这篇博客主要说一下常见的排序算法,有些算法会给出相应的java代码。
排序的目的是为了提高查找的效率。
排序算法主要分为内部排序和外部排序,或者稳定排序或不稳定排序。
内部排序是指排序序列完全存放在内存中进行的排序过程,这种方法适合数量不太大的数据元素的排序。外部排序是指待排序的数据元素非常多,以至于它们必须存储在外部存储器上,这种排序过程中需要访问外存储器,这样的排序称为外排序。这里主要讨论内排序。
内部排序方法大致可以分为以下几种类型:
一、插入排序
1.直接插入排序
2.希尔排序
二、交换排序
1.冒泡排序
2.快速排序
快速排序时一种划分交换排序方法,是冒泡排序的一种改进算法,采用了分治策略。
基本思想
通过一趟排序将要排序的记录分割成独立的两个部分,其中一部分的所有记录的关键字值都比另外一部分的所有记录关键字值小,然后再按此方法对这两部分记录分别进行快速排序,整个排序过程可以递归进行,以此达到整个记录序列变成有序。
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* 快速排序 的实现
*
* @author zhangcanlong
* @date 2021/03/07
*/
public class QuickSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] testInts = {12,3,41,5,6,6,6,6,6};
quickSort(testInts,0,testInts.length-1);
System.out.println("快速排序后的结果为:"+Arrays.toString(testInts));
}
/**
* 一趟快速排序
* @param startIndex 开始的索引
* @param maxIndex 结尾的索引
* @param ints 要排序的数组
* @return 返回支点索引
*/
public static int partition(int[] ints,int startIndex,int maxIndex){
if(ints==null||ints.length<=1){
return 0;
}
// 设置第一个数据为支点
int flayValue = ints[startIndex];
System.out.println("当前一次排序的后的结果为:"+Arrays.toString(ints));
// 从数据两边交替比较,直到比支点的大的前进一位,直到比支点小的后退一位
while(startIndex<maxIndex){
//比支点大的数据,maxIndex 会自动--,忽略不进行参与
while(startIndex<maxIndex && flayValue<ints[maxIndex]){
maxIndex--;
}
if(startIndex<maxIndex){
// 能到这里表示,后面maxIndex索引那个数一定比 支点小,因为比支点大的数据,maxIndex 会自动--
ints[startIndex]=ints[maxIndex];
startIndex++;
}
// //比支点大的数据,startIndex 会自动++,忽略不进行参与
while(startIndex<maxIndex && flayValue>ints[startIndex]){
startIndex++;
}
// 能到这里表示,后面startIndex索引那个数一定比 支点大,因为比支点小的数据,startIndex会自动++
if(startIndex<maxIndex){
ints[maxIndex]=ints[startIndex];
maxIndex--;
}
}
ints[startIndex] = flayValue;
return startIndex;
}
/**
* 快速排序
*
* @param ints 要排序的数组
* @param startIndex 开始的索引
* @param maxIndex 要排序的数组的结尾的索引
*/
public static void quickSort(int[] ints,int startIndex,int maxIndex){
if(ints==null||ints.length==1){
return;
}
if(startIndex<maxIndex){
int flay = partition(ints,startIndex,maxIndex);
quickSort(ints,flay+1,maxIndex);
quickSort(ints,startIndex,flay-1);
}
}
}
三、选择排序
1.直接选择排序
2.树形选择排序
3.堆排序
四、归并排序
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/chengxiao/p/6194356.html
package sortdemo;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* Created by chengxiao on 2016/12/8.
*/
public class MergeSort {
public static void main(String []args){
int []arr = {9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1};
sort(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
public static void sort(int []arr){
int []temp = new int[arr.length];//在排序前,先建好一个长度等于原数组长度的临时数组,避免递归中频繁开辟空间
sort(arr,0,arr.length-1,temp);
}
private static void sort(int[] arr,int left,int right,int []temp){
if(left<right){
int mid = (left+right)/2;
sort(arr,left,mid,temp);//左边归并排序,使得左子序列有序
sort(arr,mid+1,right,temp);//右边归并排序,使得右子序列有序
merge(arr,left,mid,right,temp);//将两个有序子数组合并操作
}
}
private static void merge(int[] arr,int left,int mid,int right,int[] temp){
int i = left;//左序列指针
int j = mid+1;//右序列指针
int t = 0;//临时数组指针
while (i<=mid && j<=right){
if(arr[i]<=arr[j]){
temp[t++] = arr[i++];
}else {
temp[t++] = arr[j++];
}
}
while(i<=mid){//将左边剩余元素填充进temp中
temp[t++] = arr[i++];
}
while(j<=right){//将右序列剩余元素填充进temp中
temp[t++] = arr[j++];
}
t = 0;
//将temp中的元素全部拷贝到原数组中
while(left <= right){
arr[left++] = temp[t++];
}
}
}
五、其他排序(级数排序)
1.多关键字排序
2.链式基数排序
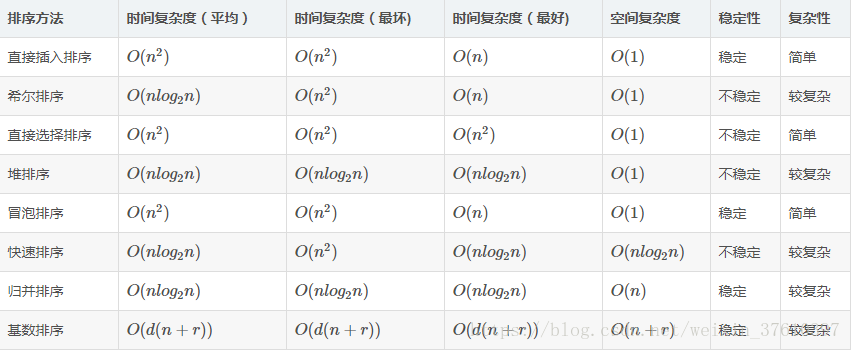
各种排序算法对比



























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








