在java中如何使用多线程
1.实现Runnable接口创建线程
public class RunnableThreadExample implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("RunnableThreadExample.run");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(new RunnableThreadExample());
thread.start();
}
}
2.继承Thread类创建线程
public class ThreadExample extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("ThreadExample.run");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadExample threadExample = new ThreadExample();
threadExample.start();
}
}
3.实现Callable接口并创建带返回值的线程
public class CallableExample implements Callable<String> {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
return "执行结果:SUCCESSS";
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CallableExample callableExample = new CallableExample();
FutureTask<String> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(callableExample);
Thread thread = new Thread(futureTask);
thread.start();
System.out.println(futureTask.get());
}
}
多线程的基本原理

线程的运行状态
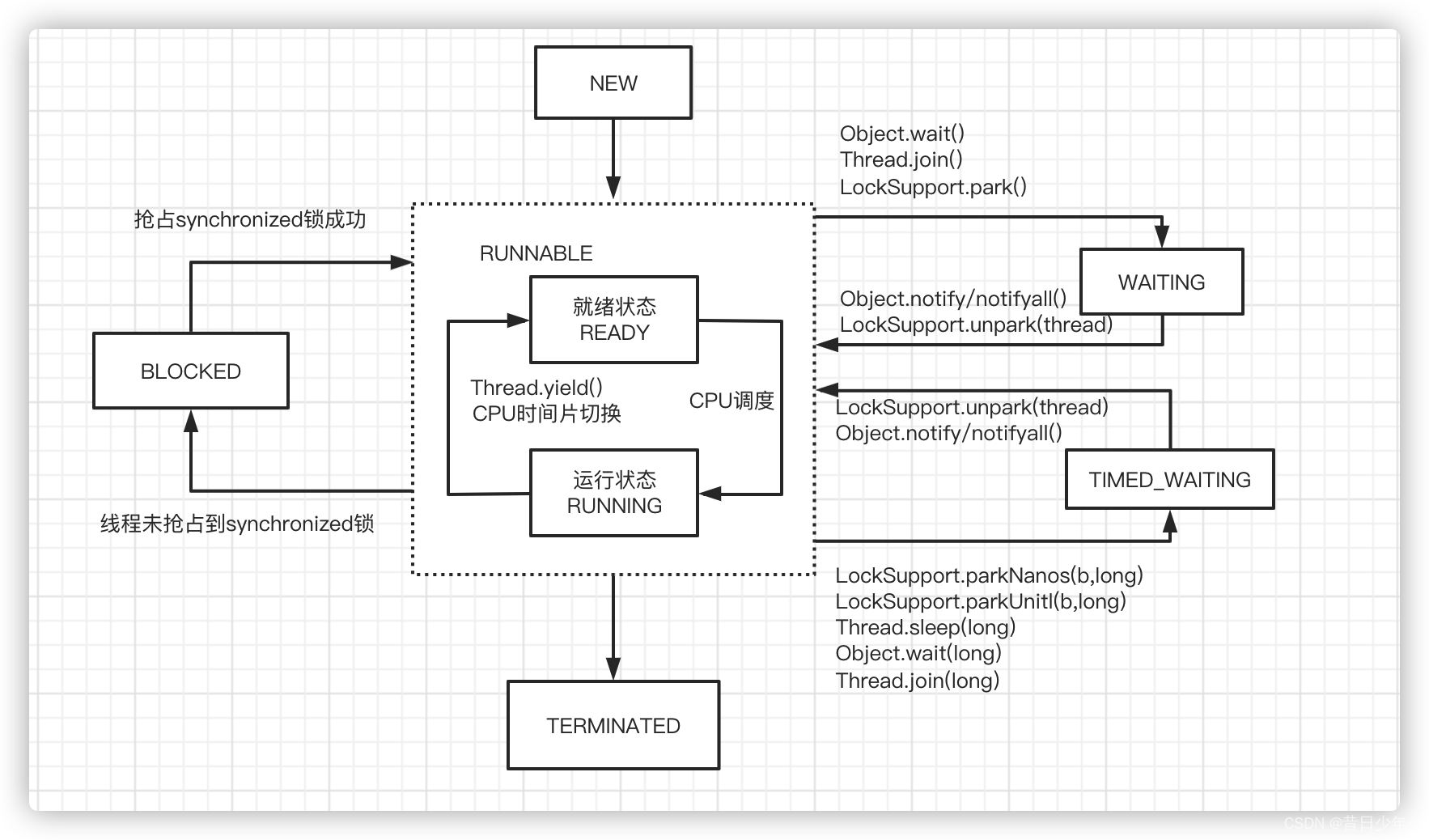
1.NEW-----新建状态--------new Thread()时的状态
2.RUNNABLE------运行状态---------start()方法启动线程后的状态
3.BLOCKED------阻塞状态-------执行synchronized代码并且未抢占到同步锁时的状态
4.WAITING-----等待状态------调用Object.wait()等方法的状态
5.TIMED_WAITING-----超时等待状态------调用sleep(timeout)时的状态,超时后会自动唤醒
6.TERMINATED----终止状态-----run()方法的指令执行完成后的状态

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








