目录
1、Android虚拟机
1.1 dalvik虚拟机
Google于2007年底正式发布了Android SDK, 作为 Android系统的重要部分,Dalvik虚拟机问世。每一个Android应用在底层都对应一个独立的Dalvik虚拟机实例, 应用代码在虚拟机中解释执行。
因为Android使用的编程语言是java,让很多人误以为 Dalvik虚拟机就是JVM,这种说法不正确,因为Dalvik虚拟机不是按照JVM规范来实现的,而且两者不兼容;
1.2 Dalvik虚拟机与JVM比较
| Dalvik虚拟机 | JVM | |
| dalvik虚拟机是基于寄存器 | JVM基于栈,必须使用指令来载入和操作栈上数据,所需指令更多 | |
|
| Dalvik运行的是自定义的.dex字节码格式。java类被编译成.class文件后,然后通过dx工具将.class文件转换成.dex文件,Dalvik虚拟机运行的是dex文件 | JVM运行的是字节码,java类文件在javac后会被编译成class文件,打包到.jar文件中,JVM从相应的.class文件和.jar文件中获取相应的字节码 |
| 在Dalvik虚拟机中,常量池被修改为只使用32位的索引,简化了解释器,Dalvik的堆和栈的参数可以通过-Xms和-Xmx更改 | ||
| 一个应用对应一个进程,一个Dalvik虚拟机实例,android应用都运行在自己的沙盒中,不同的应用在不同的进程中运行,对应一个Dalvik虚拟机实例,每个应用程序都被赋予了一个独立的PID,可类似Linux的 pid | ||
1.3 进程管理
Dalvik进程管理是基于Linux的体系结构的,如果要为应用程序创建一个进程,会fork一个进程效率更高。
Zygote是虚拟机的一个进程,而且是虚拟机实例的孵化器,它通过init进程来启动,每当系统要求执行一个android应用程序时,Zygote就fork出一个子进程来作为该应用的进程。
1.4 init进程
init进程它是一个由内核启动的用户级进程,也是是Linux内核启动的第一个进程,由内核自行启动。
启动过程就是代码init.c中main函数执行过程:system\core\init\init.c
main函数中会进行一下初始化操作:文件夹建立、挂载、rc文件解析、属性设置、各项服务的启动、动作的执行、Socket的监听等
如下面是一段源码:
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd_count = 0;
struct pollfd ufds[4];
char *tmpdev;
char* debuggable;
char tmp[32];
int property_set_fd_init = 0;
int signal_fd_init = 0;
int keychord_fd_init = 0;
bool is_charger = false;
if (!strcmp(basename(argv[0]), "ueventd"))
return ueventd_main(argc, argv);
if (!strcmp(basename(argv[0]), "watchdogd"))
return watchdogd_main(argc, argv);
/* clear the umask */
umask(0);
/* Get the basic filesystem setup we need put
* together in the initramdisk on / and then we'll
* let the rc file figure out the rest.
*/
mkdir("/dev", 0755);
mkdir("/proc", 0755);
mkdir("/sys", 0755);
mount("tmpfs", "/dev", "tmpfs", MS_NOSUID, "mode=0755");
mkdir("/dev/pts", 0755);
mkdir("/dev/socket", 0755);
mount("devpts", "/dev/pts", "devpts", 0, NULL);
mount("proc", "/proc", "proc", 0, NULL);
mount("sysfs", "/sys", "sysfs", 0, NULL);
/* indicate that booting is in progress to background fw loaders, etc */
close(open("/dev/.booting", O_WRONLY | O_CREAT, 0000));
/* We must have some place other than / to create the
* device nodes for kmsg and null, otherwise we won't
* be able to remount / read-only later on.
* Now that tmpfs is mounted on /dev, we can actually
* talk to the outside world.
*/
open_devnull_stdio();
klog_init();
property_init();
get_hardware_name(hardware, &revision);
process_kernel_cmdline();
union selinux_callback cb;
cb.func_log = klog_write;
selinux_set_callback(SELINUX_CB_LOG, cb);
cb.func_audit = audit_callback;
selinux_set_callback(SELINUX_CB_AUDIT, cb);
selinux_initialize();
/* These directories were necessarily created before initial policy load
* and therefore need their security context restored to the proper value.
* This must happen before /dev is populated by ueventd.
*/
restorecon("/dev");
restorecon("/dev/socket");
restorecon("/dev/__properties__");
restorecon_recursive("/sys");
is_charger = !strcmp(bootmode, "charger");
INFO("property init\n");
if (!is_charger)
property_load_boot_defaults();
INFO("reading config file\n");
init_parse_config_file("/init.rc");
action_for_each_trigger("early-init", action_add_queue_tail);
queue_builtin_action(wait_for_coldboot_done_action, "wait_for_coldboot_done");
queue_builtin_action(mix_hwrng_into_linux_rng_action, "mix_hwrng_into_linux_rng");
queue_builtin_action(keychord_init_action, "keychord_init");
queue_builtin_action(console_init_action, "console_init");
/* execute all the boot actions to get us started */
action_for_each_trigger("init", action_add_queue_tail);
/* skip mounting filesystems in charger mode */
if (!is_charger) {
action_for_each_trigger("early-fs", action_add_queue_tail);
action_for_each_trigger("fs", action_add_queue_tail);
action_for_each_trigger("post-fs", action_add_queue_tail);
action_for_each_trigger("post-fs-data", action_add_queue_tail);
}
/* Repeat mix_hwrng_into_linux_rng in case /dev/hw_random or /dev/random
* wasn't ready immediately after wait_for_coldboot_done
*/
queue_builtin_action(mix_hwrng_into_linux_rng_action, "mix_hwrng_into_linux_rng");
queue_builtin_action(property_service_init_action, "property_service_init");
queue_builtin_action(signal_init_action, "signal_init");
queue_builtin_action(check_startup_action, "check_startup");
if (is_charger) {
action_for_each_trigger("charger", action_add_queue_tail);
} else {
action_for_each_trigger("early-boot", action_add_queue_tail);
action_for_each_trigger("boot", action_add_queue_tail);
}
/* run all property triggers based on current state of the properties */
queue_builtin_action(queue_property_triggers_action, "queue_property_triggers");
#if BOOTCHART
queue_builtin_action(bootchart_init_action, "bootchart_init");
#endif
for(;;) {
int nr, i, timeout = -1;
execute_one_command();
restart_processes();
if (!property_set_fd_init && get_property_set_fd() > 0) {
ufds[fd_count].fd = get_property_set_fd();
ufds[fd_count].events = POLLIN;
ufds[fd_count].revents = 0;
fd_count++;
property_set_fd_init = 1;
}
if (!signal_fd_init && get_signal_fd() > 0) {
ufds[fd_count].fd = get_signal_fd();
ufds[fd_count].events = POLLIN;
ufds[fd_count].revents = 0;
fd_count++;
signal_fd_init = 1;
}
if (!keychord_fd_init && get_keychord_fd() > 0) {
ufds[fd_count].fd = get_keychord_fd();
ufds[fd_count].events = POLLIN;
ufds[fd_count].revents = 0;
fd_count++;
keychord_fd_init = 1;
}
if (process_needs_restart) {
timeout = (process_needs_restart - gettime()) * 1000;
if (timeout < 0)
timeout = 0;
}
if (!action_queue_empty() || cur_action)
timeout = 0;
#if BOOTCHART
if (bootchart_count > 0) {
if (timeout < 0 || timeout > BOOTCHART_POLLING_MS)
timeout = BOOTCHART_POLLING_MS;
if (bootchart_step() < 0 || --bootchart_count == 0) {
bootchart_finish();
bootchart_count = 0;
}
}
#endif
nr = poll(ufds, fd_count, timeout);
if (nr <= 0)
continue;
for (i = 0; i < fd_count; i++) {
if (ufds[i].revents == POLLIN) {
if (ufds[i].fd == get_property_set_fd())
handle_property_set_fd();
else if (ufds[i].fd == get_keychord_fd())
handle_keychord();
else if (ufds[i].fd == get_signal_fd())
handle_signal();
}
}
}
return 0;
}
如果没有下载源码的话可以在网上查看(http://androidxref.com/4.4_r1/s?path=init.c&project=system)

1.5 Xposed
最近有朋友问我Xposed破解某些应用的问题,就顺便看了一下Xposed的基本原理,如下:
Android基于Linux启动的第一个进程是init进程,该进程接着会启动Zygote进程(Zygote进程是所有Android应用的进程的父进程,它们都是通过Zygote进程fork出来)。Zygote进程启动的相关配置在描述在 /system/core/rootdir/init.rc 脚本中。Zygote进程对应的执行文件是/system/bin/app_process, 该文件用来加载类库以及执行一些函数的调用工作。
在Zygote进程创建后, 会根据Zygote进程fork出SystemServer进程和其他进程,如果通过socket监听到有新应用开启,也会根据Zygote进程fork出应用的进程。
Xposed Framework就是用自己实现的app_process替换掉了系统的app_process(app_process就是Zygote进程原来的名字,只是在后面被重新命名为“Zygote”)加载一个额外的jar包,入口从原来的com.android.internal.osZygoteInit.main() 被替换成了 de.robv.android.xposed.XposedBridge.main(), 然后创建的Zygote进程就变成Hook的Zygote进程了,而后面Fork出来的进程也是被Hook过的,这个Jar包的目录是: /data/data/de.rbov.android.xposed.installer/bin/XposedBridge.jar
1.6 init.rc
init.rc源码目录位于:/system/core/rootdir/init.rc
源码很长有接近600行,init进程的启动后会解析执行init.rc脚本,.rc文件是Android使用的初始化脚本文件。
在解析.rc脚本文件时,将相应的类型放入各自的List中:\system\core\init\Init_parser.c :init_parse_config_file( )存入到action_queue、 action_list、 service_list中,解析过程见parse_config函数。
.rc文件描述了一些服务,都是以service开头的,如
service servicemanager /system/bin/servicemanager
service zygote /system/bin/app_process -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server
service media /system/bin/mediaserver
service adbd /sbin/adbd
service installd /system/bin/installd等
详细见下面init.rc脚本源码
Cross Reference: init.rc
xref: /system/core/rootdir/init.rc
HomeHistoryAnnotateLine#NavigateDownload
only in init.rc
# Copyright (C) 2012 The Android Open Source Project
#
# IMPORTANT: Do not create world writable files or directories.
# This is a common source of Android security bugs.
#
import /init.environ.rc
import /init.usb.rc
import /init.${ro.hardware}.rc
import /init.trace.rc
on early-init
# Set init and its forked children's oom_adj.
write /proc/1/oom_adj -16
# Set the security context for the init process.
# This should occur before anything else (e.g. ueventd) is started.
setcon u:r:init:s0
start ueventd
# create mountpoints
mkdir /mnt 0775 root system
on init
sysclktz 0
loglevel 3
# Backward compatibility
symlink /system/etc /etc
symlink /sys/kernel/debug /d
# Right now vendor lives on the same filesystem as system,
# but someday that may change.
symlink /system/vendor /vendor
# Create cgroup mount point for cpu accounting
mkdir /acct
mount cgroup none /acct cpuacct
mkdir /acct/uid
# Create cgroup mount point for memory
mount tmpfs none /sys/fs/cgroup mode=0750,uid=0,gid=1000
mkdir /sys/fs/cgroup/memory 0750 root system
mount cgroup none /sys/fs/cgroup/memory memory
write /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/memory.move_charge_at_immigrate 1
chown root system /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/tasks
chmod 0660 /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/tasks
mkdir /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/sw 0750 root system
write /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/sw/memory.swappiness 100
write /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/sw/memory.move_charge_at_immigrate 1
chown root system /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/sw/tasks
chmod 0660 /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/sw/tasks
mkdir /system
mkdir /data 0771 system system
mkdir /cache 0770 system cache
mkdir /config 0500 root root
# See storage config details at http://source.android.com/tech/storage/
mkdir /mnt/shell 0700 shell shell
mkdir /mnt/media_rw 0700 media_rw media_rw
mkdir /storage 0751 root sdcard_r
# Directory for putting things only root should see.
mkdir /mnt/secure 0700 root root
# Create private mountpoint so we can MS_MOVE from staging
mount tmpfs tmpfs /mnt/secure mode=0700,uid=0,gid=0
# Directory for staging bindmounts
mkdir /mnt/secure/staging 0700 root root
# Directory-target for where the secure container
# imagefile directory will be bind-mounted
mkdir /mnt/secure/asec 0700 root root
# Secure container public mount points.
mkdir /mnt/asec 0700 root system
mount tmpfs tmpfs /mnt/asec mode=0755,gid=1000
# Filesystem image public mount points.
mkdir /mnt/obb 0700 root system
mount tmpfs tmpfs /mnt/obb mode=0755,gid=1000
write /proc/sys/kernel/panic_on_oops 1
write /proc/sys/kernel/hung_task_timeout_secs 0
write /proc/cpu/alignment 4
write /proc/sys/kernel/sched_latency_ns 10000000
write /proc/sys/kernel/sched_wakeup_granularity_ns 2000000
write /proc/sys/kernel/sched_compat_yield 1
write /proc/sys/kernel/sched_child_runs_first 0
write /proc/sys/kernel/randomize_va_space 2
write /proc/sys/kernel/kptr_restrict 2
write /proc/sys/kernel/dmesg_restrict 1
write /proc/sys/vm/mmap_min_addr 32768
write /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ping_group_range "0 2147483647"
write /proc/sys/kernel/sched_rt_runtime_us 950000
write /proc/sys/kernel/sched_rt_period_us 1000000
# Create cgroup mount points for process groups
mkdir /dev/cpuctl
mount cgroup none /dev/cpuctl cpu
chown system system /dev/cpuctl
chown system system /dev/cpuctl/tasks
chmod 0660 /dev/cpuctl/tasks
write /dev/cpuctl/cpu.shares 1024
write /dev/cpuctl/cpu.rt_runtime_us 950000
write /dev/cpuctl/cpu.rt_period_us 1000000
mkdir /dev/cpuctl/apps
chown system system /dev/cpuctl/apps/tasks
chmod 0666 /dev/cpuctl/apps/tasks
write /dev/cpuctl/apps/cpu.shares 1024
write /dev/cpuctl/apps/cpu.rt_runtime_us 800000
write /dev/cpuctl/apps/cpu.rt_period_us 1000000
mkdir /dev/cpuctl/apps/bg_non_interactive
chown system system /dev/cpuctl/apps/bg_non_interactive/tasks
chmod 0666 /dev/cpuctl/apps/bg_non_interactive/tasks
# 5.0 %
write /dev/cpuctl/apps/bg_non_interactive/cpu.shares 52
write /dev/cpuctl/apps/bg_non_interactive/cpu.rt_runtime_us 700000
write /dev/cpuctl/apps/bg_non_interactive/cpu.rt_period_us 1000000
# qtaguid will limit access to specific data based on group memberships.
# net_bw_acct grants impersonation of socket owners.
# net_bw_stats grants access to other apps' detailed tagged-socket stats.
chown root net_bw_acct /proc/net/xt_qtaguid/ctrl
chown root net_bw_stats /proc/net/xt_qtaguid/stats
# Allow everybody to read the xt_qtaguid resource tracking misc dev.
# This is needed by any process that uses socket tagging.
chmod 0644 /dev/xt_qtaguid
# Create location for fs_mgr to store abbreviated output from filesystem
# checker programs.
mkdir /dev/fscklogs 0770 root system
on post-fs
# once everything is setup, no need to modify /
mount rootfs rootfs / ro remount
# mount shared so changes propagate into child namespaces
mount rootfs rootfs / shared rec
mount tmpfs tmpfs /mnt/secure private rec
# We chown/chmod /cache again so because mount is run as root + defaults
chown system cache /cache
chmod 0770 /cache
# We restorecon /cache in case the cache partition has been reset.
restorecon /cache
# This may have been created by the recovery system with odd permissions
chown system cache /cache/recovery
chmod 0770 /cache/recovery
# This may have been created by the recovery system with the wrong context.
restorecon /cache/recovery
#change permissions on vmallocinfo so we can grab it from bugreports
chown root log /proc/vmallocinfo
chmod 0440 /proc/vmallocinfo
chown root log /proc/slabinfo
chmod 0440 /proc/slabinfo
#change permissions on kmsg & sysrq-trigger so bugreports can grab kthread stacks
chown root system /proc/kmsg
chmod 0440 /proc/kmsg
chown root system /proc/sysrq-trigger
chmod 0220 /proc/sysrq-trigger
chown system log /proc/last_kmsg
chmod 0440 /proc/last_kmsg
# create the lost+found directories, so as to enforce our permissions
mkdir /cache/lost+found 0770 root root
on post-fs-data
# We chown/chmod /data again so because mount is run as root + defaults
chown system system /data
chmod 0771 /data
# We restorecon /data in case the userdata partition has been reset.
restorecon /data
# Avoid predictable entropy pool. Carry over entropy from previous boot.
copy /data/system/entropy.dat /dev/urandom
# Create dump dir and collect dumps.
# Do this before we mount cache so eventually we can use cache for
# storing dumps on platforms which do not have a dedicated dump partition.
mkdir /data/dontpanic 0750 root log
# Collect apanic data, free resources and re-arm trigger
copy /proc/apanic_console /data/dontpanic/apanic_console
chown root log /data/dontpanic/apanic_console
chmod 0640 /data/dontpanic/apanic_console
copy /proc/apanic_threads /data/dontpanic/apanic_threads
chown root log /data/dontpanic/apanic_threads
chmod 0640 /data/dontpanic/apanic_threads
write /proc/apanic_console 1
# create basic filesystem structure
mkdir /data/misc 01771 system misc
mkdir /data/misc/adb 02750 system shell
mkdir /data/misc/bluedroid 0770 bluetooth net_bt_stack
mkdir /data/misc/bluetooth 0770 system system
mkdir /data/misc/keystore 0700 keystore keystore
mkdir /data/misc/keychain 0771 system system
mkdir /data/misc/radio 0770 system radio
mkdir /data/misc/sms 0770 system radio
mkdir /data/misc/zoneinfo 0775 system system
mkdir /data/misc/vpn 0770 system vpn
mkdir /data/misc/systemkeys 0700 system system
# give system access to wpa_supplicant.conf for backup and restore
mkdir /data/misc/wifi 0770 wifi wifi
chmod 0660 /data/misc/wifi/wpa_supplicant.conf
mkdir /data/local 0751 root root
mkdir /data/misc/media 0700 media media
# For security reasons, /data/local/tmp should always be empty.
# Do not place files or directories in /data/local/tmp
mkdir /data/local/tmp 0771 shell shell
mkdir /data/data 0771 system system
mkdir /data/app-private 0771 system system
mkdir /data/app-asec 0700 root root
mkdir /data/app-lib 0771 system system
mkdir /data/app 0771 system system
mkdir /data/property 0700 root root
mkdir /data/ssh 0750 root shell
mkdir /data/ssh/empty 0700 root root
# create dalvik-cache, so as to enforce our permissions
mkdir /data/dalvik-cache 0771 system system
# create resource-cache and double-check the perms
mkdir /data/resource-cache 0771 system system
chown system system /data/resource-cache
chmod 0771 /data/resource-cache
# create the lost+found directories, so as to enforce our permissions
mkdir /data/lost+found 0770 root root
# create directory for DRM plug-ins - give drm the read/write access to
# the following directory.
mkdir /data/drm 0770 drm drm
# create directory for MediaDrm plug-ins - give drma the read/write access to
# the following directory.
mkdir /data/mediadrm 0770 mediadrm mediadrm
# symlink to bugreport storage location
symlink /data/data/com.android.shell/files/bugreports /data/bugreports
# Separate location for storing security policy files on data
mkdir /data/security 0711 system system
# If there is no fs-post-data action in the init.<device>.rc file, you
# must uncomment this line, otherwise encrypted filesystems
# won't work.
# Set indication (checked by vold) that we have finished this action
#setprop vold.post_fs_data_done 1
on boot
# basic network init
ifup lo
hostname localhost
domainname localdomain
# set RLIMIT_NICE to allow priorities from 19 to -20
setrlimit 13 40 40
# Memory management. Basic kernel parameters, and allow the high
# level system server to be able to adjust the kernel OOM driver
# parameters to match how it is managing things.
write /proc/sys/vm/overcommit_memory 1
write /proc/sys/vm/min_free_order_shift 4
chown root system /sys/module/lowmemorykiller/parameters/adj
chmod 0664 /sys/module/lowmemorykiller/parameters/adj
chown root system /sys/module/lowmemorykiller/parameters/minfree
chmod 0664 /sys/module/lowmemorykiller/parameters/minfree
# Tweak background writeout
write /proc/sys/vm/dirty_expire_centisecs 200
write /proc/sys/vm/dirty_background_ratio 5
# Permissions for System Server and daemons.
chown radio system /sys/android_power/state
chown radio system /sys/android_power/request_state
chown radio system /sys/android_power/acquire_full_wake_lock
chown radio system /sys/android_power/acquire_partial_wake_lock
chown radio system /sys/android_power/release_wake_lock
chown system system /sys/power/autosleep
chown system system /sys/power/state
chown system system /sys/power/wakeup_count
chown radio system /sys/power/wake_lock
chown radio system /sys/power/wake_unlock
chmod 0660 /sys/power/state
chmod 0660 /sys/power/wake_lock
chmod 0660 /sys/power/wake_unlock
chown system system /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpufreq/interactive/timer_rate
chmod 0660 /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpufreq/interactive/timer_rate
chown system system /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpufreq/interactive/timer_slack
chmod 0660 /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpufreq/interactive/timer_slack
chown system system /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpufreq/interactive/min_sample_time
chmod 0660 /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpufreq/interactive/min_sample_time
chown system system /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpufreq/interactive/hispeed_freq
chmod 0660 /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpufreq/interactive/hispeed_freq
chown system system /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpufreq/interactive/target_loads
chmod 0660 /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpufreq/interactive/target_loads
chown system system /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpufreq/interactive/go_hispeed_load
chmod 0660 /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpufreq/interactive/go_hispeed_load
chown system system /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpufreq/interactive/above_hispeed_delay
chmod 0660 /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpufreq/interactive/above_hispeed_delay
chown system system /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpufreq/interactive/boost
chmod 0660 /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpufreq/interactive/boost
chown system system /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpufreq/interactive/boostpulse
chown system system /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpufreq/interactive/input_boost
chmod 0660 /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpufreq/interactive/input_boost
chown system system /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpufreq/interactive/boostpulse_duration
chmod 0660 /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpufreq/interactive/boostpulse_duration
chown system system /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpufreq/interactive/io_is_busy
chmod 0660 /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpufreq/interactive/io_is_busy
# Assume SMP uses shared cpufreq policy for all CPUs
chown system system /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/scaling_max_freq
chmod 0660 /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/scaling_max_freq
chown system system /sys/class/timed_output/vibrator/enable
chown system system /sys/class/leds/keyboard-backlight/brightness
chown system system /sys/class/leds/lcd-backlight/brightness
chown system system /sys/class/leds/button-backlight/brightness
chown system system /sys/class/leds/jogball-backlight/brightness
chown system system /sys/class/leds/red/brightness
chown system system /sys/class/leds/green/brightness
chown system system /sys/class/leds/blue/brightness
chown system system /sys/class/leds/red/device/grpfreq
chown system system /sys/class/leds/red/device/grppwm
chown system system /sys/class/leds/red/device/blink
chown system system /sys/class/timed_output/vibrator/enable
chown system system /sys/module/sco/parameters/disable_esco
chown system system /sys/kernel/ipv4/tcp_wmem_min
chown system system /sys/kernel/ipv4/tcp_wmem_def
chown system system /sys/kernel/ipv4/tcp_wmem_max
chown system system /sys/kernel/ipv4/tcp_rmem_min
chown system system /sys/kernel/ipv4/tcp_rmem_def
chown system system /sys/kernel/ipv4/tcp_rmem_max
chown root radio /proc/cmdline
# Set these so we can remotely update SELinux policy
chown system system /sys/fs/selinux/load
chown system system /sys/fs/selinux/enforce
# Define TCP buffer sizes for various networks
# ReadMin, ReadInitial, ReadMax, WriteMin, WriteInitial, WriteMax,
setprop net.tcp.buffersize.default 4096,87380,110208,4096,16384,110208
setprop net.tcp.buffersize.wifi 524288,1048576,2097152,262144,524288,1048576
setprop net.tcp.buffersize.lte 524288,1048576,2097152,262144,524288,1048576
setprop net.tcp.buffersize.umts 4094,87380,110208,4096,16384,110208
setprop net.tcp.buffersize.hspa 4094,87380,262144,4096,16384,262144
setprop net.tcp.buffersize.hsupa 4094,87380,262144,4096,16384,262144
setprop net.tcp.buffersize.hsdpa 4094,87380,262144,4096,16384,262144
setprop net.tcp.buffersize.hspap 4094,87380,1220608,4096,16384,1220608
setprop net.tcp.buffersize.edge 4093,26280,35040,4096,16384,35040
setprop net.tcp.buffersize.gprs 4092,8760,11680,4096,8760,11680
setprop net.tcp.buffersize.evdo 4094,87380,262144,4096,16384,262144
class_start core
class_start main
on nonencrypted
class_start late_start
on charger
class_start charger
on property:vold.decrypt=trigger_reset_main
class_reset main
on property:vold.decrypt=trigger_load_persist_props
load_persist_props
on property:vold.decrypt=trigger_post_fs_data
trigger post-fs-data
on property:vold.decrypt=trigger_restart_min_framework
class_start main
on property:vold.decrypt=trigger_restart_framework
class_start main
class_start late_start
on property:vold.decrypt=trigger_shutdown_framework
class_reset late_start
class_reset main
on property:sys.powerctl=*
powerctl ${sys.powerctl}
# system server cannot write to /proc/sys files, so proxy it through init
on property:sys.sysctl.extra_free_kbytes=*
write /proc/sys/vm/extra_free_kbytes ${sys.sysctl.extra_free_kbytes}
## Daemon processes to be run by init.
##
service ueventd /sbin/ueventd
class core
critical
seclabel u:r:ueventd:s0
service healthd /sbin/healthd
class core
critical
seclabel u:r:healthd:s0
service healthd-charger /sbin/healthd -n
class charger
critical
seclabel u:r:healthd:s0
on property:selinux.reload_policy=1
restart ueventd
restart installd
service console /system/bin/sh
class core
console
disabled
user shell
group log
on property:ro.debuggable=1
start console
# adbd is controlled via property triggers in init.<platform>.usb.rc
service adbd /sbin/adbd
class core
socket adbd stream 660 system system
disabled
seclabel u:r:adbd:s0
# adbd on at boot in emulator
on property:ro.kernel.qemu=1
start adbd
service servicemanager /system/bin/servicemanager
class core
user system
group system
critical
onrestart restart healthd
onrestart restart zygote
onrestart restart media
onrestart restart surfaceflinger
onrestart restart drm
service vold /system/bin/vold
class core
socket vold stream 0660 root mount
ioprio be 2
service netd /system/bin/netd
class main
socket netd stream 0660 root system
socket dnsproxyd stream 0660 root inet
socket mdns stream 0660 root system
service debuggerd /system/bin/debuggerd
class main
service ril-daemon /system/bin/rild
class main
socket rild stream 660 root radio
socket rild-debug stream 660 radio system
user root
group radio cache inet misc audio log
service surfaceflinger /system/bin/surfaceflinger
class main
user system
group graphics drmrpc
onrestart restart zygote
service zygote /system/bin/app_process -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server
class main
socket zygote stream 660 root system
onrestart write /sys/android_power/request_state wake
onrestart write /sys/power/state on
onrestart restart media
onrestart restart netd
service drm /system/bin/drmserver
class main
user drm
group drm system inet drmrpc
service media /system/bin/mediaserver
class main
user media
group audio camera inet net_bt net_bt_admin net_bw_acct drmrpc mediadrm
ioprio rt 4
service bootanim /system/bin/bootanimation
class main
user graphics
group graphics
disabled
oneshot
service installd /system/bin/installd
class main
socket installd stream 600 system system
service flash_recovery /system/etc/install-recovery.sh
class main
oneshot
service racoon /system/bin/racoon
class main
socket racoon stream 600 system system
# IKE uses UDP port 500. Racoon will setuid to vpn after binding the port.
group vpn net_admin inet
disabled
oneshot
service mtpd /system/bin/mtpd
class main
socket mtpd stream 600 system system
user vpn
group vpn net_admin inet net_raw
disabled
oneshot
service keystore /system/bin/keystore /data/misc/keystore
class main
user keystore
group keystore drmrpc
service dumpstate /system/bin/dumpstate -s
class main
socket dumpstate stream 0660 shell log
disabled
oneshot
service sshd /system/bin/start-ssh
class main
disabled
service mdnsd /system/bin/mdnsd
class main
user mdnsr
group inet net_raw
socket mdnsd stream 0660 mdnsr inet
disabled
oneshot
Indexes created Fri Nov 01 14:58:10 CET 2013
1.7 android关键服务的启动
init是Android系统中启动的第一个进程,是基于linux的,然后在init进程中通过解析init.rc文件来依次启动其他关键进程,其中最为重要的三个进程是:ServiceManager、Zygote和SystemServer
1.7.1 ServiceManager
ServiceManager对应在init.rc中的描述是:
service servicemanager /system/bin/servicemanager
class core
user system
group system
critical
onrestart restart healthd
onrestart restart zygote
onrestart restart media
onrestart restart surfaceflinger
onrestart restart drmServiceManager是Linux程序,其在设备中的存储路径是/system/bin/servicemanager,
ServiceManager所属的class 是core,从上面的描述中可以看到,与之相同的同类系统进程包括:uevetd、healthd、console、adbd,参见面init.rc的源码描述。根据core分组的特性,这些进程会同时被启动、停止。
ritical 说明ServiceManager是系统关键进程。
onrestart选项表示ServiceManager被重启的时候healthd、zygote、media、surfaceflinger、drm、vold等进程也会跟着被重启。
1.7.2 Zygote
Zygote中文意思的“受精卵”,想来命名的时候还是考虑了这个进程的特点的,如其名,Android系统中的大多数系统级进程和应用进程就是通过Zygote进程fork出来了。
下面是init.rc脚本描述的Zygote的内容,它也是init进程解析init.rc脚本启动的。
service zygote /system/bin/app_process -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server
class main
socket zygote stream 660 root system
onrestart write /sys/android_power/request_state wake
onrestart write /sys/power/state on
onrestart restart media
onrestart restart netd从描述中可以看到
service的名字是zygote
路径path是:/system/bin/app_process,说明zygote进程对应的执行文件是app_process
参数:-Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server
class:main,这与ServiceManager不同属于core不同,同属于mian组的还有netd、debuggerd、ril-daemon、surfaceflinger、drm、media、installd、flash_recovery等。
从path路径可以看到zygote所在的程序名叫“app_process”,通过--zygote 参数 “--start-system-server”,可以识别用户是否要启动Zygote进程。
app_process对应的源码路径是:/frameworks/base/cmds/app_process/app_main.cpp,主要看main函数
int main(int argc, char* const argv[])
{
... ...
AppRuntime runtime;
... ...
// Parse runtime arguments. Stop at first unrecognized option.
bool zygote = false;
bool startSystemServer = false;
bool application = false;
const char* parentDir = NULL;
const char* niceName = NULL;
const char* className = NULL;
while (i < argc) {
const char* arg = argv[i++];
if (!parentDir) {
parentDir = arg;
} else if (strcmp(arg, "--zygote") == 0) {
zygote = true;
niceName = "zygote";
} else if (strcmp(arg, "--start-system-server") == 0) {
startSystemServer = true;
} else if (strcmp(arg, "--application") == 0) {
application = true;
} else if (strncmp(arg, "--nice-name=", 12) == 0) {
niceName = arg + 12;
} else {
className = arg;
break;
}
}
if (niceName && *niceName) {
setArgv0(argv0, niceName);
set_process_name(niceName);
}
runtime.mParentDir = parentDir;
if (zygote) {
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit",
startSystemServer ? "start-system-server" : "");
} else if (className) {
// Remainder of args get passed to startup class main()
runtime.mClassName = className;
runtime.mArgC = argc - i;
runtime.mArgV = argv + i;
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.RuntimeInit",
application ? "application" : "tool");
} else {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: no class name or --zygote supplied.\n");
app_usage();
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("app_process: no class name or --zygote supplied.");
return 10;
}
}init.rc指定了--zygote选项,因此zygote = true,if条件通过,通过AppRuntime来启动ZygoteInit,并传入参数“start-system-server”,这样ZygoteInit会运行在java虚拟机上,runtime其实是AndroidRuntime对象。
if (zygote) {
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit",
startSystemServer ? "start-system-server" : "");
}
1.7.2.1 zygote的名字由来
同时会给procee_name设置一个niceName,这也就是zygote的名字由来。
if (niceName && *niceName) {
setArgv0(argv0, niceName);
set_process_name(niceName);
}
1.7.2.2 AndroidRuntime
AndroidRuntime源码位于:/frameworks/base/core/jni/AndroidRuntime.cpp
AndroidRuntime这里通过JNI调用Android 的java代码,
/*
* Start the Android runtime. This involves starting the virtual machine
* and calling the "static void main(String[] args)" method in the class
* named by "className".
*
* Passes the main function two arguments, the class name and the specified
* options string.
*/
void AndroidRuntime::start(const char* className, const char* options)
{
... ...
JNIEnv* env;
if (startVm(&mJavaVM, &env) != 0) {
return;
}
onVmCreated(env);//虚拟机启动后会回调这个方法
... ...
}
1.7.3 SystemServer的启动
SystemServer是andriod进入Launcher前的最后准备,ZygoteInit通过forkSystemServer生成一个新进程来承载各项系统服务。根据fork的特新子进程和父进程的代码环境相同。
启动参数:--zygote --start-system-server
在frameworks/base/cmds/app_process/app_main.cpp类中会用到以上参数,如下源码
int main( ){
AppRuntime runtime;
if (zygote) {
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit",
startSystemServer ? "start-system-server" : "");
}
}
class AppRuntime : public AndroidRuntime{};通过AndroiRuntime的start方法启动ZygoteInit.java类,然后调用其startSystemServer()方法,启动SystemServer服务。
源码位于:/frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java
从下面源码中可以看到:
Zygote调用forkSystemServer来fork出SystemServer进程,并返回一个pid,下面判断pid == 0,说明是子进程,!=0的话则是父进程。
/* For child process */
if (pid == 0) {
handleSystemServerProcess(parsedArgs);
}
/**
* Prepare the arguments and fork for the system server process.
*/
private static boolean startSystemServer() throws MethodAndArgsCaller, RuntimeException
{
... ...
/* Hardcoded command line to start the system server */
String args[] = {
"--setuid=1000",
"--setgid=1000",
"--setgroups=1001,1002,1003,1004,1005,1006,1007,1008,1009,1010,1018,1032,3001,3002,3003,3006,3007",
"--capabilities=" + capabilities + "," + capabilities,
"--runtime-init",
"--nice-name=system_server",
"com.android.server.SystemServer",
};
ZygoteConnection.Arguments parsedArgs = null;
int pid;
try {
parsedArgs = new ZygoteConnection.Arguments(args);
ZygoteConnection.applyDebuggerSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
ZygoteConnection.applyInvokeWithSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
/* Request to fork the system server process */
pid = Zygote.forkSystemServer(
parsedArgs.uid, parsedArgs.gid,
parsedArgs.gids,
parsedArgs.debugFlags,
null,
parsedArgs.permittedCapabilities,
parsedArgs.effectiveCapabilities);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
/* For child process */
if (pid == 0) {
handleSystemServerProcess(parsedArgs);
}
return true;
}
/**
* Finish remaining work for the newly forked system server process.
*/
private static void handleSystemServerProcess(
ZygoteConnection.Arguments parsedArgs)
throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
closeServerSocket();
// set umask to 0077 so new files and directories will default to owner-only permissions.
Libcore.os.umask(S_IRWXG | S_IRWXO);
if (parsedArgs.niceName != null) {
Process.setArgV0(parsedArgs.niceName);
}
if (parsedArgs.invokeWith != null) {
WrapperInit.execApplication(parsedArgs.invokeWith,
parsedArgs.niceName, parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion,
null, parsedArgs.remainingArgs);
} else {
/*
* Pass the remaining arguments to SystemServer.
*/
RuntimeInit.zygoteInit(parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion, parsedArgs.remainingArgs);
}
/* should never reach here */
}SystemServer启动之后,会执行main函数如下(4.4版本的源码,后续版本会有变化)
public static void main(String[] args) {
if (System.currentTimeMillis() < EARLIEST_SUPPORTED_TIME) {
// If a device's clock is before 1970 (before 0), a lot of
// APIs crash dealing with negative numbers, notably
// java.io.File#setLastModified, so instead we fake it and
// hope that time from cell towers or NTP fixes it
// shortly.
Slog.w(TAG, "System clock is before 1970; setting to 1970.");
SystemClock.setCurrentTimeMillis(EARLIEST_SUPPORTED_TIME);
}
if (SamplingProfilerIntegration.isEnabled()) {
SamplingProfilerIntegration.start();
timer = new Timer();
timer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
SamplingProfilerIntegration.writeSnapshot("system_server", null);
}
}, SNAPSHOT_INTERVAL, SNAPSHOT_INTERVAL);
}
// Mmmmmm... more memory!
dalvik.system.VMRuntime.getRuntime().clearGrowthLimit();
// The system server has to run all of the time, so it needs to be
// as efficient as possible with its memory usage.
VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetHeapUtilization(0.8f);
Environment.setUserRequired(true);
System.loadLibrary("android_servers");
Slog.i(TAG, "Entered the Android system server!");
// Initialize native services.
nativeInit();
// This used to be its own separate thread, but now it is
// just the loop we run on the main thread.
ServerThread thr = new ServerThread();
thr.initAndLoop();
}
}
/**
* Called to initialize native system services.
*/
private static native void nativeInit();ServerThread新建一个线程来启动各项服务,通过在initAndLoop函数调用ServiceManager的addService注册各项服务。
类似ServiceManager.addService(Context.POWER_SERVICE, power);
但是就现在新版本来说,比如26,SystemServer的代码结构变了,没有ServerThread了,SystemServer的main方法还是静态方法,
如下:
/**
* The main entry point from zygote.
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SystemServer().run();
}
同时提供了run方法代替了initAndLoop方法,里面做了相同的事情,代码结构优化了
private void run() {
try {
traceBeginAndSlog("InitBeforeStartServices");
// If a device's clock is before 1970 (before 0), a lot of
// APIs crash dealing with negative numbers, notably
// java.io.File#setLastModified, so instead we fake it and
// hope that time from cell towers or NTP fixes it shortly.
if (System.currentTimeMillis() < EARLIEST_SUPPORTED_TIME) {
Slog.w(TAG, "System clock is before 1970; setting to 1970.");
SystemClock.setCurrentTimeMillis(EARLIEST_SUPPORTED_TIME);
}
//
// Default the timezone property to GMT if not set.
//
String timezoneProperty = SystemProperties.get("persist.sys.timezone");
if (timezoneProperty == null || timezoneProperty.isEmpty()) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Timezone not set; setting to GMT.");
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.timezone", "GMT");
}
// If the system has "persist.sys.language" and friends set, replace them with
// "persist.sys.locale". Note that the default locale at this point is calculated
// using the "-Duser.locale" command line flag. That flag is usually populated by
// AndroidRuntime using the same set of system properties, but only the system_server
// and system apps are allowed to set them.
//
// NOTE: Most changes made here will need an equivalent change to
// core/jni/AndroidRuntime.cpp
if (!SystemProperties.get("persist.sys.language").isEmpty()) {
final String languageTag = Locale.getDefault().toLanguageTag();
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.locale", languageTag);
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.language", "");
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.country", "");
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.localevar", "");
}
// The system server should never make non-oneway calls
Binder.setWarnOnBlocking(true);
// Here we go!
Slog.i(TAG, "Entered the Android system server!");
int uptimeMillis = (int) SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.BOOT_PROGRESS_SYSTEM_RUN, uptimeMillis);
if (!mRuntimeRestart) {
MetricsLogger.histogram(null, "boot_system_server_init", uptimeMillis);
}
// In case the runtime switched since last boot (such as when
// the old runtime was removed in an OTA), set the system
// property so that it is in sync. We can | xq oqi't do this in
// libnativehelper's JniInvocation::Init code where we already
// had to fallback to a different runtime because it is
// running as root and we need to be the system user to set
// the property. http://b/11463182
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.dalvik.vm.lib.2", VMRuntime.getRuntime().vmLibrary());
// Enable the sampling profiler.
if (SamplingProfilerIntegration.isEnabled()) {
SamplingProfilerIntegration.start();
mProfilerSnapshotTimer = new Timer();
mProfilerSnapshotTimer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
SamplingProfilerIntegration.writeSnapshot("system_server", null);
}
}, SNAPSHOT_INTERVAL, SNAPSHOT_INTERVAL);
}
// Mmmmmm... more memory!
VMRuntime.getRuntime().clearGrowthLimit();
// The system server has to run all of the time, so it needs to be
// as efficient as possible with its memory usage.
VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetHeapUtilization(0.8f);
// Some devices rely on runtime fingerprint generation, so make sure
// we've defined it before booting further.
Build.ensureFingerprintProperty();
// Within the system server, it is an error to access Environment paths without
// explicitly specifying a user.
Environment.setUserRequired(true);
// Within the system server, any incoming Bundles should be defused
// to avoid throwing BadParcelableException.
BaseBundle.setShouldDefuse(true);
// Ensure binder calls into the system always run at foreground priority.
BinderInternal.disableBackgroundScheduling(true);
// Increase the number of binder threads in system_server
BinderInternal.setMaxThreads(sMaxBinderThreads);
// Prepare the main looper thread (this thread).
android.os.Process.setThreadPriority(
android.os.Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_FOREGROUND);
android.os.Process.setCanSelfBackground(false);
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
// Initialize native services.
System.loadLibrary("android_servers");
// Check whether we failed to shut down last time we tried.
// This call may not return.
performPendingShutdown();
// Initialize the system context.
createSystemContext();
// Create the system service manager.
mSystemServiceManager = new SystemServiceManager(mSystemContext);
mSystemServiceManager.setRuntimeRestarted(mRuntimeRestart);
LocalServices.addService(SystemServiceManager.class, mSystemServiceManager);
// Prepare the thread pool for init tasks that can be parallelized
SystemServerInitThreadPool.get();
} finally {
traceEnd(); // InitBeforeStartServices
}
// Start services.
try {
traceBeginAndSlog("StartServices");
startBootstrapServices();
startCoreServices();
startOtherServices();
SystemServerInitThreadPool.shutdown();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
Slog.e("System", "******************************************");
Slog.e("System", "************ Failure starting system services", ex);
throw ex;
} finally {
traceEnd();
}
// For debug builds, log event loop stalls to dropbox for analysis.
if (StrictMode.conditionallyEnableDebugLogging()) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Enabled StrictMode for system server main thread.");
}
if (!mRuntimeRestart && !isFirstBootOrUpgrade()) {
int uptimeMillis = (int) SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
MetricsLogger.histogram(null, "boot_system_server_ready", uptimeMillis);
final int MAX_UPTIME_MILLIS = 60 * 1000;
if (uptimeMillis > MAX_UPTIME_MILLIS) {
Slog.wtf(SYSTEM_SERVER_TIMING_TAG,
"SystemServer init took too long. uptimeMillis=" + uptimeMillis);
}
}
// Loop forever.
Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}
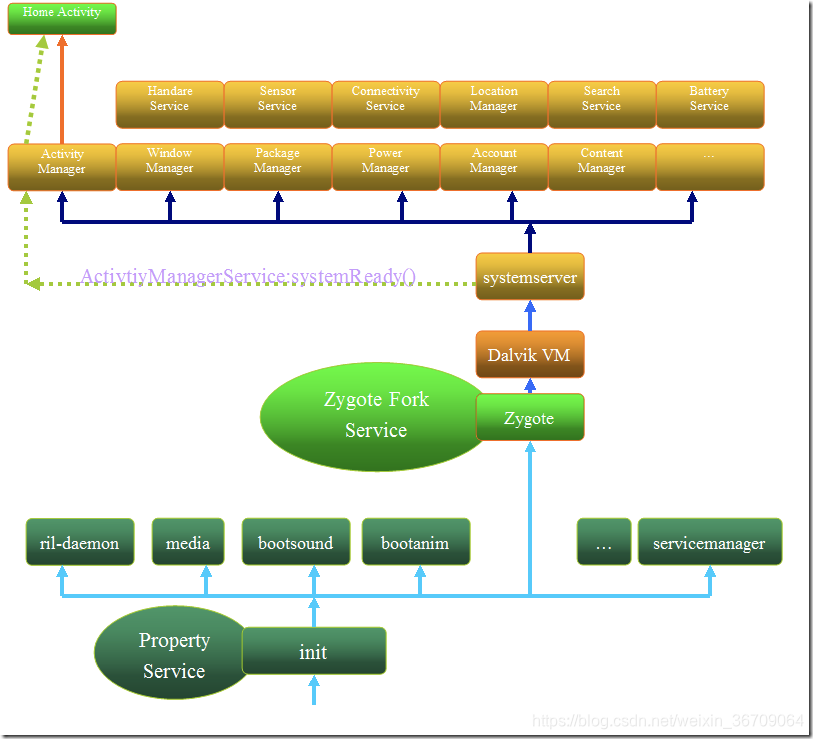
1.8 android相关服务和应用启动过程图
android相关服务和应用启动过程见下图








 本文深入剖析了Android系统的启动过程,从init进程开始,详细阐述了Dalvik虚拟机、Zygote进程的启动,包括Zygote的孵化机制和AndroidRuntime的角色。此外,还介绍了ServiceManager以及SystemServer如何启动,并探讨了关键服务与应用的启动流程。
本文深入剖析了Android系统的启动过程,从init进程开始,详细阐述了Dalvik虚拟机、Zygote进程的启动,包括Zygote的孵化机制和AndroidRuntime的角色。此外,还介绍了ServiceManager以及SystemServer如何启动,并探讨了关键服务与应用的启动流程。
















 1513
1513

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








