主要流程
1、创建IOC容器,容器调用refresh()方法刷新容器
2、初始化IOC容器配置(例如加载配置文件、设置参数等)
3、注册BeanFactoryPostProcessor后置处理器(其中容器内置的ConfigurationClassPostProcessor处理器扫描解析容器的配置类,将解析后得到的组件beanDefinition保存到IOC容器中)
4、注册BeanPostProcessor后置处理器(在创建初始化组件对象时调用对应方法)
5、初始化事件多播器、注册事件监听器、初始化国际化配置等
6、实例化剩余的非延迟加载的单例组件
->判断容器是否含有该组件
->执行实现了InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcess接口的BeanPostProcessor后置处理器的postProcessBeforeInstantiation方法
->实例化对象
->执行MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor接口的postProcessMergedBeanDefinition方法
->执行populateBean方法设置属性(执行postProcessAfterInstantiation方法
->postProcessProperties方法
->进一步初始化属性)
->执行initializeBean方法初始化(执行BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法(例如InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor是处理标识@PostConstruct、@PreDestroy的方法)
->执行实现InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet方法
->initMethod方法
->执行BeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInitialization方法)
->注册销毁方法(registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary)
7、关闭IOC容器前(执行@PreDestroy方法
->DispoableBean接口的destroy方法
->destroyMethod方法)
以下是相关源码
1、refresh()
通过AbstractApplicationContext中的refresh()刷新IOC容器和注册bean组件等,
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
//创建IOC容器前准备一些环境变量,例如将配置文件加载到容器中
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
//得到IOC容器
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
//设置容器可直接注入接口、不可依赖注入接口等
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
//空方法
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
//扫描并将bean的相关定义信息放到容器中,创建BeanFactory级别的后置处理器对象并注册到容器中,可在BeanFactory后置处理器中获取并修改bean组件的相关信息
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
//注册Bean后置处理器,在创建组件前后调用Bean后置处理器的相关方法
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
//设置一些国际化信息
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
//创建不是延迟加载的单例对象
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}2、创建BeanFactoryPostProcessor后置处理器
1、通过invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory)该方法创建。
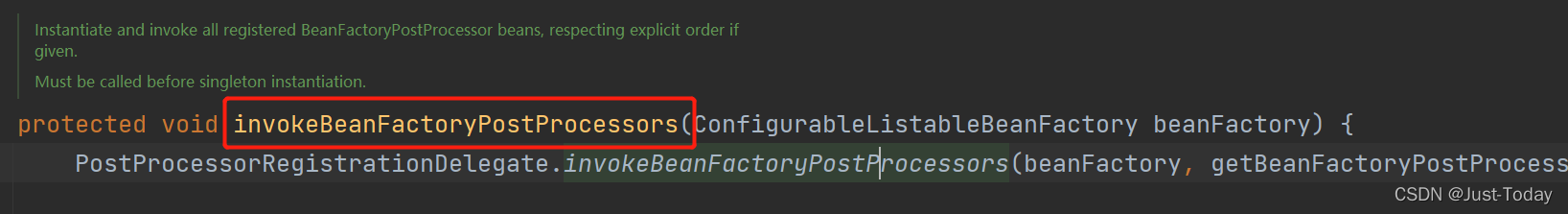 2、在PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate的invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors中,获取并创建容器中类型为BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的后置处理器,然后通过invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors方法运行postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法。
2、在PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate的invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors中,获取并创建容器中类型为BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的后置处理器,然后通过invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors方法运行postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法。
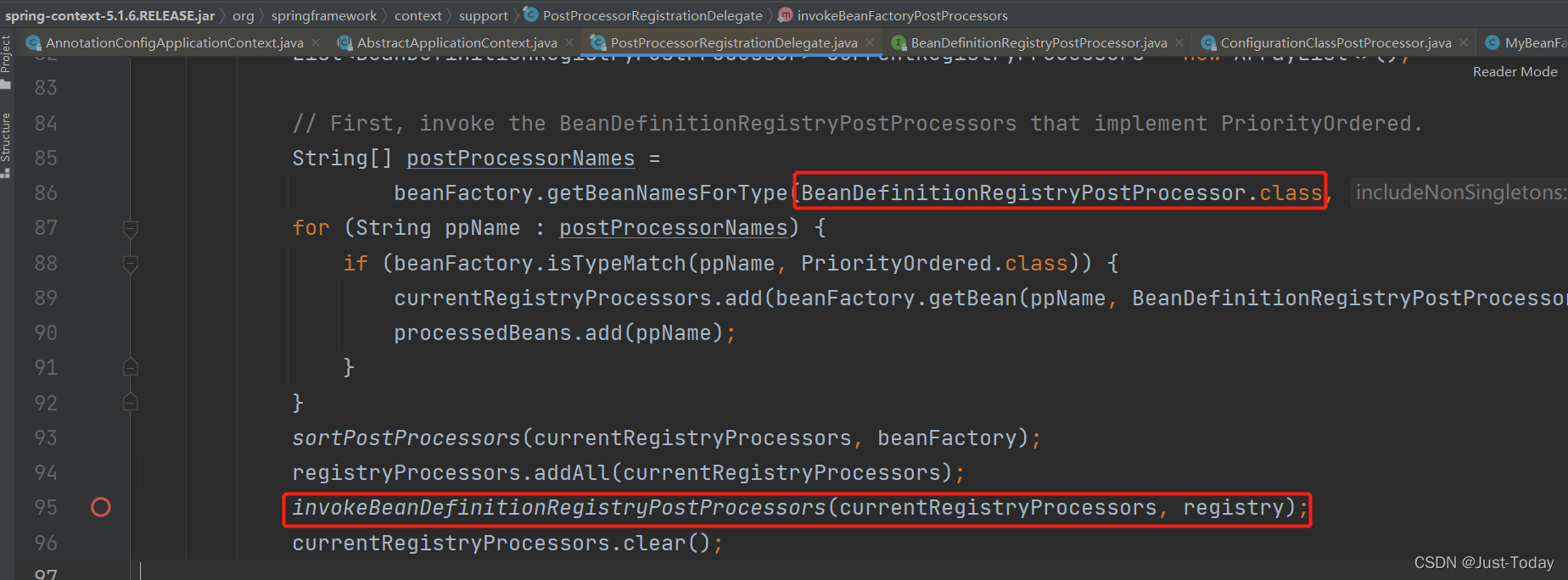
例如通过容器内置的ConfigurationClassPostProcessor后置处理器的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry中的processConfigBeanDefinitions方法解析配置类,并将解析得到组件信息保存到容器中,
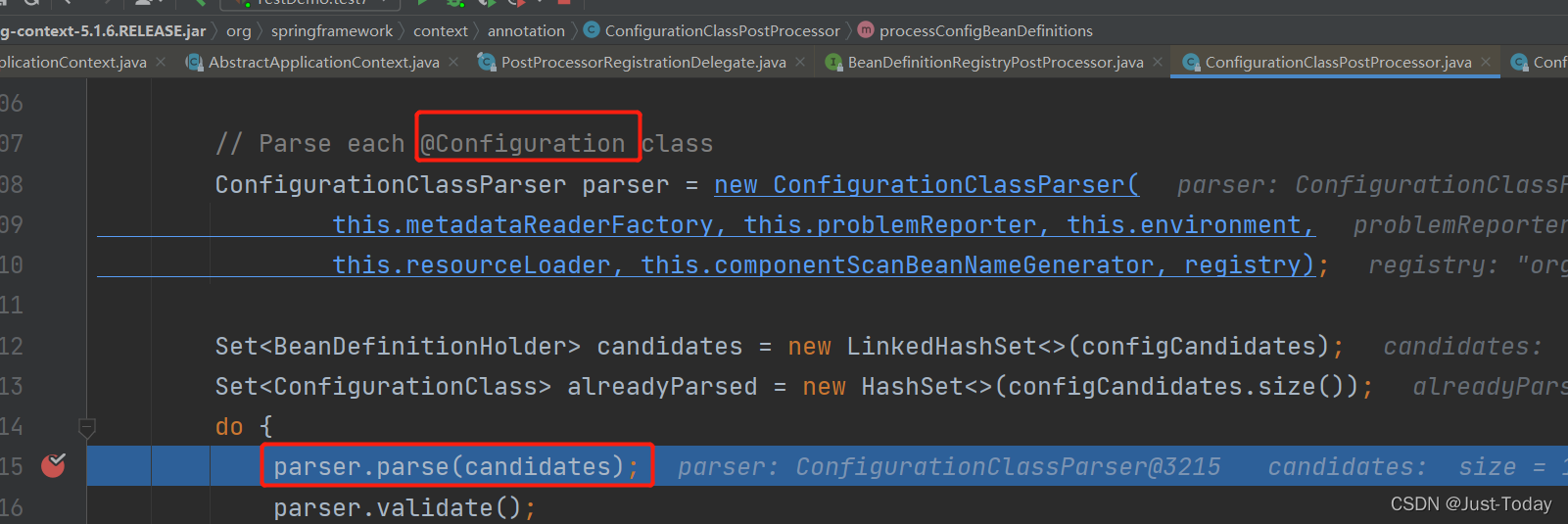
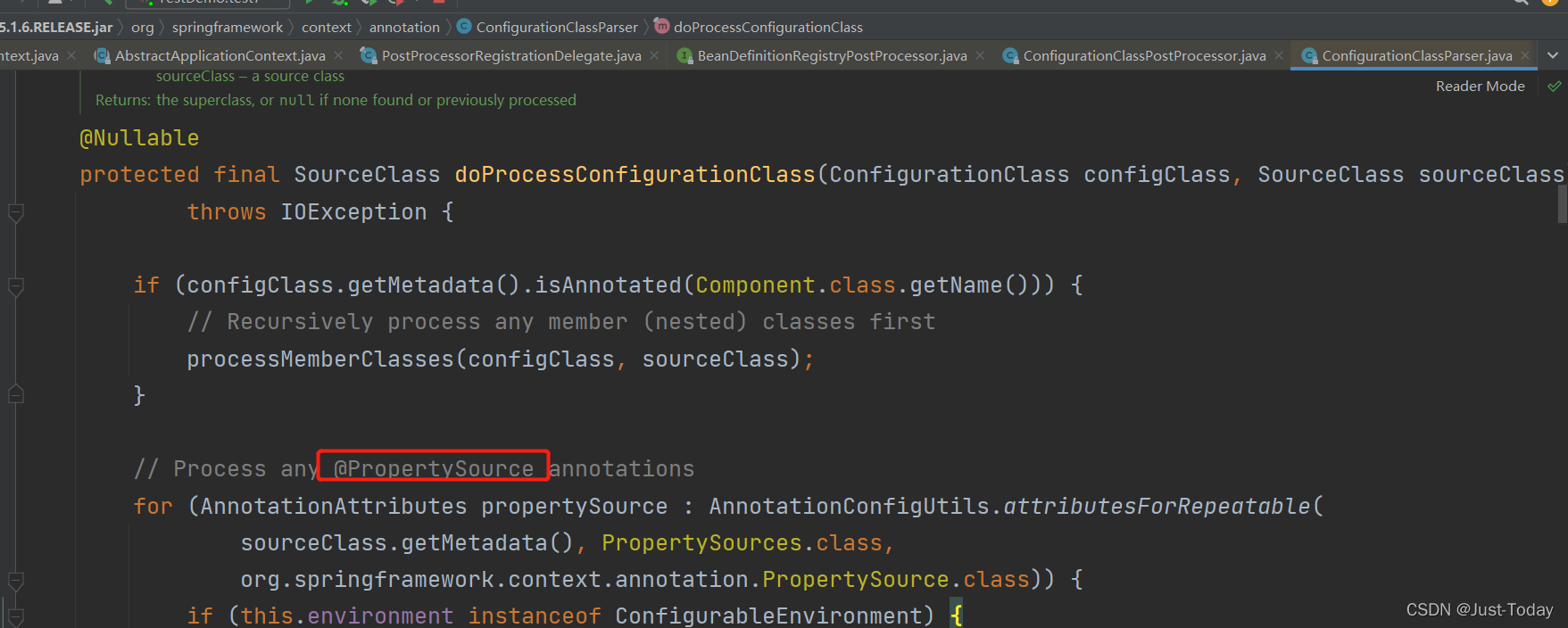
在ConfigurationClassParser的processConfigurationClass方法递归扫描配置类,
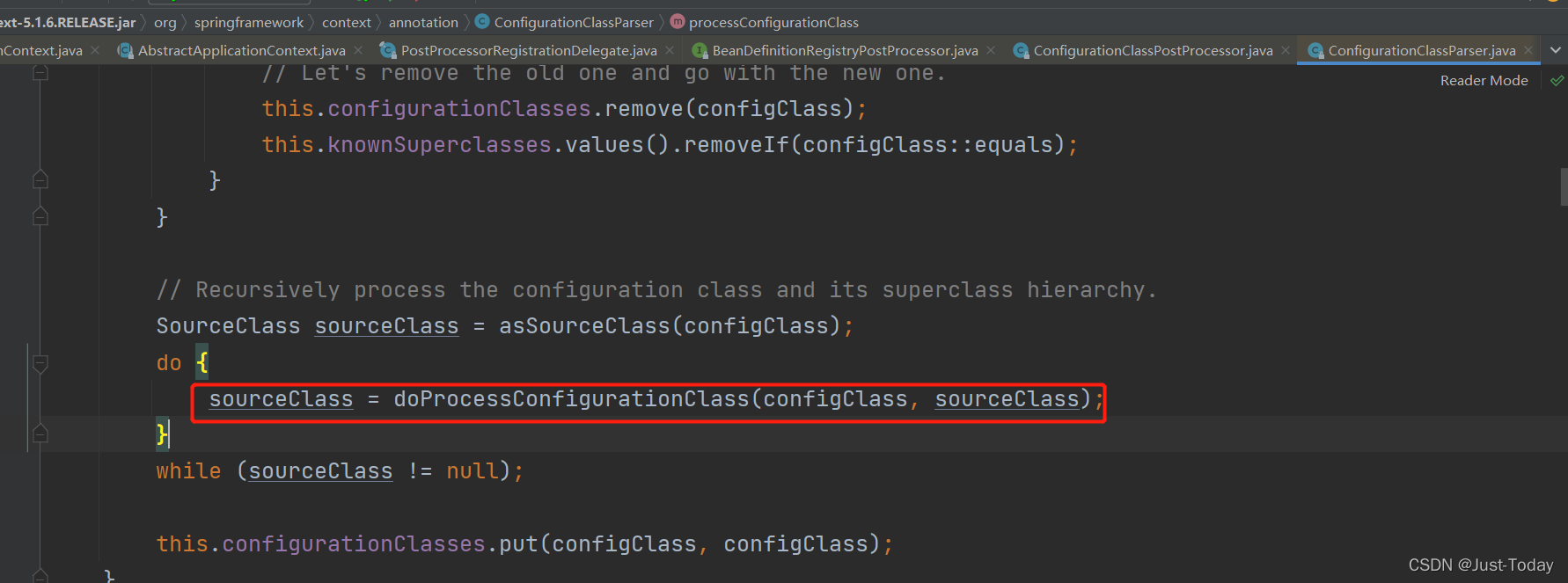
doProcessConfigurationClass方法将解析配置类的相关注解,并将信息保存到容器中,
例如通过@PropertySource将配置文件信息保存到容器中,
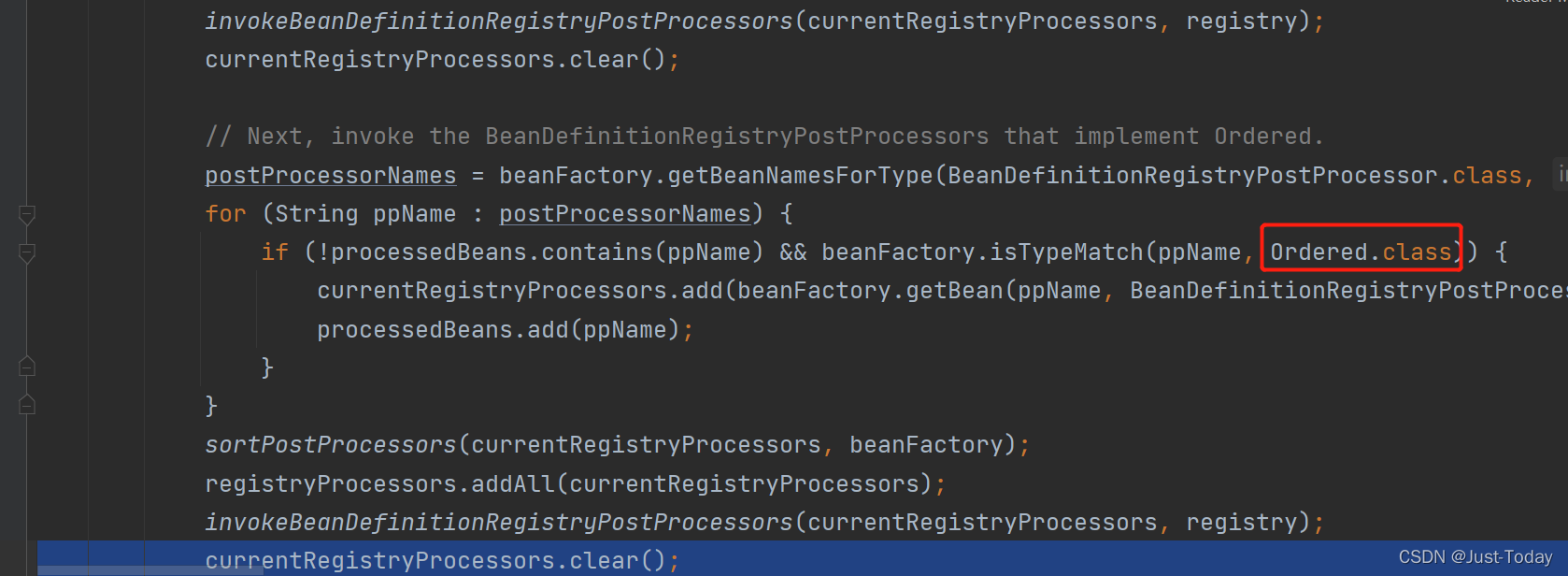
4、接着返回到一开始的invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors,我们可以自定义实现BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口,容器会在下面运行相关的类,若想要排序,可通过实现Ordered等class来实现,先运行有排序的PostProcessor,在循环运行没有排序的,
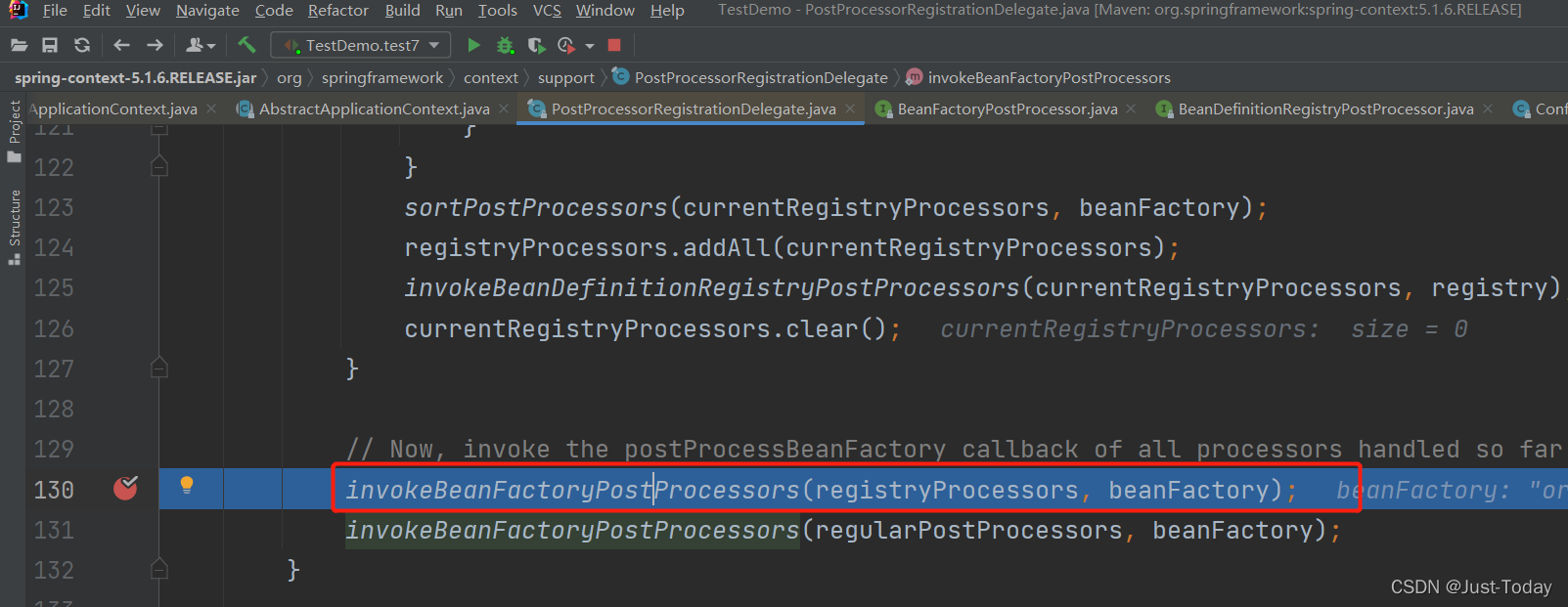
5、在下图就是红色框就是创建并运行实现BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的类,可以自定义实现BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口,对容器中的组件信息BeanDefinition进行修改,
3、创建BeanPostProcessor
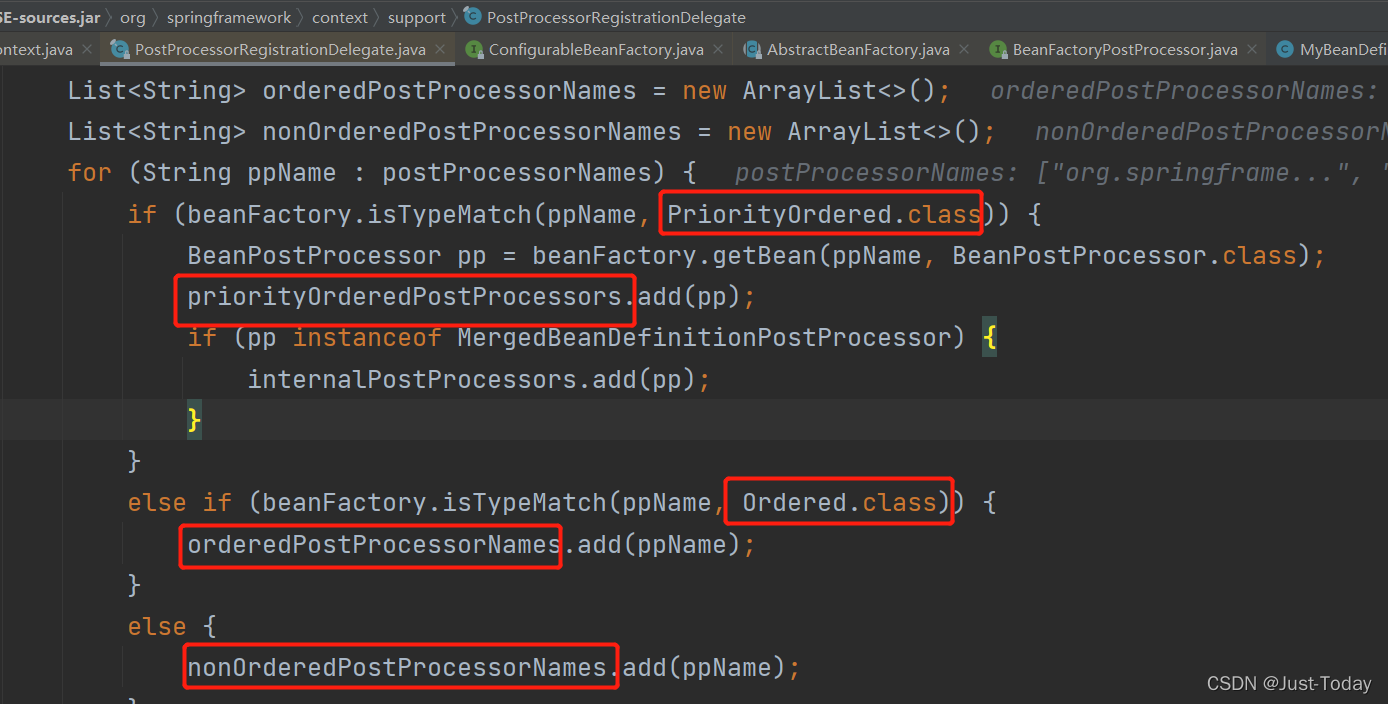
通过registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory)注册容器中实现BeanPostProcessor接口的实现类,先创建实现排序接口(PriorityOrdered.class,Ordered.class)的实现类,无排序的最后创建,并将创建的实现类放到容器的beanPostProcessors集合中,在后续创建初始化组件对象时将会遍历该集合,运行对应的方法。
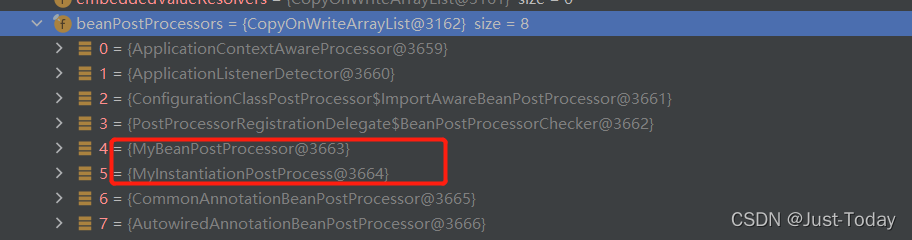
4、创建组件对象(单例)
1、通过 finishBeanFactoryInitialization方法创建剩余的非延迟加载的单实例对象,
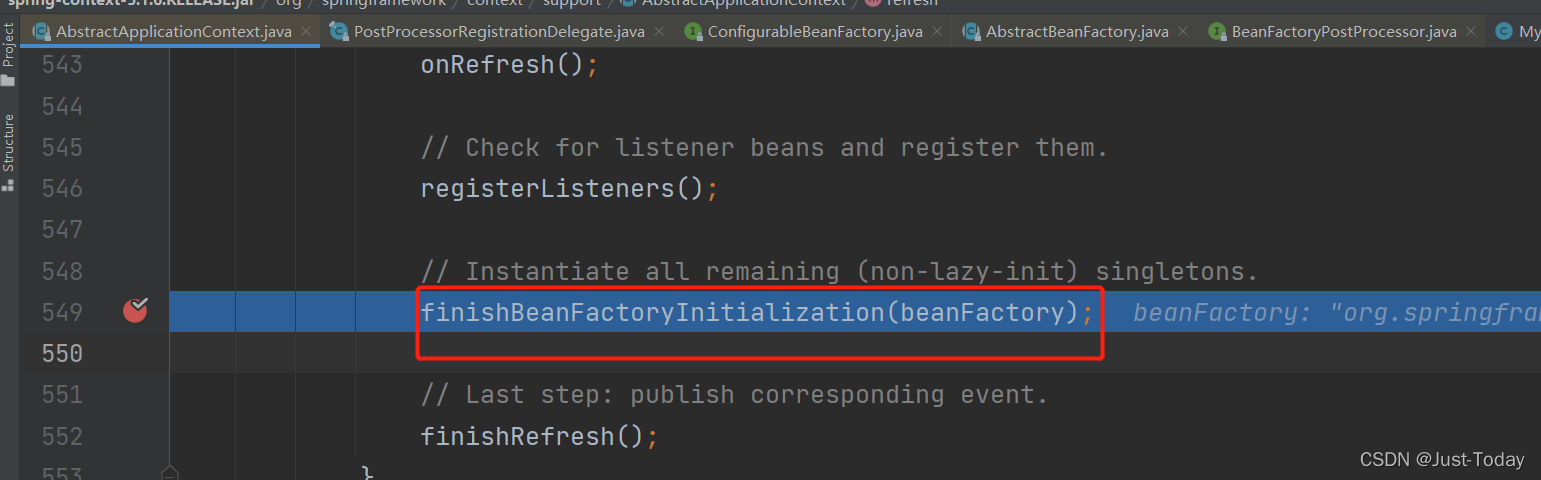
2、创建组件对象通过容器的getBean方法中的doGetBean方法获取,
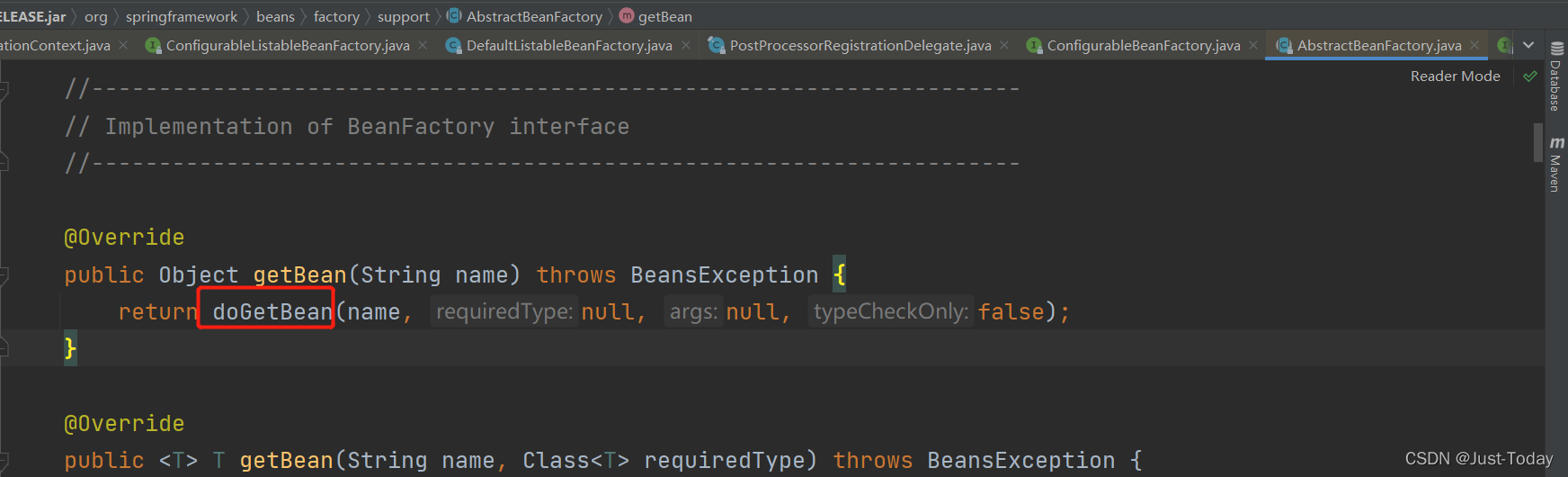
3、进入doGetBean方法, 先判断容器中是否已存在该组件对象,若有,则从容器中返回,不在创建,
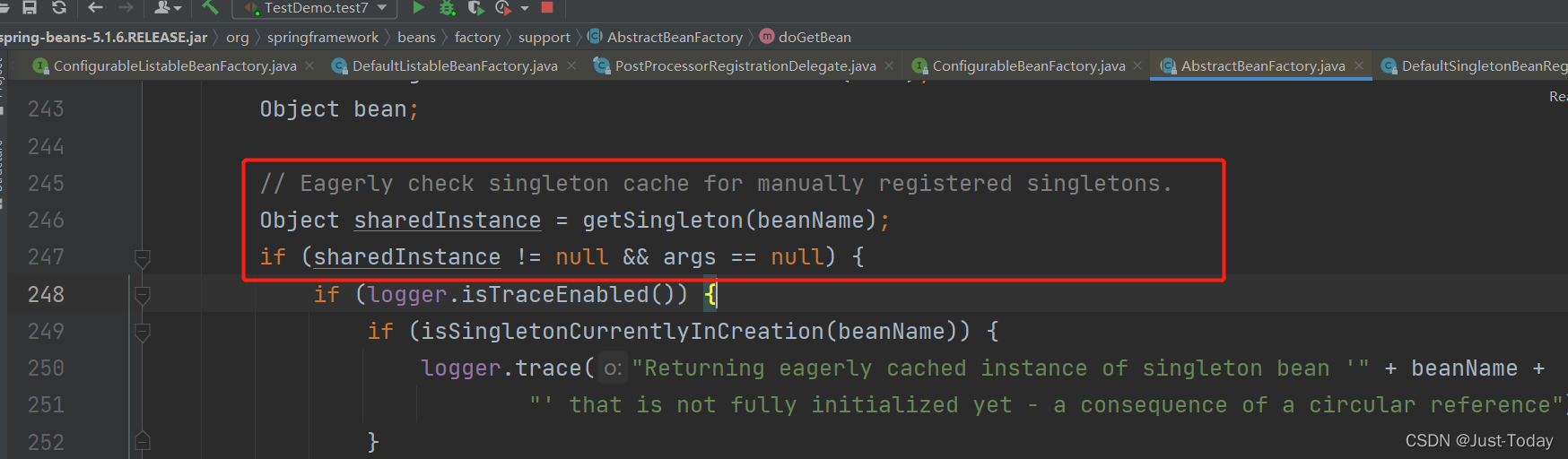
4、创建单例对象通过createBean方法,
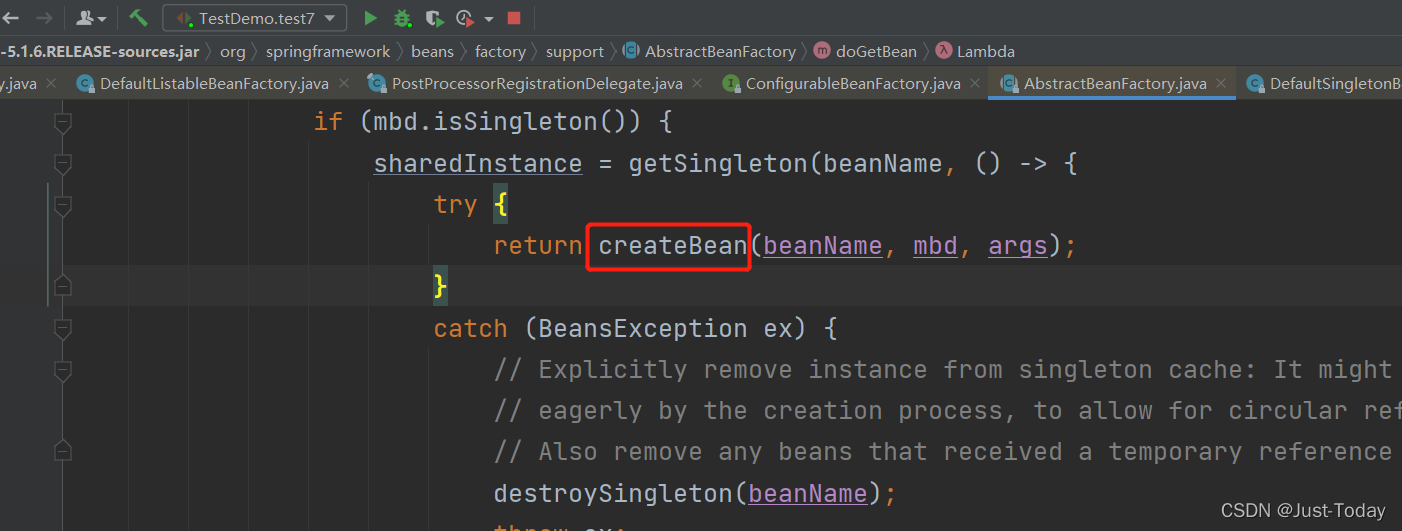
5、createBean方法中的resolveBeforeInstantiation方法是在实例化对象前遍历beanPostProcessors集合中实现InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口的实现类,运行对应的方法,我们可以自定义实现InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口的实现类,在方法内部执行一些操作,例如创建并返回对象或者该对象的代理对象。
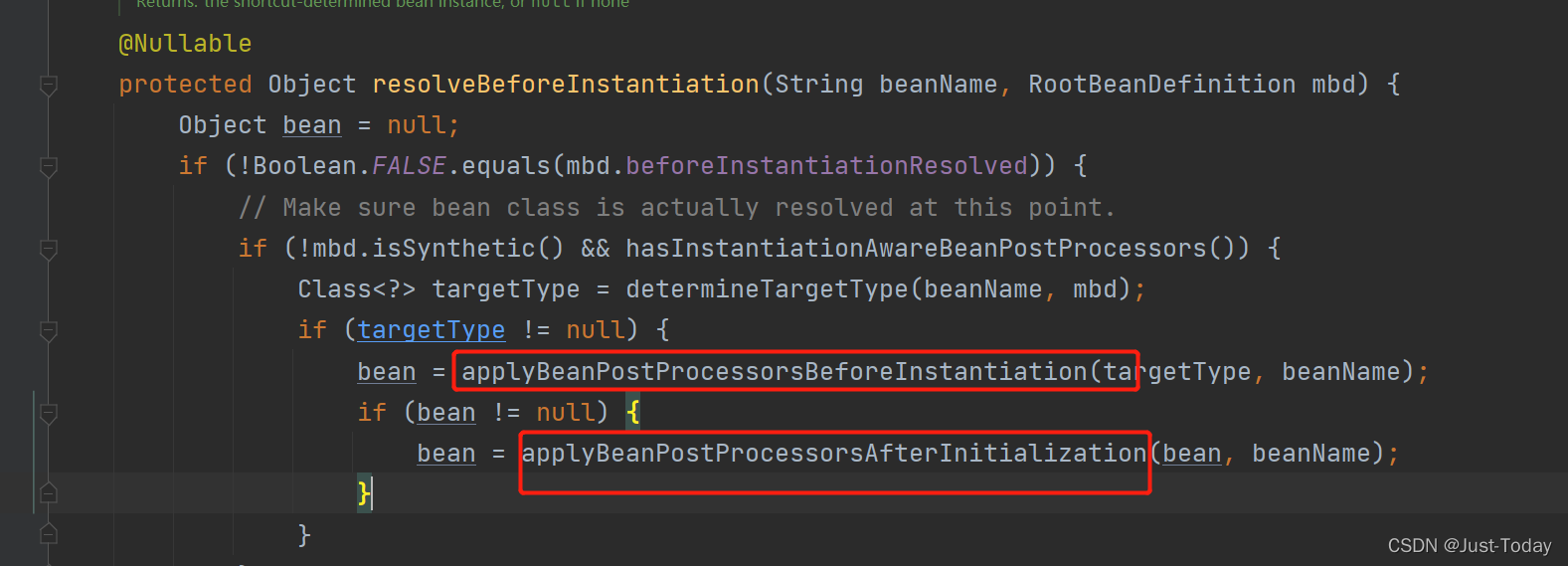
6、resolveBeforeInstantiation方法遍历beanPostProcessors集合,判断是否有实现InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口(该接口是在容器创建组件对象前后调用对应方法)的实现类,若有,则先执行该类的postProcessBeforeInstantiation方法,若方法返回值非空,则说明对象已被创建,不需要容器再去创建对象,直接通过applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization方法遍历容器的beanPostProcessors集合,执行后置处理器的postProcessAfterInitialization方法。
7、若是resolveBeforeInstantiation方法返回对象为空,则说明需要容器去调用doCreateBean方法去实例化对象。在doCreateBean方法中先通过反射创建对象,后根据populateBean方法和initializeBean方法初始化对象。
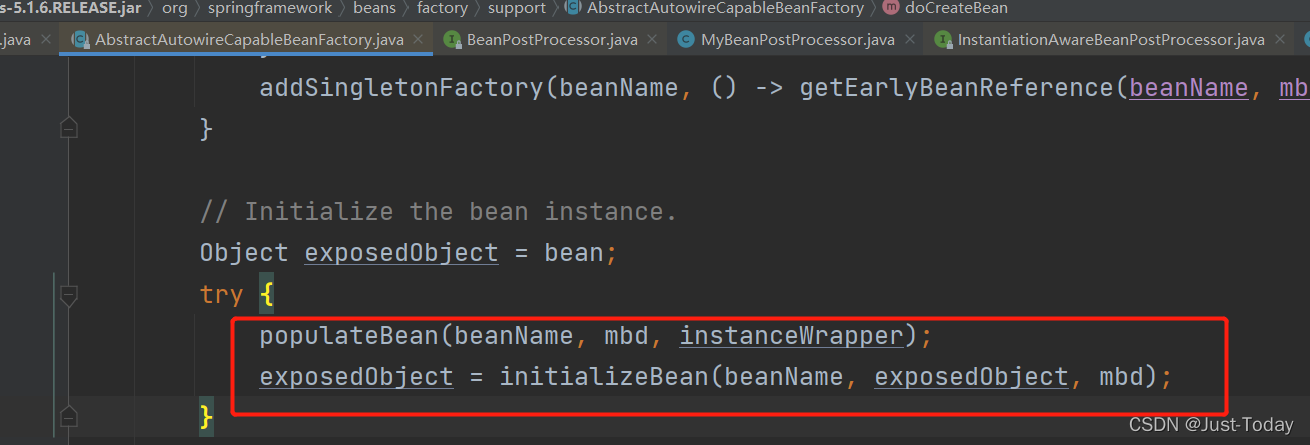
8、在populateBean方法中先遍历容器的beanPostProcessors接口,运行实现InstantiationAwareBeanProcessor接口的postProcessAfterInstantiation方法,接着判断是否有根据名称或者类型注入属性,若有,则运行。
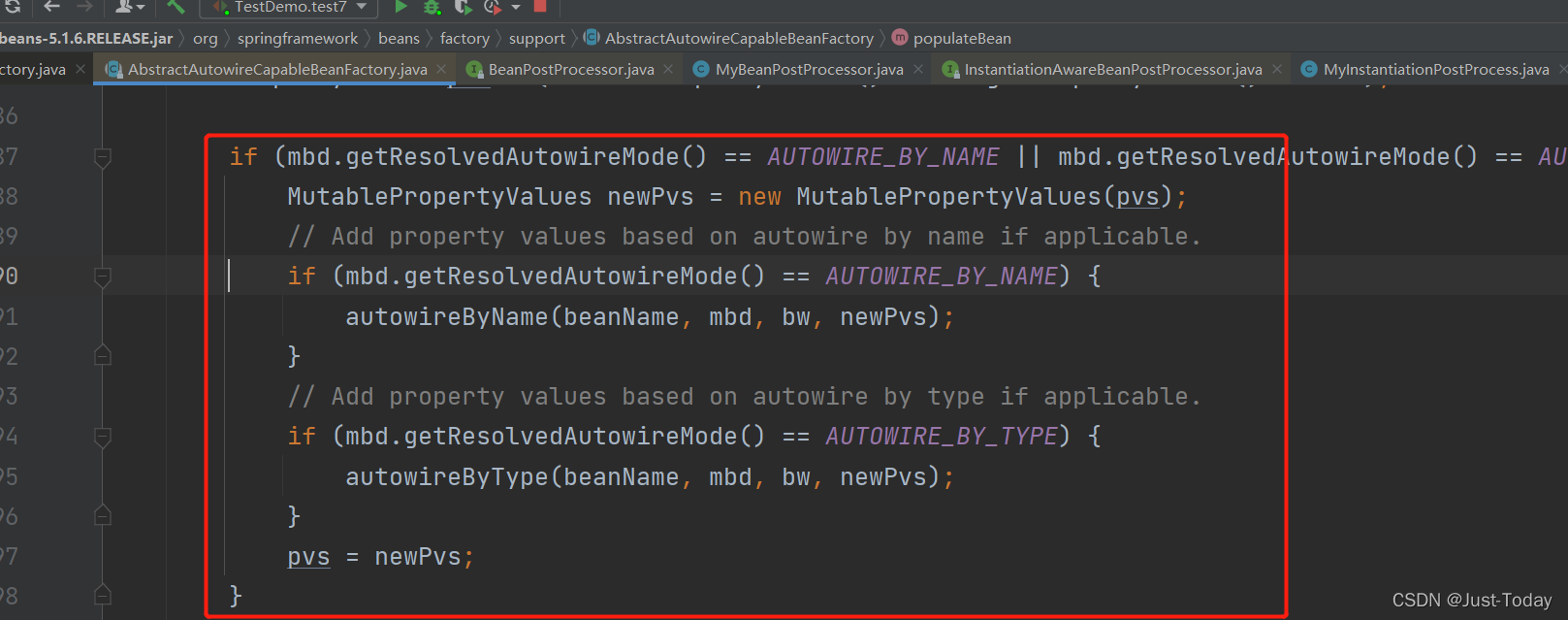
9、接下来就是再次遍历容器的beanPostProcessors集合,找到实现InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口的实现类,运行postProcessProperties或postProcessPropertyValues方法。
例如容器中的AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor实例类对标识@Value的属性进行初始化,若是@Value("${}")这个标有${}则会先去配置文件查找是否有对应值,若有则返回该对应值,若没则直接将该字符串赋值给属性。
最后根据组件的PropertyValues对属性进一步进行赋值,
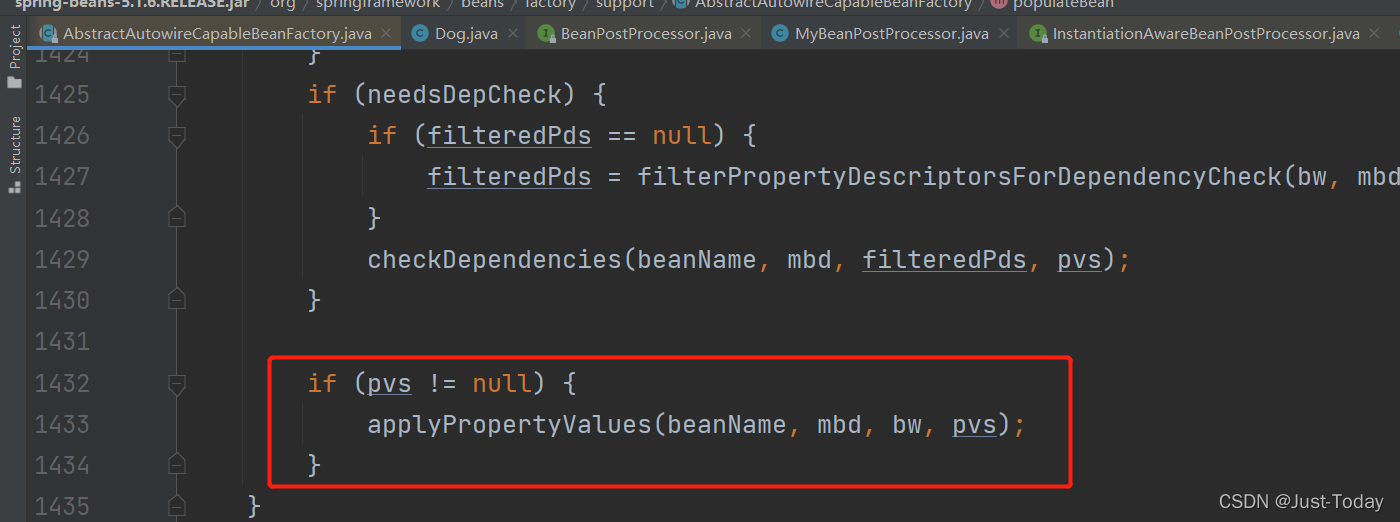
10、在initializeBean方法中主要是处理标识@PostConstruct、@PreDestroy、initMethod、destroyMethod等方法。
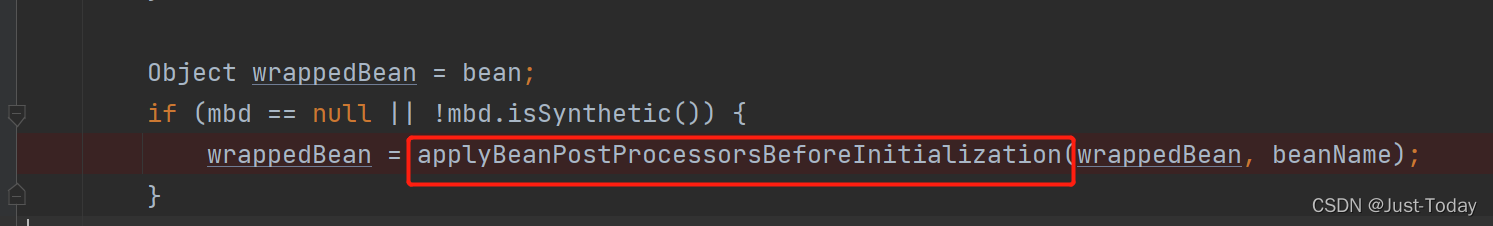
applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization是遍历beanPostProcessors集合,运行其中的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法,例如InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor是处理标识@PostConstruct、@PreDestroy的方法,
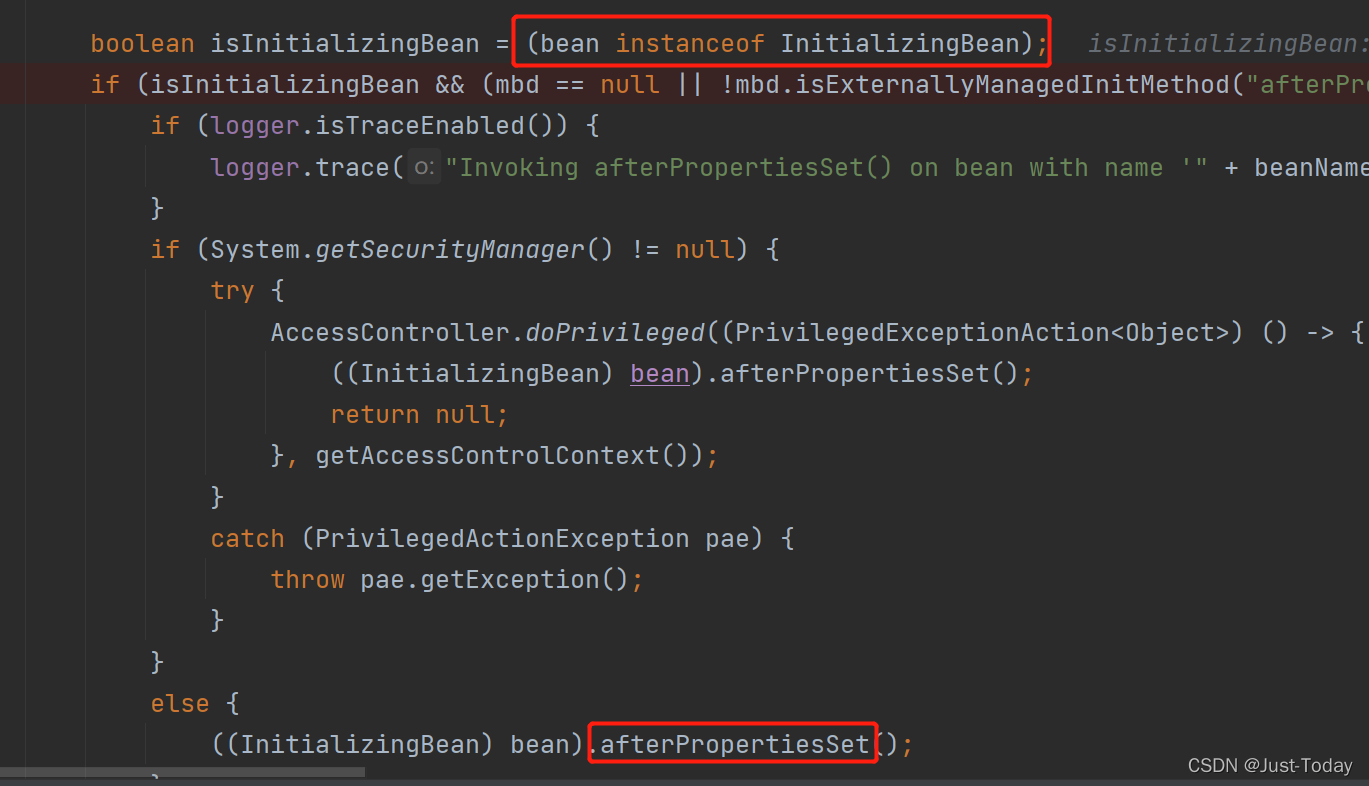
invokeInitMethods方法处理实现InitializingBean接口的afterPropertiesSet(),
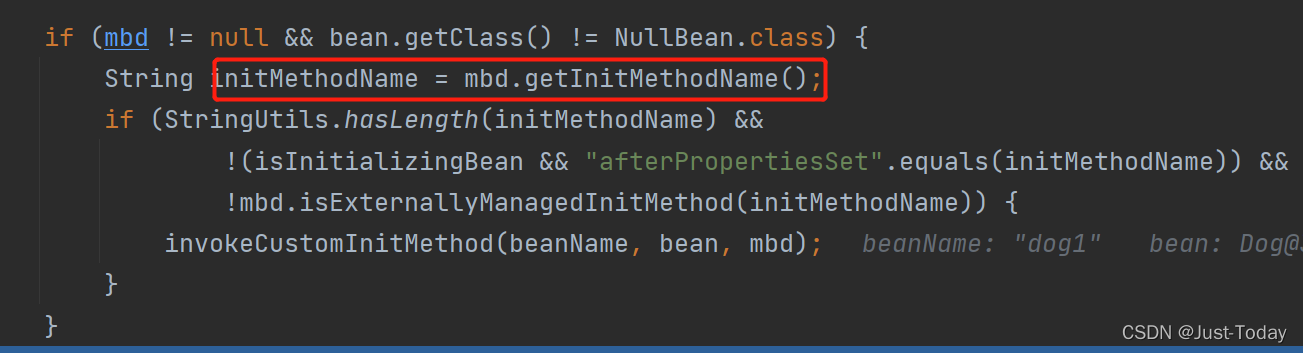
initMethod方法,
接着在执行beanPostProcessors集合的postProcessAfterInitialization方法,
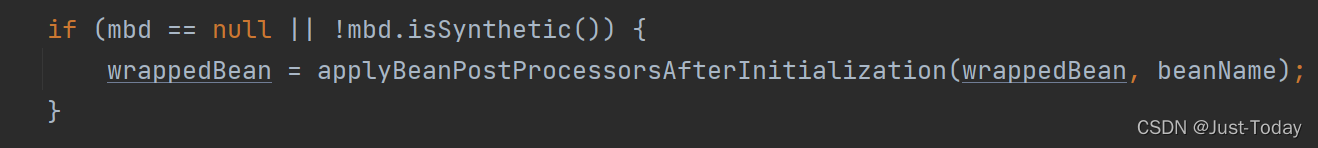
最后注册销毁方法,
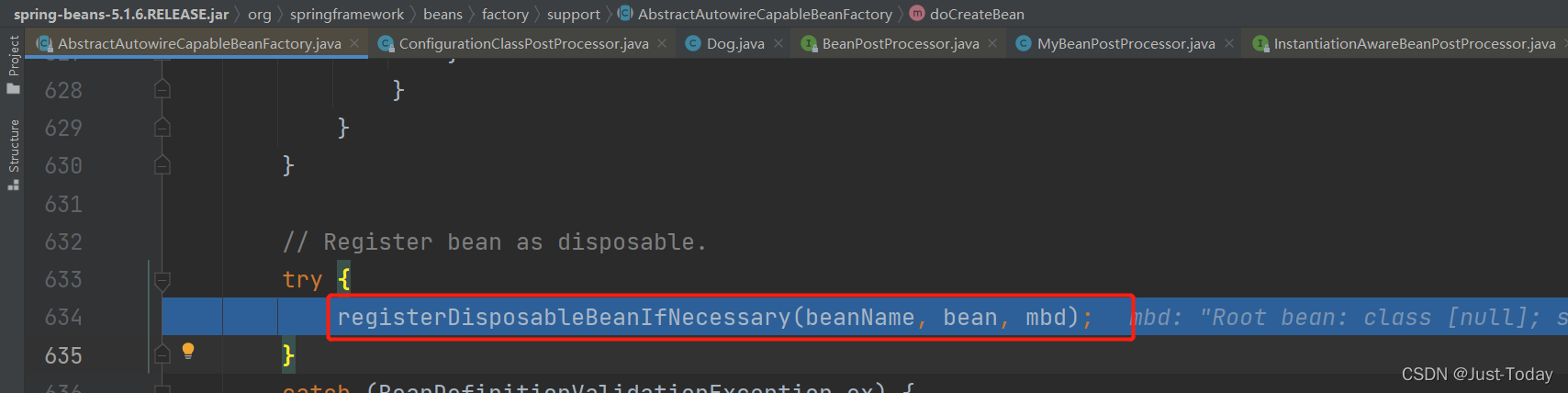
11、最后将创建的对象交由容器管理并返回。
总结:
spring容器加载的过程主要就是执行AbstractApplicationContext类中的refresh方法,首先对容器初始化进行同步处理,防止同时有多线程处理加载,然后就是对上下文进行初始化,例如:初始化closed和active属性,上下文环境初始化和事件容器set的初始化。
然后,就是通过obtainFreshBeanFactory(AbtractRefreshableApplicationContext:获取一个beanFactory容器对象,其实在这一步不仅仅只是实现化bean工厂,它首先重新刷新了beanFactory,如果存在就销毁重建一个DefaultListableBeanFactory,并且使用loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory)拿到资源文件resource,再通过AbstractBeanDefinitionReader中的loadBeanDefinitions方法加载resource中的内容并解析,最后通过BeanDefinitionReaderUtils这个工具类把解析后的beanDefinition保存到beanFactory中,到这里xml中的bean就加载完成了)(GenericApplicationContext:设置序列号id等,返回容器对象)。
接下来就是prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory)方法,主要是对实例化完成的beanFacotry进行相关的设置处理,然后就是postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory)和invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory)主要用于处理各种BeanFactoryPostProcessor,查看是否有自定义的后处理器BeanFactoryPostProcessor,如果有则获取bean实例并执行相关的方法。再就是registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory)它也是处理BeanPostProcessor的,只不过这个方法不是立即执行,而是在实例化bean的时候调用BeanPostProcessor中的方法,这里处理的都是BeanPostProcessor,然后就是处理国际化initMessageSource(),initApplicationEventMulticaster()初始化事件广播器类型为SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster并注册到beanFactory中,registerListeners()注册事件监听器,通过查询BeanFacotry中是否存在ApplicationListener类型的bean,将实现ApplicationListener接口的Bean的名称添加到事件广播器中,在事件触发的时候可回调监听器中的方法,再着就是finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory)完成BeanFactory的初始化。最后就是使用finishRefresh()清理一些缓存,触发相关的一些事件。
运行代码
Dog实体类
package com.mzp.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
public class Dog implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
public Dog(){
name = "dog2";
System.out.println("Dog Construct() " + info());
}
@Value("${test.name}")
private String name;
private Integer age;
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void initMethod(){
System.out.println("dog initMethod()" + info());
}
public void destroyMethod(){
System.out.println("dog destoryMethod()");
}
@PostConstruct
public void postConstruct(){
System.out.println("dog postConstruct()");
}
@PreDestroy
public void preDestroy(){
System.out.println("dog preDestroy()");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("dog dispoableBean destroy()");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("dog initializingBean afterPropertiesSet()");
}
public String info() {
return "Dog{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
实现BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 接口
package com.mzp.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.PropertyValue;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistry;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MyBeanDefinitionPostProcess implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor {
public MyBeanDefinitionPostProcess(){
System.out.println("MyBeanDefinitionPostProcess construct()");
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MyBeanDefinitionPostProcess postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry()");
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MyBeanDefinitionPostProcess postProcessBeanFactory()");
}
}
实现BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口
package com.mzp.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.MutablePropertyValues;
import org.springframework.beans.PropertyValue;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
public MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor(){
System.out.println("MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor construct()");
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
if(beanFactory.containsBeanDefinition("dog1")){
MutablePropertyValues dog1 = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition("dog1").getPropertyValues();
dog1.addPropertyValue("age", 11);
}
System.out.println("MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor-》postProcessBeanFactory方法 ");
}
}
实现BeanPostProcessor接口
package com.mzp.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.PropertyValue;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
public MyBeanPostProcessor(){
System.out.println("MyBeanPostProcessor construct()");
}
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MyBeanPostProcessor postProcessBeforeInitialization " + beanName);
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MyBeanPostProcessor postProcessAfterInitialization " + beanName);
return bean;
}
}
实现InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口
package com.mzp.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.PropertyValue;
import org.springframework.beans.PropertyValues;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor;
@Component
public class MyInstantiationPostProcess implements InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor {
public MyInstantiationPostProcess() {
System.out.println("MyInstantiationPostProcess construct()");
}
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MyInstantiationPostProcess postProcessBeforeInstantiation()" + beanName);
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MyInstantiationPostProcess postProcessAfterInstantiation()"+ beanName);
return true;
}
@Override
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MyInstantiationPostProcess postProcessProperties() "+ beanName + " ");
return null;
}
}
配置类
package com.mzp.component.config;
import com.mzp.bean.Dog;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.mzp.bean")
@PropertySource(name="test", value={"classpath:test.properties"})
public class TestLifeCycleConfig {
public TestLifeCycleConfig(){
System.out.println("TestLifeCycleConfig construct()");
}
@Bean(value={"dog1","dog2"}, initMethod = "initMethod", destroyMethod="destroyMethod")
public Dog getDog(){
return new Dog();
}
}
测试类
package com.mzp.test;
import com.mzp.annotation.User;
import com.mzp.bean.Dog;
import com.mzp.bean.Student;
import com.mzp.component.Config;
import com.mzp.component.config.TestConditional;
import com.mzp.component.config.TestLifeCycleConfig;
import com.mzp.component.factory.MyFactoryBean;
import com.mzp.component.service.Blue;
import com.mzp.component.service.Green;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class TestDemo {
@Test
public void test7(){
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(TestLifeCycleConfig.class);
applicationContext.close();
}
}
运行结果
MyBeanDefinitionPostProcess construct()
MyBeanDefinitionPostProcess postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry()
MyBeanDefinitionPostProcess postProcessBeanFactory()
MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor construct()
MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor-》postProcessBeanFactory方法
MyBeanPostProcessor construct()
MyInstantiationPostProcess construct()
MyInstantiationPostProcess postProcessBeforeInstantiation()testLifeCycleConfig
TestLifeCycleConfig construct()
MyInstantiationPostProcess postProcessAfterInstantiation()testLifeCycleConfig
MyInstantiationPostProcess postProcessProperties() testLifeCycleConfig
MyBeanPostProcessor postProcessBeforeInitialization testLifeCycleConfig
MyBeanPostProcessor postProcessAfterInitialization testLifeCycleConfig
MyInstantiationPostProcess postProcessBeforeInstantiation()dog1
Dog Construct() Dog{name='dog2', age=null}
MyInstantiationPostProcess postProcessAfterInstantiation()dog1
MyInstantiationPostProcess postProcessProperties() dog1
MyBeanPostProcessor postProcessBeforeInitialization dog1
dog postConstruct()
dog initializingBean afterPropertiesSet()
dog initMethod()Dog{name='propertiesname', age=11}
MyBeanPostProcessor postProcessAfterInitialization dog1
dog preDestroy()
dog dispoableBean destroy()
dog destoryMethod()
Disconnected from the target VM, address: '127.0.0.1:53741', transport: 'socket'参考地址:





















 4943
4943

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








