文章目录
🐶一、线程池
1、自定义线程池
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestPool")
public class TestPool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPool threadPool = new ThreadPool(1,
1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, 1, (queue, task)->{
// 1. 死等
queue.put(task);
// 2) 带超时等待
// queue.offer(task, 1500, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
// 3) 让调用者放弃任务执行
// log.debug("放弃{}", task);
// 4) 让调用者抛出异常
// throw new RuntimeException("任务执行失败 " + task);
// 5) 让调用者自己执行任务
task.run();
});
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int j = i;
threadPool.execute(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.debug("{}", j);
});
}
}
}
@FunctionalInterface // 拒绝策略
interface RejectPolicy<T> {
void reject(BlockingQueue<T> queue, T task);
}
@Slf4j(topic = "c.ThreadPool")
class ThreadPool {
// 任务队列
private BlockingQueue<Runnable> taskQueue;
// 线程集合
private HashSet<Worker> workers = new HashSet<>();
// 核心线程数
private int coreSize;
// 获取任务时的超时时间
private long timeout;
private TimeUnit timeUnit;
private RejectPolicy<Runnable> rejectPolicy;
// 执行任务
public void execute(Runnable task) {
// 当任务数没有超过 coreSize 时,直接交给 worker 对象执行
// 如果任务数超过 coreSize 时,加入任务队列暂存
synchronized (workers) {
if(workers.size() < coreSize) {
Worker worker = new Worker(task);
log.debug("新增 worker{}, {}", worker, task);
workers.add(worker);
worker.start();
} else {
// taskQueue.put(task);
// 1) 死等
// 2) 带超时等待
// 3) 让调用者放弃任务执行
// 4) 让调用者抛出异常
// 5) 让调用者自己执行任务
taskQueue.tryPut(rejectPolicy, task);
}
}
}
public ThreadPool(int coreSize, long timeout, TimeUnit timeUnit, int queueCapcity, RejectPolicy<Runnable> rejectPolicy) {
this.coreSize = coreSize;
this.timeout = timeout;
this.timeUnit = timeUnit;
this.taskQueue = new BlockingQueue<>(queueCapcity);
this.rejectPolicy = rejectPolicy;
}
class Worker extends Thread{
private Runnable task;
public Worker(Runnable task) {
this.task = task;
}
@Override
public void run() {
// 执行任务
// 1) 当 task 不为空,执行任务
// 2) 当 task 执行完毕,再接着从任务队列获取任务并执行
// while(task != null || (task = taskQueue.take()) != null) {
while(task != null || (task = taskQueue.poll(timeout, timeUnit)) != null) {
try {
log.debug("正在执行...{}", task);
task.run();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
task = null;
}
}
synchronized (workers) {
log.debug("worker 被移除{}", this);
workers.remove(this);
}
}
}
}
@Slf4j(topic = "c.BlockingQueue")
class BlockingQueue<T> {
// 1. 任务队列
private Deque<T> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
// 2. 锁
private ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
// 3. 生产者条件变量
private Condition fullWaitSet = lock.newCondition();
// 4. 消费者条件变量
private Condition emptyWaitSet = lock.newCondition();
// 5. 容量
private int capcity;
public BlockingQueue(int capcity) {
this.capcity = capcity;
}
// 带超时阻塞获取
public T poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {
lock.lock();
try {
// 将 timeout 统一转换为 纳秒
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
while (queue.isEmpty()) {
try {
// 返回值是剩余时间
if (nanos <= 0) {
return null;
}
nanos = emptyWaitSet.awaitNanos(nanos);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
T t = queue.removeFirst();
fullWaitSet.signal();
return t;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
// 阻塞获取
public T take() {
lock.lock();
try {
while (queue.isEmpty()) {
try {
emptyWaitSet.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
T t = queue.removeFirst();
fullWaitSet.signal();
return t;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
// 阻塞添加
public void put(T task) {
lock.lock();
try {
while (queue.size() == capcity) {
try {
log.debug("等待加入任务队列 {} ...", task);
fullWaitSet.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
log.debug("加入任务队列 {}", task);
queue.addLast(task);
emptyWaitSet.signal();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
// 带超时时间阻塞添加
public boolean offer(T task, long timeout, TimeUnit timeUnit) {
lock.lock();
try {
long nanos = timeUnit.toNanos(timeout);
while (queue.size() == capcity) {
try {
if(nanos <= 0) {
return false;
}
log.debug("等待加入任务队列 {} ...", task);
nanos = fullWaitSet.awaitNanos(nanos);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
log.debug("加入任务队列 {}", task);
queue.addLast(task);
emptyWaitSet.signal();
return true;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public int size() {
lock.lock();
try {
return queue.size();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void tryPut(RejectPolicy<T> rejectPolicy, T task) {
lock.lock();
try {
// 判断队列是否满
if(queue.size() == capcity) {
rejectPolicy.reject(this, task);
} else { // 有空闲
log.debug("加入任务队列 {}", task);
queue.addLast(task);
emptyWaitSet.signal();
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
执行结果:

2、JDK为我们提供的线程池(ThreadPoolExecutor)

(1)线程池状态 
(2)构造方法
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler)

工作方式:


(3)根据上面的构造方法,JDK也提供了众多的工厂方法来创建各种用途的线程池,下面我们来看看
newFixedThreadPool
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
}

newCachedThreadPool
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
}

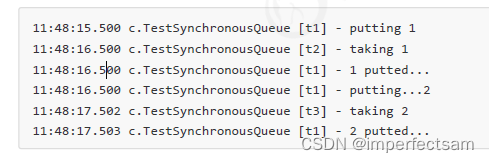
SynchronousQueue<Integer> integers = new SynchronousQueue<>();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
log.debug("putting {} ", 1);
integers.put(1);
log.debug("{} putted...", 1);
log.debug("putting...{} ", 2);
integers.put(2);
log.debug("{} putted...", 2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"t1").start();
sleep(1);
new Thread(() -> {
try {
log.debug("taking {}", 1);
integers.take();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"t2").start();
sleep(1);
new Thread(() -> {
try {
log.debug("taking {}", 2);
integers.take();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"t3").start();
输出结果:
newSingleThreadExecutor
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));
}

3、提交任务

submit方法代码演示:
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestSubmit")
public class TestSubmit {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
method1(pool);
}
private static void method1(ExecutorService pool) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
Future<String> future = pool.submit(() -> {
log.debug("running");
Thread.sleep(1000);
return "ok";
});
log.debug("{}", future.get());
}
}
执行结果:

invokeAll方法代码:
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestSubmit")
public class TestSubmit {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
method2(pool);
}
private static void method2(ExecutorService pool) throws InterruptedException {
List<Future<String>> futures = pool.invokeAll(Arrays.asList(
() -> {
log.debug("begin");
Thread.sleep(1000);
return "1";
},
() -> {
log.debug("begin");
Thread.sleep(500);
return "2";
},
() -> {
log.debug("begin");
Thread.sleep(2000);
return "3";
}
));
futures.forEach( f -> {
try {
log.debug("{}", f.get());
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
}
执行结果:

invokeAny方法代码:
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestSubmit")
public class TestSubmit {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
method3(pool);
}
private static void method3(ExecutorService pool) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
String result = pool.invokeAny(Arrays.asList(
() -> {
log.debug("begin 1");
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.debug("end 1");
return "1";
},
() -> {
log.debug("begin 2");
Thread.sleep(500);
log.debug("end 2");
return "2";
},
() -> {
log.debug("begin 3");
Thread.sleep(2000);
log.debug("end 3");
return "3";
}
));
log.debug("{}", result);
}
}
执行结果:

invokeAny用于返回一个最先得到的结果
4、关闭线程池
(1)、shutdown

代码演示:
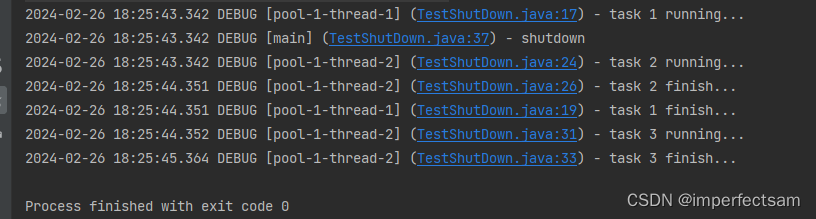
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestShutDown")
public class TestShutDown {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
Future<Integer> result1 = pool.submit(() -> {
log.debug("task 1 running...");
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.debug("task 1 finish...");
return 1;
});
Future<Integer> result2 = pool.submit(() -> {
log.debug("task 2 running...");
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.debug("task 2 finish...");
return 2;
});
Future<Integer> result3 = pool.submit(() -> {
log.debug("task 3 running...");
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.debug("task 3 finish...");
return 3;
});
log.debug("shutdown");
pool.shutdown();
// pool.awaitTermination(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// List<Runnable> runnables = pool.shutdownNow();
// log.debug("other.... {}" , runnables);
}
}
执行结果:
(2)shutdownNow
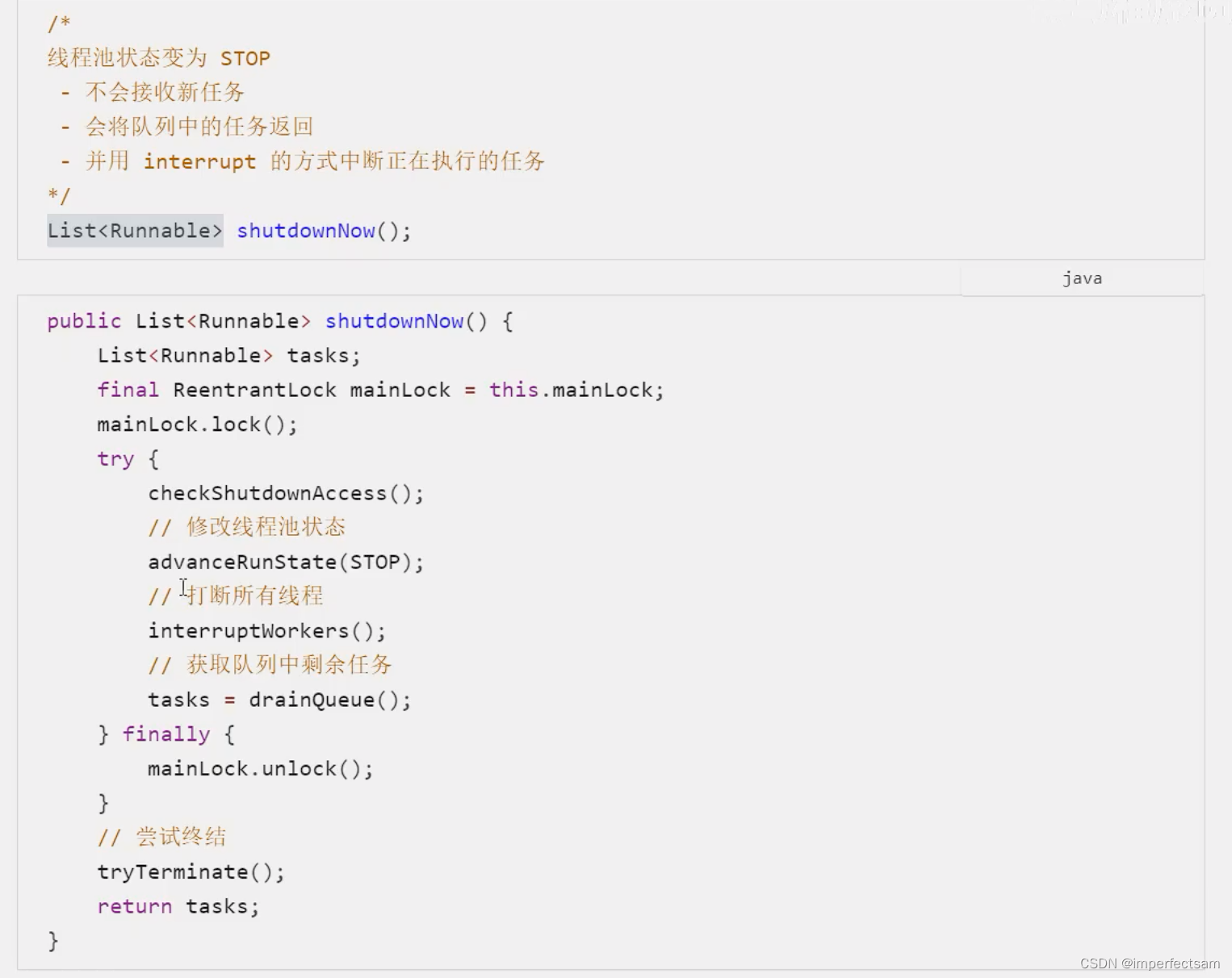
代码演示:
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestShutDown")
public class TestShutDown {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
Future<Integer> result1 = pool.submit(() -> {
log.debug("task 1 running...");
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.debug("task 1 finish...");
return 1;
});
Future<Integer> result2 = pool.submit(() -> {
log.debug("task 2 running...");
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.debug("task 2 finish...");
return 2;
});
Future<Integer> result3 = pool.submit(() -> {
log.debug("task 3 running...");
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.debug("task 3 finish...");
return 3;
});
log.debug("shutdown");
// pool.shutdown();
// pool.awaitTermination(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
List<Runnable> runnables = pool.shutdownNow();
log.debug("other.... {}" , runnables);
}
}
执行结果:

(3)其他方法

5、设计模式-工作线程
(1)定义:

(2)饥饿

代码演示:
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestDeadLock")
public class TestStarvation {
static final List<String> MENU = Arrays.asList("地三鲜", "宫保鸡丁", "辣子鸡丁", "烤鸡翅");
static Random RANDOM = new Random();
static String cooking() {
return MENU.get(RANDOM.nextInt(MENU.size()));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
pool.execute(() -> {
log.debug("处理点餐...");
Future<String> f = pool.submit(() -> {
log.debug("做菜");
return cooking();
});
try {
log.debug("上菜: {}", f.get());
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
pool.execute(() -> {
log.debug("处理点餐...");
Future<String> f = pool.submit(() -> {
log.debug("做菜");
return cooking();
});
try {
log.debug("上菜: {}", f.get());
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
}
执行结果:

这里我们可以看到这两个线程都进行点餐了,而没有可用的线程去做菜了,这就导致了饥饿死锁了。
那我们应该如何解决这种饥饿的现象呢?
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestDeadLock")
public class TestStarvation {
static final List<String> MENU = Arrays.asList("地三鲜", "宫保鸡丁", "辣子鸡丁", "烤鸡翅");
static Random RANDOM = new Random();
static String cooking() {
return MENU.get(RANDOM.nextInt(MENU.size()));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService waiterPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
ExecutorService cookPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
waiterPool.execute(() -> {
log.debug("处理点餐...");
Future<String> f = cookPool.submit(() -> {
log.debug("做菜");
return cooking();
});
try {
log.debug("上菜: {}", f.get());
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
waiterPool.execute(() -> {
log.debug("处理点餐...");
Future<String> f = cookPool.submit(() -> {
log.debug("做菜");
return cooking();
});
try {
log.debug("上菜: {}", f.get());
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
}
执行结果:

我们可以专门有点餐的线程和专门进行做菜的线程。
6、创建多少线程池合适

7、ScheduledThreadPool(任务调度线程池)
定义:ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor 是 Java 中的一个线程池类,用于执行定时任务。它是 ThreadPoolExecutor 的子类,因此继承了线程池的所有特性,并且增加了一些支持定时任务的功能。
代码编写:
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestTimer")
public class TestTimer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ScheduledExecutorService pool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);
method2(pool);
}
private static void method2(ScheduledExecutorService pool) {
pool.schedule(() -> {
log.debug("task1");
int i = 1 / 0;
}, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
pool.schedule(() -> {
log.debug("task2");
}, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
执行结果:
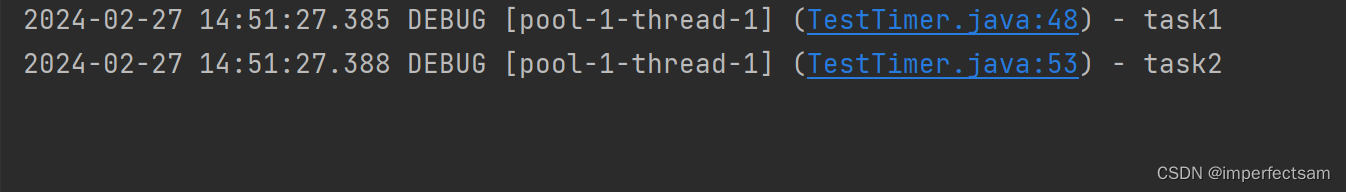
我们可以看到这里的即使task1发生了异常也不会影响task2的执行。
代码编写:
private static void method3() {
ScheduledExecutorService pool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);
log.debug("start...");
pool.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
log.debug("running...");
}, 1, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
执行结果:

scheduleAtFixedRate这样子任务就会定时的去执行,每隔一秒就会去打印running。
8、正确处理线程池异常
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
pool.submit(() -> {
try {
log.debug("task1");
int i = 1 / 0;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("error:", e);
}
});
执行结果:

🐱二、JUC
1、AQS

2、自定义不可重入锁
编写代码:
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestAqs")
public class TestAqs {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLock lock = new MyLock();
new Thread(() -> {
lock.lock();
try {
log.debug("locking...");
sleep(1);
} finally {
log.debug("unlocking...");
lock.unlock();
}
},"t1").start();
new Thread(() -> {
lock.lock();
try {
log.debug("locking...");
} finally {
log.debug("unlocking...");
lock.unlock();
}
},"t2").start();
}
}
// 自定义锁(不可重入锁)
class MyLock implements Lock {
// 独占锁 同步器类
class MySync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
@Override
protected boolean tryAcquire(int arg) {
if(compareAndSetState(0, 1)) {
// 加上了锁,并设置 owner 为当前线程
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
return true;
}
return false;
}
@Override
protected boolean tryRelease(int arg) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
setState(0);
return true;
}
@Override // 是否持有独占锁
protected boolean isHeldExclusively() {
return getState() == 1;
}
public Condition newCondition() {
return new ConditionObject();
}
}
private MySync sync = new MySync();
@Override // 加锁(不成功会进入等待队列)
public void lock() {
sync.acquire(1);
}
@Override // 加锁,可打断
public void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException {
sync.acquireInterruptibly(1);
}
@Override // 尝试加锁(一次)
public boolean tryLock() {
return sync.tryAcquire(1);
}
@Override // 尝试加锁,带超时
public boolean tryLock(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
return sync.tryAcquireNanos(1, unit.toNanos(time));
}
@Override // 解锁
public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}
@Override // 创建条件变量
public Condition newCondition() {
return sync.newCondition();
}
}
执行结果:

3、ReentrantLock原理

(1)非公平锁实现原理
先从构造器开始看,默认为非公平锁实现
public ReentrantLock() {
sync = new NonfairSync();
}




(2)加锁源码
// Sync 继承自 AQS
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7316153563782823691L;
// 加锁实现
final void lock() {
// 首先用 cas 尝试(仅尝试一次)将 state 从 0 改为 1, 如果成功表示获得了独占锁
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
else
// 如果尝试失败,进入 ㈠
acquire(1);
}
// ㈠ AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
public final void acquire(int arg) {
// ㈡ tryAcquire
if (
!tryAcquire(arg) &&
// 当 tryAcquire 返回为 false 时, 先调用 addWaiter ㈣, 接着 acquireQueued ㈤
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg)
) {
selfInterrupt();
}
}
// ㈡ 进入 ㈢
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);
}
// ㈢ Sync 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
// 如果还没有获得锁
if (c == 0) {
// 尝试用 cas 获得, 这里体现了非公平性: 不去检查 AQS 队列
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
// 如果已经获得了锁, 线程还是当前线程, 表示发生了锁重入
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
// state++
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
// 获取失败, 回到调用处
return false;
}
// ㈣ AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
// 将当前线程关联到一个 Node 对象上, 模式为独占模式
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
// 如果 tail 不为 null, cas 尝试将 Node 对象加入 AQS 队列尾部
Node pred = tail;
if (pred != null) {
node.prev = pred;
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
// 双向链表
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
// 尝试将 Node 加入 AQS, 进入 ㈥
enq(node);
return node;
}
// ㈥ AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
private Node enq(final Node node) {
for (;;) {
Node t = tail;
if (t == null) {
// 还没有, 设置 head 为哨兵节点(不对应线程,状态为 0)
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node())) {
tail = head;
}
} else {
// cas 尝试将 Node 对象加入 AQS 队列尾部
node.prev = t;
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {
t.next = node;
return t;
}
}
}
}
// ㈤ AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
// 上一个节点是 head, 表示轮到自己(当前线程对应的 node)了, 尝试获取
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
// 获取成功, 设置自己(当前线程对应的 node)为 head
setHead(node);
// 上一个节点 help GC
p.next = null;
failed = false;
// 返回中断标记 false
return interrupted;
}
if (
// 判断是否应当 park, 进入 ㈦
shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
// park 等待, 此时 Node 的状态被置为 Node.SIGNAL ㈧
parkAndCheckInterrupt()
) {
interrupted = true;
}
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
// ㈦ AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {
// 获取上一个节点的状态
int ws = pred.waitStatus;
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) {
// 上一个节点都在阻塞, 那么自己也阻塞好了
return true;
}
// > 0 表示取消状态
if (ws > 0) {
// 上一个节点取消, 那么重构删除前面所有取消的节点, 返回到外层循环重试
do {
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);
pred.next = node;
} else {
// 这次还没有阻塞
// 但下次如果重试不成功, 则需要阻塞,这时需要设置上一个节点状态为 Node.SIGNAL
compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);
}
return false;
}
// ㈧ 阻塞当前线程
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
LockSupport.park(this);
return Thread.interrupted();
}
}
是否需要 unpark 是由当前节点的前驱节点的 waitStatus == Node.SIGNAL 来决定,而不是本节点的
waitStatus 决定
(3)解锁源码
// Sync 继承自 AQS
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
// 解锁实现
public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}
// AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
public final boolean release(int arg) {
// 尝试释放锁, 进入 ㈠
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
// 队列头节点 unpark
Node h = head;
if (
// 队列不为 null
h != null &&
// waitStatus == Node.SIGNAL 才需要 unpark
h.waitStatus != 0
) {
// unpark AQS 中等待的线程, 进入 ㈡
unparkSuccessor(h);
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
// ㈠ Sync 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
// state--
int c = getState() - releases;
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
// 支持锁重入, 只有 state 减为 0, 才释放成功
if (c == 0) {
free = true;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
setState(c);
return free;
}
// ㈡ AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
// 如果状态为 Node.SIGNAL 尝试重置状态为 0
// 不成功也可以
int ws = node.waitStatus;
if (ws < 0) {
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);
}
// 找到需要 unpark 的节点, 但本节点从 AQS 队列中脱离, 是由唤醒节点完成的
Node s = node.next;
// 不考虑已取消的节点, 从 AQS 队列从后至前找到队列最前面需要 unpark 的节点
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
s = null;
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
if (s != null)
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}
}
(4)可重入原理
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
// ...
// Sync 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
// 如果已经获得了锁, 线程还是当前线程, 表示发生了锁重入
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
// state++
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Sync 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
// state--
int c = getState() - releases;
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
// 支持锁重入, 只有 state 减为 0, 才释放成功
if (c == 0) {
free = true;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
setState(c);
return free;
}
}
(5)可打断原理(不可打断模式)
在此模式下,即使它被打断,仍会驻留在 AQS 队列中,一直要等到获得锁后方能得知自己被打断了
// Sync 继承自 AQS
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
// ...
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
// 如果打断标记已经是 true, 则 park 会失效
LockSupport.park(this);
// interrupted 会清除打断标记
return Thread.interrupted();
}
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null;
failed = false;
// 还是需要获得锁后, 才能返回打断状态
return interrupted;
}
if (
shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt()
) {
// 如果是因为 interrupt 被唤醒, 返回打断状态为 true
interrupted = true;
}
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (
!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg)
) {
// 如果打断状态为 true
selfInterrupt();
}
}
static void selfInterrupt() {
// 重新产生一次中断
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
(6)可打断原理(可打断模式)
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
public final void acquireInterruptibly(int arg) throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
// 如果没有获得到锁, 进入 ㈠
if (!tryAcquire(arg))
doAcquireInterruptibly(arg);
}
// ㈠ 可打断的获取锁流程
private void doAcquireInterruptibly(int arg) throws InterruptedException {
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE);
boolean failed = true;
try {
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt()) {
// 在 park 过程中如果被 interrupt 会进入此
// 这时候抛出异常, 而不会再次进入 for (;;)
throw new InterruptedException();
}
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
}
(7)公平锁实现原理
static final class FairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -3000897897090466540L;
final void lock() {
acquire(1);
}
// AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (
!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg)
) {
selfInterrupt();
}
}
// 与非公平锁主要区别在于 tryAcquire 方法的实现
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
// 先检查 AQS 队列中是否有前驱节点, 没有才去竞争
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() &&
compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
// ㈠ AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
public final boolean hasQueuedPredecessors() {
Node t = tail;
Node h = head;
Node s;
// h != t 时表示队列中有 Node
return h != t &&
(
// (s = h.next) == null 表示队列中还有没有老二
(s = h.next) == null ||
// 或者队列中老二线程不是此线程
s.thread != Thread.currentThread()
);
}
}
(8)条件变量实现原理


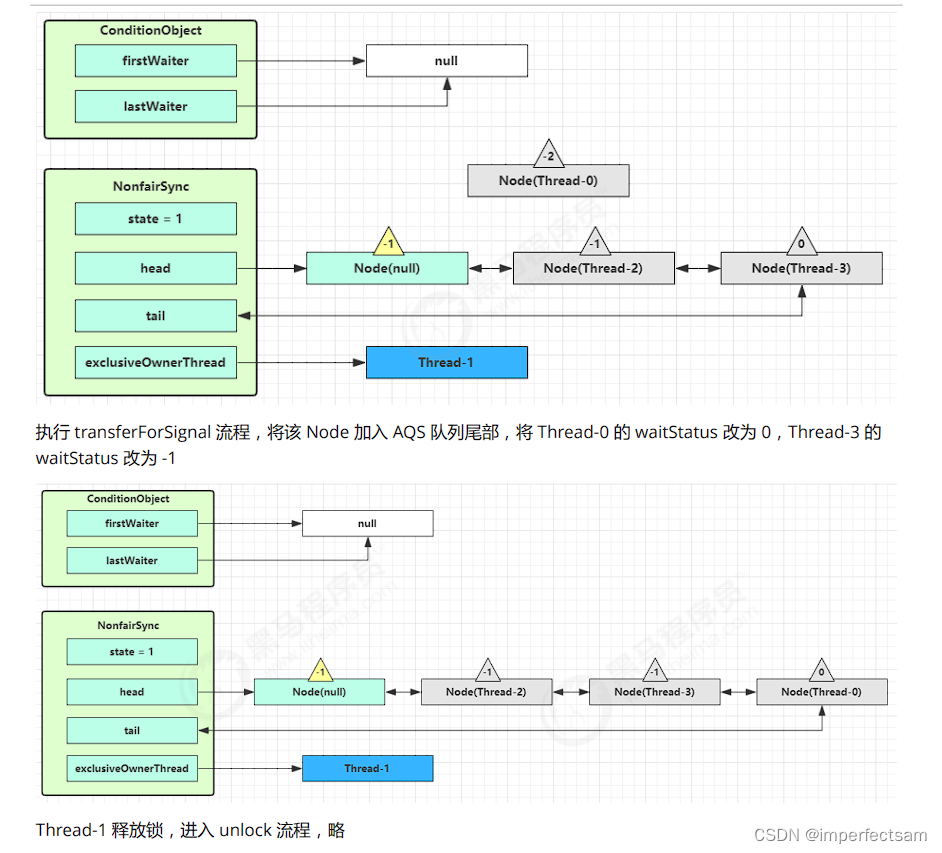
4、ReentrantReadWriteLock原理


在这里插入图片描述



5、StampedLock
该类自 JDK 8 加入,是为了进一步优化读性能,它的特点是在使用读锁、写锁时都必须配合【戳】使用。
读-读优化
编写代码:
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestStampedLock")
public class TestStampedLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DataContainerStamped dataContainer = new DataContainerStamped(1);
new Thread(() -> {
dataContainer.read(1);
}, "t1").start();
sleep(0.5);
new Thread(() -> {
dataContainer.read(0);
}, "t2").start();
}
}
@Slf4j(topic = "c.DataContainerStamped")
class DataContainerStamped {
private int data;
private final StampedLock lock = new StampedLock();
public DataContainerStamped(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
public int read(int readTime) {
long stamp = lock.tryOptimisticRead();
log.debug("optimistic read locking...{}", stamp);
sleep(readTime);
if (lock.validate(stamp)) {
log.debug("read finish...{}, data:{}", stamp, data);
return data;
}
// 锁升级 - 读锁
log.debug("updating to read lock... {}", stamp);
try {
stamp = lock.readLock();
log.debug("read lock {}", stamp);
sleep(readTime);
log.debug("read finish...{}, data:{}", stamp, data);
return data;
} finally {
log.debug("read unlock {}", stamp);
lock.unlockRead(stamp);
}
}
public void write(int newData) {
long stamp = lock.writeLock();
log.debug("write lock {}", stamp);
try {
sleep(2);
this.data = newData;
} finally {
log.debug("write unlock {}", stamp);
lock.unlockWrite(stamp);
}
}
}
执行结果
:
读-写优化
编写代码:
public class TestStampedLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DataContainerStamped dataContainer = new DataContainerStamped(1);
new Thread(() -> {
dataContainer.read(1);
}, "t1").start();
sleep(0.5);
new Thread(() -> {
dataContainer.write(100);
}, "t2").start();
}
}
执行结果:

5、Semaphore
信号量,用来限制能同时访问共享资源的线程上限。
编写代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 创建 semaphore 对象
Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(3);
// 2. 10个线程同时运行
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
// 3. 获取许可
try {
semaphore.acquire();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
log.debug("running...");
sleep(1);
log.debug("end...");
} finally {
// 4. 释放许可
semaphore.release();
}
}).start();
}
}
执行结果:

6、CountdownLatch
用来进行线程同步协作,等待所有线程完成倒计时。
其中构造参数用来初始化等待计数值,await() 用来等待计数归零,countDown() 用来让计数减一。
编写代码:
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestCountDownLatch")
public class TestCountDownLatch {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
test5();
}
private static void test5() {
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(3);
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4);
service.submit(() -> {
log.debug("begin...");
sleep(1);
latch.countDown();
log.debug("end...{}", latch.getCount());
});
service.submit(() -> {
log.debug("begin...");
sleep(1.5);
latch.countDown();
log.debug("end...{}", latch.getCount());
});
service.submit(() -> {
log.debug("begin...");
sleep(2);
latch.countDown();
log.debug("end...{}", latch.getCount());
});
service.submit(()->{
try {
log.debug("waiting...");
latch.await();
log.debug("wait end...");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
private static void test4() throws InterruptedException {
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(3);
new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("begin...");
sleep(1);
latch.countDown();
log.debug("end...{}", latch.getCount());
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("begin...");
sleep(2);
latch.countDown();
log.debug("end...{}", latch.getCount());
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("begin...");
sleep(1.5);
latch.countDown();
log.debug("end...{}", latch.getCount());
}).start();
log.debug("waiting...");
latch.await();
log.debug("wait end...");
}
private static void test2() throws InterruptedException {
AtomicInteger num = new AtomicInteger(0);
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10, (r) -> {
return new Thread(r, "t" + num.getAndIncrement());
});
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(10);
String[] all = new String[10];
Random r = new Random();
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
int x = j;
service.submit(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(r.nextInt(100));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
all[x] = Thread.currentThread().getName() + "(" + (i + "%") + ")";
System.out.print("\r" + Arrays.toString(all));
}
latch.countDown();
});
}
latch.await();
System.out.println("\n游戏开始...");
service.shutdown();
}
}
执行结果:

6、CyclicBarrier
循环栅栏,用来进行线程协作,等待线程满足某个计数。构造时设置『计数个数』,每个线程执
行到某个需要“同步”的时刻调用 await() 方法进行等待,当等待的线程数满足『计数个数』时,继续执行。
编写代码:
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestCyclicBarrier")
public class TestCyclicBarrier {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
CyclicBarrier barrier = new CyclicBarrier(2, ()-> {
log.debug("task1, task2 finish...");
});
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { // task1 task2 task1
service.submit(() -> {
log.debug("task1 begin...");
sleep(1);
try {
barrier.await(); // 2-1=1
} catch (InterruptedException | BrokenBarrierException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
service.submit(() -> {
log.debug("task2 begin...");
sleep(2);
try {
barrier.await(); // 1-1=0
} catch (InterruptedException | BrokenBarrierException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
service.shutdown();
}
private static void test1() {
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(2);
service.submit(() -> {
log.debug("task1 start...");
sleep(1);
latch.countDown();
});
service.submit(() -> {
log.debug("task2 start...");
sleep(2);
latch.countDown();
});
try {
latch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.debug("task1 task2 finish...");
}
service.shutdown();
}
}
执行结果:

🐯三、线程安全集合类

1、ConcurrentHashMap
重要属性和内部类
// 默认为 0
// 当初始化时, 为 -1
// 当扩容时, 为 -(1 + 扩容线程数)
// 当初始化或扩容完成后,为 下一次的扩容的阈值大小
private transient volatile int sizeCtl;
// 整个 ConcurrentHashMap 就是一个 Node[]
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {}
// hash 表
transient volatile Node<K,V>[] table;
// 扩容时的 新 hash 表
private transient volatile Node<K,V>[] nextTable;
// 扩容时如果某个 bin 迁移完毕, 用 ForwardingNode 作为旧 table bin 的头结点
static final class ForwardingNode<K,V> extends Node<K,V> {}
// 用在 compute 以及 computeIfAbsent 时, 用来占位, 计算完成后替换为普通 Node
static final class ReservationNode<K,V> extends Node<K,V> {}
// 作为 treebin 的头节点, 存储 root 和 first
static final class TreeBin<K,V> extends Node<K,V> {}
// 作为 treebin 的节点, 存储 parent, left, right
static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends Node<K,V> {}
重要方法
// 获取 Node[] 中第 i 个 Node
static final <K,V> Node<K,V> tabAt(Node<K,V>[] tab, int i)
// cas 修改 Node[] 中第 i 个 Node 的值, c 为旧值, v 为新值
static final <K,V> boolean casTabAt(Node<K,V>[] tab, int i, Node<K,V> c, Node<K,V> v)
// 直接修改 Node[] 中第 i 个 Node 的值, v 为新值
static final <K,V> void setTabAt(Node<K,V>[] tab, int i, Node<K,V> v)
2、LinkedBlockingQueue
基本的入队出队
public class LinkedBlockingQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E>
implements BlockingQueue<E>, java.io.Serializable {
static class Node<E> {
E item;
/**
* 下列三种情况之一
* - 真正的后继节点
* - 自己, 发生在出队时
* - null, 表示是没有后继节点, 是最后了
*/
Node<E> next;
Node(E x) { item = x; }
}
}

出队:
Node<E> h = head;
Node<E> first = h.next;
h.next = h; // help GC
head = first;
E x = first.item;
first.item = null;
return x;


3、ConcurrentLinkedQueue
非阻塞算法: ConcurrentLinkedQueue 使用一种称为无锁(lock-free)的非阻塞算法实现,这意味着多个线程可以并发地访问队列而无需阻塞等待。
线程安全性: ConcurrentLinkedQueue 提供了线程安全的队列操作,包括添加元素、移除元素和检查队列是否为空等操作。这意味着你可以在多个线程之间安全地使用该队列,而无需额外的同步机制。
高性能: 由于使用了无锁算法,ConcurrentLinkedQueue 在高并发环境下具有良好的性能表现。它适用于生产者-消费者模式,其中多个线程同时生产和消费队列中的元素。
FIFO顺序: ConcurrentLinkedQueue 是一个先进先出(FIFO)的队列,保持了元素插入顺序。
迭代器支持: ConcurrentLinkedQueue 提供了迭代器,你可以通过迭代器遍历队列中的元素。需要注意的是,迭代器是弱一致的(weakly consistent),因此在迭代过程中队列可能会发生变化,但不会抛出 ConcurrentModificationException 异常。
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








