给你一个 n * n 矩阵 grid ,矩阵由若干 0 和 1 组成。请你用四叉树表示该矩阵 grid 。
你需要返回能表示矩阵 grid 的 四叉树 的根结点。
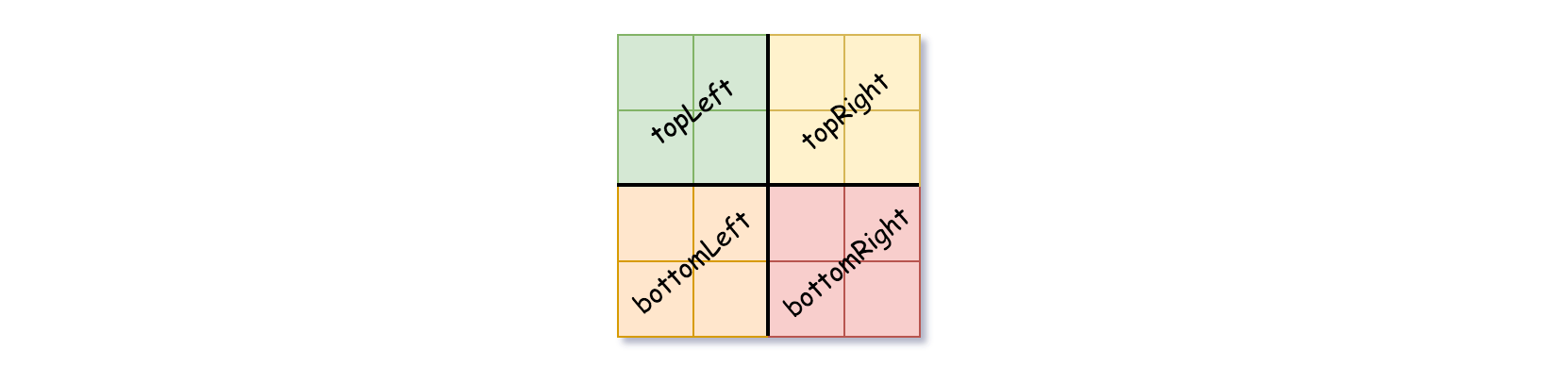
四叉树数据结构中,每个内部节点只有四个子节点。此外,每个节点都有两个属性:
val:储存叶子结点所代表的区域的值。1 对应 True,0 对应 False。注意,当isLeaf为 False 时,你可以把 True 或者 False 赋值给节点,两种值都会被判题机制 接受 。isLeaf: 当这个节点是一个叶子结点时为 True,如果它有 4 个子节点则为 False 。
class Node {
public boolean val;
public boolean isLeaf;
public Node topLeft;
public Node topRight;
public Node bottomLeft;
public Node bottomRight;
}
我们可以按以下步骤为二维区域构建四叉树:
- 如果当前网格的值相同(即,全为
0或者全为1),将isLeaf设为 True ,将val设为网格相应的值,并将四个子节点都设为 Null 然后停止。 - 如果当前网格的值不同,将
isLeaf设为 False, 将val设为任意值,然后如下图所示,将当前网格划分为四个子网格。 - 使用适当的子网格递归每个子节点。
如果你想了解更多关于四叉树的内容,可以参考 wiki 。
四叉树格式:
你不需要阅读本节来解决这个问题。只有当你想了解输出格式时才会这样做。输出为使用层序遍历后四叉树的序列化形式,其中 null 表示路径终止符,其下面不存在节点。
它与二叉树的序列化非常相似。唯一的区别是节点以列表形式表示 [isLeaf, val] 。
如果 isLeaf 或者 val 的值为 True ,则表示它在列表 [isLeaf, val] 中的值为 1 ;如果 isLeaf 或者 val 的值为 False ,则表示值为 0 。
示例 1:
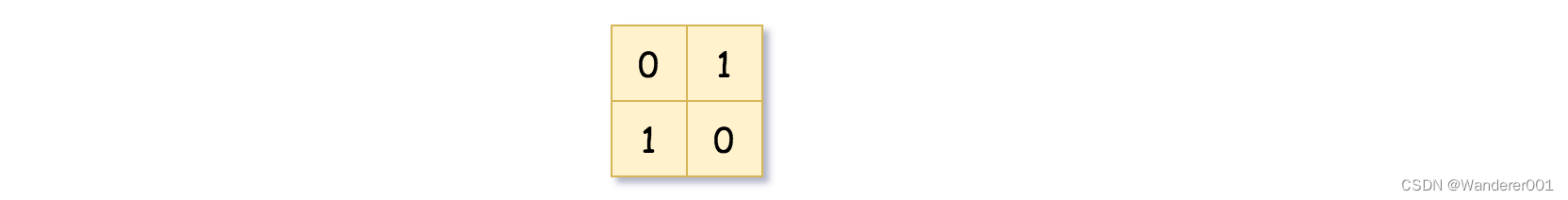
输入:grid = [[0,1],[1,0]] 输出:[[0,1],[1,0],[1,1],[1,1],[1,0]] 解释:此示例的解释如下: 请注意,在下面四叉树的图示中,0 表示 false,1 表示 True 。
示例 2:

输入:grid = [[1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0],[1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0],[1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0],[1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0],[1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0],[1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0]] 输出:[[0,1],[1,1],[0,1],[1,1],[1,0],null,null,null,null,[1,0],[1,0],[1,1],[1,1]] 解释:网格中的所有值都不相同。我们将网格划分为四个子网格。 topLeft,bottomLeft 和 bottomRight 均具有相同的值。 topRight 具有不同的值,因此我们将其再分为 4 个子网格,这样每个子网格都具有相同的值。 解释如下图所示:
提示:
n == grid.length == grid[i].lengthn == 2x其中0 <= x <= 6
思路与算法
我们可以使用递归的方法构建出四叉树。
具体地,我们用递归函数处理给定的矩阵
从
行开始到
行,从
和
列的部分。我们首先判定这一部分是否均为
或
,如果是,那么这一部分对应的是一个叶节点,我们构造出对应的叶节点并结束递归;如果不是,那么这一部分对应的是一个非叶节点,我们需要将其分成四个部分:行的分界线为
,列的分界线为
,根据这两条分界线递归地调用 dfs\text{dfs}dfs 函数得到四个部分对应的树,再将它们对应地挂在非叶节点的四个子节点上。
代码
class Solution {
public:
Node *construct(vector<vector<int>> &grid) {
function<Node*(int, int, int, int)> dfs = [&](int r0, int c0, int r1, int c1) {
for (int i = r0; i < r1; ++i) {
for (int j = c0; j < c1; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] != grid[r0][c0]) { // 不是叶节点
return new Node(
true,
false,
dfs(r0, c0, (r0 + r1) / 2, (c0 + c1) / 2),
dfs(r0, (c0 + c1) / 2, (r0 + r1) / 2, c1),
dfs((r0 + r1) / 2, c0, r1, (c0 + c1) / 2),
dfs((r0 + r1) / 2, (c0 + c1) / 2, r1, c1)
);
}
}
}
// 是叶节点
return new Node(grid[r0][c0], true);
};
return dfs(0, 0, grid.size(), grid.size());
}
};
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:。这里给出一个较为宽松的时间复杂度上界。记
为边长为
的数组需要的时间复杂度,那么「判定这一部分是否均为
或
」需要的时间为
,在这之后会递归调用
规模为
的子问题,那么有:
以及:
根据主定理,可以得到。但如果判定需要的时间达到了渐近紧界
,那么说明这一部分包含的元素大部分都是相同的,也就是说,有很大概率在深入递归时遇到元素完全相同的一部分,从而提前结束递归。因此
的时间复杂度是很宽松的,实际运行过程中可以跑出与方法二
时间复杂度代码相似的速度。
空间复杂度:,即为递归需要使用的栈空间。







 文章详述了利用递归构建n*n矩阵的四叉树结构,区分叶节点和非叶节点,输出以层次遍历序列化形式。
文章详述了利用递归构建n*n矩阵的四叉树结构,区分叶节点和非叶节点,输出以层次遍历序列化形式。

















 693
693

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










