println("当前扫描到的类名:"+className);
return false;
}
}

@Scope
-
singleton:单例的(默认值),容器启动时会创建对象放在容器中,以后每次获取都是从容器中拿。
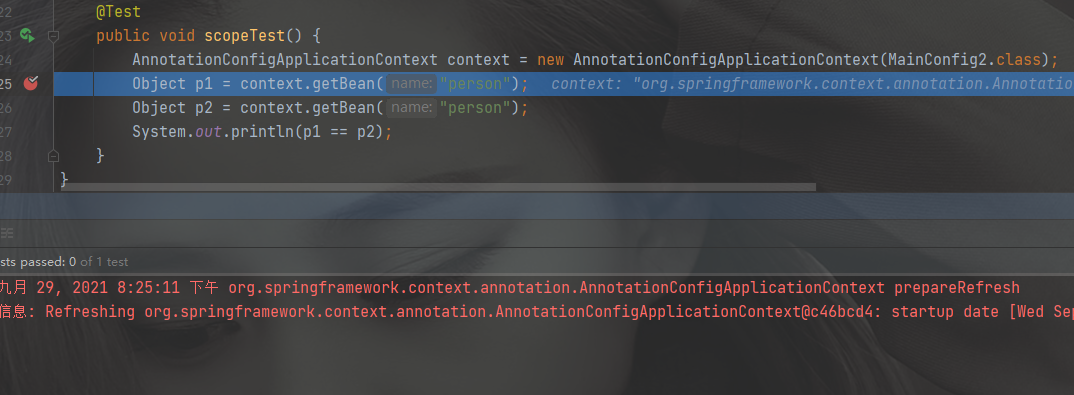
@Configuration public class MainConfig2 { @Bean public Person person(){ System.out.println("创建person"); return new Person("李四", 18); } }@Test public void scopeTest() { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig2.class); Object p1 = context.getBean("person"); Object p2 = context.getBean("person"); System.out.println(p1 == p2); }

-
prototype:多实例的,容器启动时不会创建对象,每次获取的时候才创建对象
@Configuration public class MainConfig2 { @Scope("prototype") @Bean public Person person(){ System.out.println("创建person"); return new Person("李四", 18); } }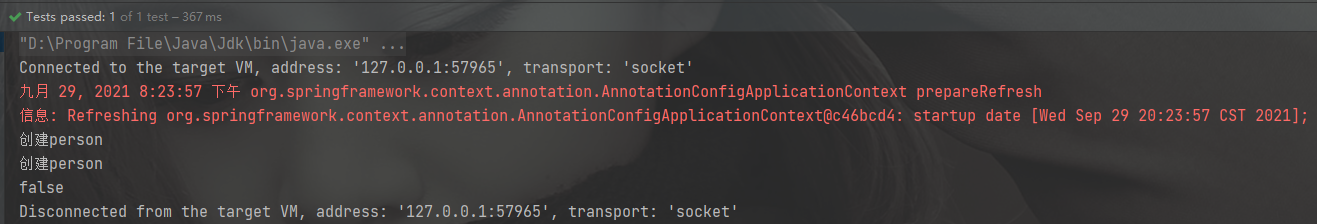
-
request:同一个请求创建一个实例
-
session:同一个session创建一个实例
@Lazy
单实例bean,默认在容器启动的时候创建对象。懒加载:容器启动时不创建对象。第一次获取bean时才创建对象,并初始化。
@Lazy
@Bean
public Person person(){
System.out.println("创建person");
return new Person("李四", 18);
}
@Test
public void scopeTest() {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig2.class);
System.out.println("容器创建完成");
// Object p1 = context.getBean("person");
// Object p2 = context.getBean("person");
// System.out.println(p1 == p2);
}
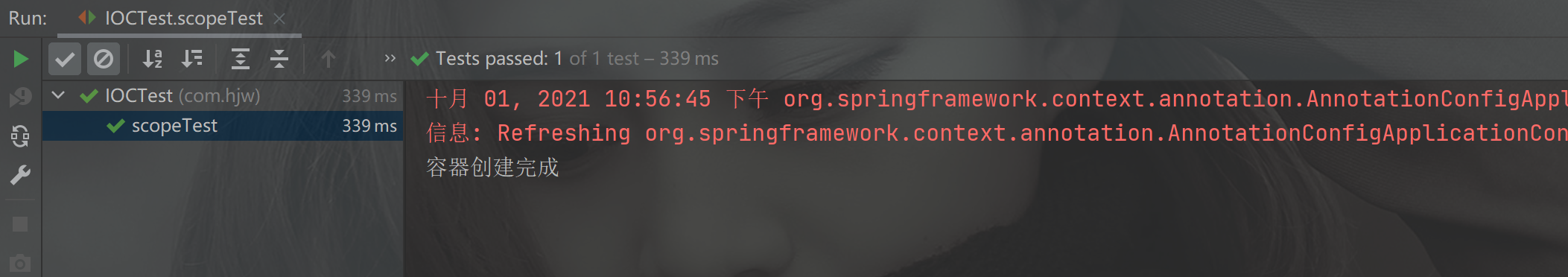
打开注解时

@Conditional
按照一定条件进行判断,满足条件则给容器中注册bean
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Conditional {
/**
* All {@link Condition}s that must {@linkplain Condition#matches match}
* in order for the component to be registered.
*/
Class<? extends Condition>[] value();
}
可以作用在类和方法上,值Condition类
public class MyConditional implements Condition {
@Override
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = context.getRegistry();
return registry.containsBeanDefinition("person");
}
}
@Configuration
public class MainConfig2 {
// @Scope("prototype")
// @Lazy
// @Bean
// public Person person(){
// System.out.println("创建person");
// return new Person("李四", 18);
// }
@Conditional({MyConditional.class})
@Bean
public Person james() {
System.out.println("创建James");
return new Person("james", 23);
}
@Bean
public Person kobe() {
System.out.println("创建Kobe");
return new Person("Kobe", 24);
}
}
@Test
public void scopeTest() {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig2.class);
System.out.println("容器创建完成");
}

@Import
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Import {
/**
* {@link Configuration}, {@link ImportSelector}, {@link ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar}
* or regular component classes to import.
*/
Class<?>[] value();
}
-
@Import(要导入容器的组件),id默认是全类名
@Configuration @Import({Person.class}) public class MainConfig2 { // @Scope("prototype") // @Lazy // @Bean // public Person person(){ // System.out.println("创建person"); // return new Person("李四", 18); // } // @Conditional({MyConditional.class}) @Bean public Person james() { System.out.println("创建James"); return new Person("james", 23); } @Bean public Person kobe() { System.out.println("创建Kobe"); return new Person("Kobe", 24); } }@Test public void scopeTest() { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig2.class); System.out.println("容器创建完成"); String[] definitionNames = context.getBeanDefinitionNames(); for (int i = 0; i < definitionNames.length; i++) { System.out.println(definitionNames[i]); } }
-
ImportSelector:返回要导入组件的全类名
public interface ImportSelector { /** * Select and return the names of which class(es) should be imported based on * the {@link AnnotationMetadata} of the importing @{@link Configuration} class. * @return the class names, or an empty array if none */ String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata); }@Configuration @Import({MyImportSelect.class}) public class MainConfig3 { }public class MyImportSelect implements ImportSelector { @Override public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) { return new String[]{"com.hjw.bean.person","com.hjw.bean.animal"}; } }@Test public void mainConfig3Test() { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig3.class); String[] definitionNames = context.getBeanDefinitionNames(); for (int i = 0; i < definitionNames.length; i++) { System.out.println(definitionNames[i]); } }

-
ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar:手动注册
public interface ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar { /** * Register bean definitions as necessary based on the given annotation metadata of * the importing {@code @Configuration} class. * <p>Note that {@link BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor} types may <em>not</em> be * registered here, due to lifecycle constraints related to {@code @Configuration} * class processing. * @param importingClassMetadata annotation metadata of the importing class * @param registry current bean definition registry */ void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry); }@Configuration @Import({MyImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar.class}) public class MainConfig3 { }public class MyImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar { @Override public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(Card.class); registry.registerBeanDefinition("myCard", beanDefinition); } }@Test public void mainConfig3Test() { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig3.class); String[] definitionNames = context.getBeanDefinitionNames(); for (int i = 0; i < definitionNames.length; i++) { System.out.println(definitionNames[i]); } }
总结
给容器中注册组件:
- 包扫描+组件标注注解(@Controller/@Service/@Respository/@Component)
- @Bean,导入第三方包里的组件
- @Import
生命周期
@Bean指定init和destroy方法
public class Plane {
public Plane(){
System.out.println("plane constructor");
}
public void initMethod() {
System.out.println("plane initMethod");
}
public void destroyMethod() {
System.out.println("plane destroyMethod");
}
}
@Configuration
public class MainConfig4 {
@Bean(initMethod = "initMethod", destroyMethod = "destroyMethod")
public Plane plane(){
return new Plane();
}
}
@Test
public void mainConfig4Test() {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig4.class);
System.out.println("容器创建完成");
context.close();
}

InitializingBean接口&DisposableBean接口欧
public interface InitializingBean {
/**
* Invoked by the containing {@code BeanFactory} after it has set all bean properties
* and satisfied {@link BeanFactoryAware}, {@code ApplicationContextAware} etc.
* <p>This method allows the bean instance to perform validation of its overall
* configuration and final initialization when all bean properties have been set.
* @throws Exception in the event of misconfiguration (such as failure to set an
* essential property) or if initialization fails for any other reason
*/
// 在所有属性设置完成后会调用
void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception;
}
public interface DisposableBean {
/**
* Invoked by the containing {@code BeanFactory} on destruction of a bean.
* @throws Exception in case of shutdown errors. Exceptions will get logged
* but not rethrown to allow other beans to release their resources as well.
*/
// 在BeanFactory销毁时调用
void destroy() throws Exception;
}
public class Plane implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
public Plane(){
System.out.println("plane constructor");
}
public void initMethod() {
System.out.println("plane initMethod");
}
public void destroyMethod() {
System.out.println("plane destroyMethod");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("plane afterPropertiesSet");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("plane destroy");
}
}

@PostConstruct&@PreDestroy
/**
* The PostConstruct annotation is used on a method that needs to be executed
* after dependency injection is done to perform any initialization. This
* method MUST be invoked before the class is put into service. This
* annotation MUST be supported on all classes that support dependency
* injection. The method annotated with PostConstruct MUST be invoked even
* if the class does not request any resources to be injected. Only one
* method can be annotated with this annotation. The method on which the
* PostConstruct annotation is applied MUST fulfill all of the following
* criteria:
* <p>
* <ul>
* <li>The method MUST NOT have any parameters except in the case of
* interceptors in which case it takes an InvocationContext object as
* defined by the Interceptors specification.</li>
* <li>The method defined on an interceptor class MUST HAVE one of the
* following signatures:
* <p>
* void <METHOD>(InvocationContext)
* <p>
* Object <METHOD>(InvocationContext) throws Exception
* <p>
* <i>Note: A PostConstruct interceptor method must not throw application
* exceptions, but it may be declared to throw checked exceptions including
* the java.lang.Exception if the same interceptor method interposes on
* business or timeout methods in addition to lifecycle events. If a
* PostConstruct interceptor method returns a value, it is ignored by
* the container.</i>
* </li>
* <li>The method defined on a non-interceptor class MUST HAVE the
* following signature:
* <p>
* void <METHOD>()
* </li>
* <li>The method on which PostConstruct is applied MAY be public, protected,
* package private or private.</li>
* <li>The method MUST NOT be static except for the application client.</li>
* <li>The method MAY be final.</li>
* <li>If the method throws an unchecked exception the class MUST NOT be put into
* service except in the case of EJBs where the EJB can handle exceptions and
* even recover from them.</li></ul>
* @since Common Annotations 1.0
* @see javax.annotation.PreDestroy
* @see javax.annotation.Resource
*/
@Documented
@Retention (RUNTIME)
@Target(METHOD)
public @interface PostConstruct {
// 在bean初始化完成并且依赖注入完成执行方法
}
/**
* The PreDestroy annotation is used on methods as a callback notification to
* signal that the instance is in the process of being removed by the
* container. The method annotated with PreDestroy is typically used to
* release resources that it has been holding. This annotation MUST be
* supported by all container managed objects that support PostConstruct
* except the application client container in Java EE 5. The method on which
* the PreDestroy annotation is applied MUST fulfill all of the following
* criteria:
* <p>
* <ul>
* <li>The method MUST NOT have any parameters except in the case of
* interceptors in which case it takes an InvocationContext object as
* defined by the Interceptors specification.</li>
* <li>The method defined on an interceptor class MUST HAVE one of the
* following signatures:
* <p>
* void <METHOD>(InvocationContext)
* <p>
* Object <METHOD>(InvocationContext) throws Exception
* <p>
* <i>Note: A PreDestroy interceptor method must not throw application
* exceptions, but it may be declared to throw checked exceptions including
* the java.lang.Exception if the same interceptor method interposes on
* business or timeout methods in addition to lifecycle events. If a
* PreDestroy interceptor method returns a value, it is ignored by
* the container.</i>
* </li>
* <li>The method defined on a non-interceptor class MUST HAVE the
* following signature:
* <p>
* void <METHOD>()
* </li>
* <li>The method on which PreDestroy is applied MAY be public, protected,
* package private or private.</li>
* <li>The method MUST NOT be static.</li>
* <li>The method MAY be final.</li>
* <li>If the method throws an unchecked exception it is ignored except in the
* case of EJBs where the EJB can handle exceptions.</li>
* </ul>
*
* @see javax.annotation.PostConstruct
* @see javax.annotation.Resource
* @since Common Annotations 1.0
*/
@Documented
@Retention (RUNTIME)
@Target(METHOD)
public @interface PreDestroy {
// 在容器移除bean之前回调通知
}
public class Plane implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
public Plane(){
System.out.println("plane constructor");
}
public void initMethod() {
System.out.println("plane initMethod");
}
public void destroyMethod() {
System.out.println("plane destroyMethod");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("plane afterPropertiesSet");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("plane destroy");
}
@PostConstruct
public void post() {
System.out.println("plane PostConstruct");
}
@PreDestroy
public void preDestroy() {
System.out.println("plane PreDestroy");
}
}

BeanPostProcessor接口
/**
* Factory hook that allows for custom modification of new bean instances,
* e.g. checking for marker interfaces or wrapping them with proxies.
*
* <p>ApplicationContexts can autodetect BeanPostProcessor beans in their
* bean definitions and apply them to any beans subsequently created.
* Plain bean factories allow for programmatic registration of post-processors,
* applying to all beans created through this factory.
*
* <p>Typically, post-processors that populate beans via marker interfaces
* or the like will implement {@link #postProcessBeforeInitialization},
* while post-processors that wrap beans with proxies will normally
* implement {@link #postProcessAfterInitialization}.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 10.10.2003
* @see InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
* @see DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor
* @see ConfigurableBeanFactory#addBeanPostProcessor
* @see BeanFactoryPostProcessor
*/
// bean的后置处理器,在bean初始化前后进行一些操作
public interface BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance <i>before</i> any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.
* @param bean the new bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one;
* if {@code null}, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
*/
// 在已经创建的bean实例任何初始化方法调用前调用该方法
Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
/**
* Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance <i>after</i> any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.
* <p>In case of a FactoryBean, this callback will be invoked for both the FactoryBean
* instance and the objects created by the FactoryBean (as of Spring 2.0). The
* post-processor can decide whether to apply to either the FactoryBean or created
* objects or both through corresponding {@code bean instanceof FactoryBean} checks.
* <p>This callback will also be invoked after a short-circuiting triggered by a
* {@link InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation} method,
* in contrast to all other BeanPostProcessor callbacks.
* @param bean the new bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one;
* if {@code null}, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean
*/
// 在已经创建的bean实例任何初始化方法调用后调用该方法
Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
}
@Component
public class MyPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("postProcessBeforeInitialization beanName:" + beanName);
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("postProcessAfterInitialization beanName:" + beanName);
return bean;
}
}
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.hjw.bean")
public class MainConfig4 {
@Bean(initMethod = "initMethod", destroyMethod = "destroyMethod")
public Plane plane(){
return new Plane();
}
}

-
原理
打个断点看下大致的方法调用栈

到mainConfig4Test,创建IOC容器

创建IOC容器

调用refresh方法,实例化所有剩下的单实例对象

实例化所有剩下的单例

创建bean>属性赋值>初始化

在初始化方法前后执行applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName)和applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName)

遍历所有的BeanPostProcessor,调用postProcessBeforeInitialization方法,如果返回null,不再执行后面的BeanPostProcessor

-
BeanPostProcessor在Spring底层的使用
BeanPostProcessor的实现类

-
ApplicationContextAwareProcessor注入IOC容器
在ApplicationContextAwareProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法中会调用invokeAwareInterfaces方法,在invokeAwareInterfaces方法中根据bean实现的接口注入相对应的资源


-
InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor处理@PostConstruct和@PreDestroy注解的方法
找到生命周期注解标注的方法,调用对应的方法
-


属性赋值
@Value
- 可以使用基本数值
- 可以使用SpEL:#{}
- 可以使用${}:取配置文件中的值(运行环境变量的值 )



自动装配
Spring利用依赖注入(DI),完成对IOC容器中各个组件的依赖关系赋值。通过AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor实现自动装配。
@Autowired
- 默认优先按类型去容器中找对应的组件
- 如果找到多个相同类型的组件,再将属性名作为组件的id在容器中查找
- 可以使用@Qualifier指定需要装配的组件id,而不是属性名作为组件id
- 可以使用@Primary让Spring在自动装配的时候,默认使用首选的bean
@Configuration
@ComponentScan({"com.hjw.service"})
public class AutowriredConfig {
@Bean("cardDao")
public CardDao cardDao() {
return new CardDao("cardDao");
}
@Primary
@Bean("cardDao1")
public CardDao cardDao1() {
return new CardDao("cardDao1");
}
}
@org.springframework.stereotype.Service
public class Service {
@Autowired
private CardDao cardDao;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Service{" +
"cardDao=" + cardDao +
'}';
}
}
@Test
public void autowireTest() {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AutowriredConfig.class);
Service service = context.getBean(Service.class);
System.out.println(service);
}

@Resource(JSR250)&@Inject(JSR330)【java规范的注解】
-
@Resource
可以和@Autowired一样实现自动装配,默认按组件名称装配。不支持@Primary,没有required属性
-
@Inject
需要导入javax.inject包
<dependency> <groupId>javax.inject</groupId> <artifactId>javax.inject</artifactId> <version>1</version> </dependency>
Aware接口
自定义组件想要使用Spring容器底层的一些组件(eg:ApplicationContext,BeanFactory…),可以通过实现xxxAware接口注入Spring底层组件。在创建对象的时候,会调用接口中定义的相关方法完成组件注入。对应的xxxAware接口通过xxxAwareProcesssor实现。
@Profile
根据环境注册bean。加了注解的bean,只有在这个环境被激活的时候才能注册到容器中。默认是default环境。
public class DataSource {
}
@Configuration
public class MainConfig5 {
@Profile("default")
@Bean("defaultDataSource")
public DataSource defaultDataSource() {
return new DataSource();
}
@Profile("test")
@Bean("testDataSource")
public DataSource testDataSource() {
return new DataSource();
}
@Profile("dev")
@Bean("devDataSource")
public DataSource devDataSource() {
return new DataSource();
}
}
/**
* 切换环境:
* 1.使用命令行参数,-Dspring.profiles.active=dev
* 2.使用编码方式指定激活环境
*/
@Test
public void profileTest() {
// AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig5.class);
// 创建容器
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
// 设置激活的环境
context.getEnvironment().setActiveProfiles("dev","test");
// 注册配置类
context.register(MainConfig5.class);
// 启动刷新容器
context.refresh();
String[] beanNamesForType = context.getBeanNamesForType(DataSource.class);
for (String beanName : beanNamesForType) {
System.out.println(beanName);
}
context.close();
}






















 796
796

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








