# encoding:utf-8
import cv2
from PyQt5.QtGui import QPixmap, QImage
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image,ImageDraw,ImageFont
import csv
import os
# fontC = ImageFont.truetype("Font/platech.ttf", 20, 0)
# 绘图展示
def cv_show(name,img):
cv2.imshow(name, img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
def drawRectBox(image, rect, addText, fontC, color):
"""
绘制矩形框与结果
:param image: 原始图像
:param rect: 矩形框坐标, int类型
:param addText: 类别名称
:param fontC: 字体
:return:
"""
# 绘制位置方框
cv2.rectangle(image, (rect[0], rect[1]),
(rect[2], rect[3]),
color, 2)
# 绘制字体背景框
cv2.rectangle(image, (rect[0] - 1, rect[1] - 25), (rect[0] + 60, rect[1]), color, -1, cv2.LINE_AA)
# 图片 添加的文字 位置 字体 字体大小 字体颜色 字体粗细
# cv2.putText(image, addText, (int(rect[0])+2, int(rect[1])-3), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.8, (255, 255, 255), 2)
img = Image.fromarray(image)
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
draw.text((rect[0]+2, rect[1]-27), addText, (255, 255, 255), font=fontC)
imagex = np.array(img)
return imagex
def img_cvread(path):
# 读取含中文名的图片文件
# img = cv2.imread(path)
img = cv2.imdecode(np.fromfile(path, dtype=np.uint8), cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
return img
def draw_boxes(img, boxes):
for each in boxes:
x1 = each[0]
y1 = each[1]
x2 = each[2]
y2 = each[3]
cv2.rectangle(img, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 255, 0), 2)
return img
def cvimg_to_qpiximg(cvimg):
height, width, depth = cvimg.shape
cvimg = cv2.cvtColor(cvimg, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
qimg = QImage(cvimg.data, width, height, width * depth, QImage.Format_RGB888)
qpix_img = QPixmap(qimg)
return qpix_img
def save_video():
# VideoCapture方法是cv2库提供的读取视频方法
cap = cv2.VideoCapture('C:\\Users\\xxx\\Desktop\\sweet.mp4')
# 设置需要保存视频的格式“xvid”
# 该参数是MPEG-4编码类型,文件名后缀为.avi
fourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'XVID')
# 设置视频帧频
fps = cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)
# 设置视频大小
size = (int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH)), int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT)))
# VideoWriter方法是cv2库提供的保存视频方法
# 按照设置的格式来out输出
out = cv2.VideoWriter('C:\\Users\\xxx\\Desktop\\out.avi', fourcc, fps, size)
# 确定视频打开并循环读取
while (cap.isOpened()):
# 逐帧读取,ret返回布尔值
# 参数ret为True 或者False,代表有没有读取到图片
# frame表示截取到一帧的图片
ret, frame = cap.read()
if ret == True:
# 垂直翻转矩阵
frame = cv2.flip(frame, 0)
out.write(frame)
cv2.imshow('frame', frame)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
else:
break
# 释放资源
cap.release()
out.release()
# 关闭窗口
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
# 封装函数:图片上显示中文
def cv2AddChineseText(img, text, position, textColor=(0, 255, 0), textSize=50):
if (isinstance(img, np.ndarray)): # 判断是否OpenCV图片类型
img = Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
# 创建一个可以在给定图像上绘图的对象
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
# 字体的格式
fontStyle = ImageFont.truetype(
"simsun.ttc", textSize, encoding="utf-8")
# 绘制文本
draw.text(position, text, textColor, font=fontStyle)
# 转换回OpenCV格式
return cv2.cvtColor(np.asarray(img), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
def insert_rows(path, lines ,header):
"""
将n行数据写入csv文件
:param path:
:param lines:
:return:
"""
no_header = False
if not os.path.exists(path):
no_header = True
start_num = 1
else:
start_num = len(open(path).readlines())
csv_head = header
with open(path, 'a', newline='') as f:
csv_write = csv.writer(f)
if no_header:
csv_write.writerow(csv_head) # 写入表头
for each_list in lines:
# 添加序号
each_list = [start_num] + each_list
csv_write.writerow(each_list)
# 序号 + 1
start_num += 1
class Colors:
# 用于绘制不同颜色
def __init__(self):
"""Initialize colors as hex = matplotlib.colors.TABLEAU_COLORS.values()."""
hexs = ('FF3838', 'FF9D97', 'FF701F', 'FFB21D', 'CFD231', '48F90A', '92CC17', '3DDB86', '1A9334', '00D4BB',
'2C99A8', '00C2FF', '344593', '6473FF', '0018EC', '8438FF', '520085', 'CB38FF', 'FF95C8', 'FF37C7')
self.palette = [self.hex2rgb(f'#{c}') for c in hexs]
self.n = len(self.palette)
self.pose_palette = np.array([[255, 128, 0], [255, 153, 51], [255, 178, 102], [230, 230, 0], [255, 153, 255],
[153, 204, 255], [255, 102, 255], [255, 51, 255], [102, 178, 255], [51, 153, 255],
[255, 153, 153], [255, 102, 102], [255, 51, 51], [153, 255, 153], [102, 255, 102],
[51, 255, 51], [0, 255, 0], [0, 0, 255], [255, 0, 0], [255, 255, 255]],
dtype=np.uint8)
def __call__(self, i, bgr=False):
"""Converts hex color codes to rgb values."""
c = self.palette[int(i) % self.n]
return (c[2], c[1], c[0]) if bgr else c
@staticmethod
def hex2rgb(h): # rgb order (PIL)
return tuple(int(h[1 + i:1 + i + 2], 16) for i in (0, 2, 4))
def yolo_to_location(w,h,yolo_data):
# yolo文件转两点坐标,注意画图坐标要转换成int格式
x_, y_, w_, h_ = yolo_data
x1 = int(w * x_ - 0.5 * w * w_)
x2 = int(w * x_ + 0.5 * w * w_)
y1 = int(h * y_ - 0.5 * h * h_)
y2 = int(h * y_ + 0.5 * h * h_)
# cv2.rectangle(img, (int(x1), int(y1)), (int(x2), int(y2)), (255, 0, 0))
return [x1,y1,x2,y2]
def location_to_yolo(w, h, locations):
# x1,y1左上角坐标,x2,y2右上角坐标
x1, y1, x2, y2 = locations
x_ = (x1 + x2) / 2 / w
x_ = float('%.5f' % x_)
y_ = (y1 + y2) / 2 / h
y_ = float('%.5f' % y_)
w_ = (x2 - x1) / w
w_ = float('%.5f' % w_)
h_ = (y2 - y1) / h
h_ = float('%.5f' % h_)
return [x_,y_,w_,h_]
def draw_yolo_data(img_path, yolo_file_path):
# 读取yolo标注数据并显示
img = cv2.imread(img_path)
h, w, _ = img.shape
print(img.shape)
# yolo标注数据文件名为786_rgb_0616.txt
with open(yolo_file_path, 'r') as f:
data = f.readlines()
for each in data:
temp = each.split()
# ['1', '0.43906', '0.52083', '0.34687', '0.15']
# YOLO转换为两点坐标x1, x2, y1, y2
x_, y_, w_, h_ = eval(temp[1]), eval(temp[2]), eval(temp[3]), eval(temp[4])
x1, y1, x2, y2 = yolo_to_location(w,h,[x_, y_, w_, h_])
# 画图验证框是否正确
cv2.rectangle(img, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 0, 255))
cv2.imshow('windows', img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
if __name__ == '__main__':
img_path = 'TestFiles/1.jpg'
yolo_file_path = 'save_data/yolo_labels/1.txt'
draw_yolo_data(img_path, yolo_file_path)
详细解释这段代码
最新发布
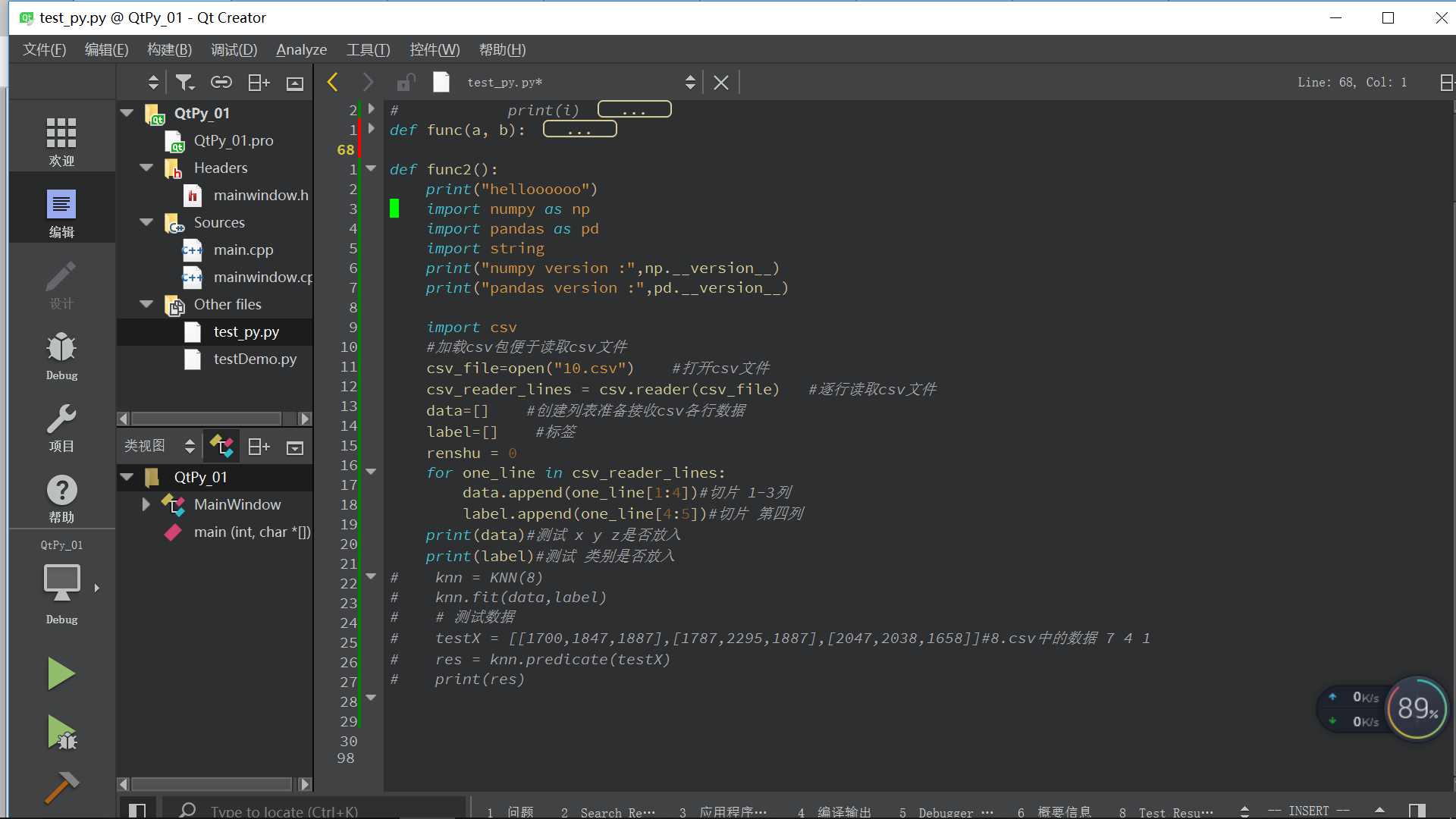
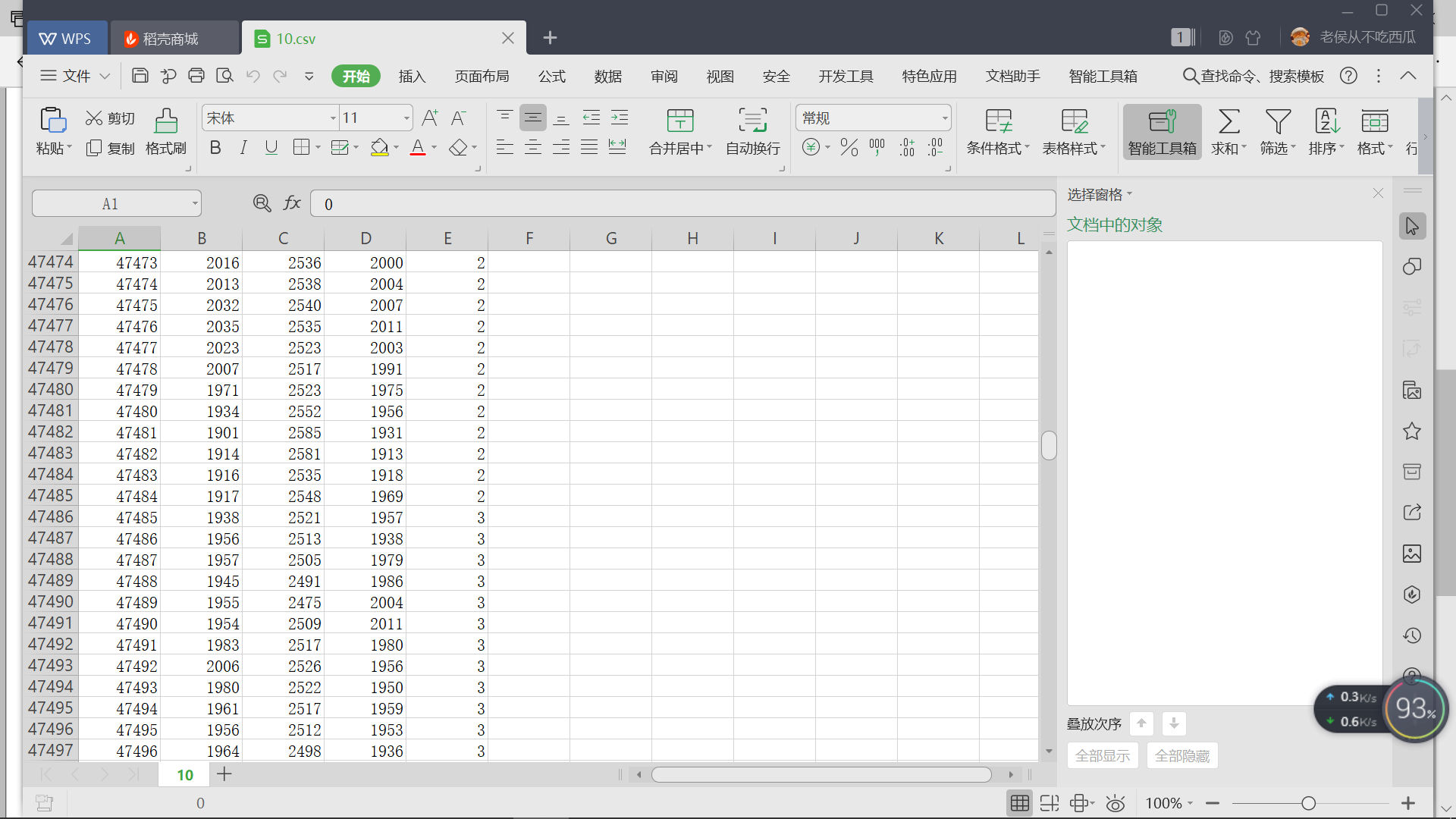
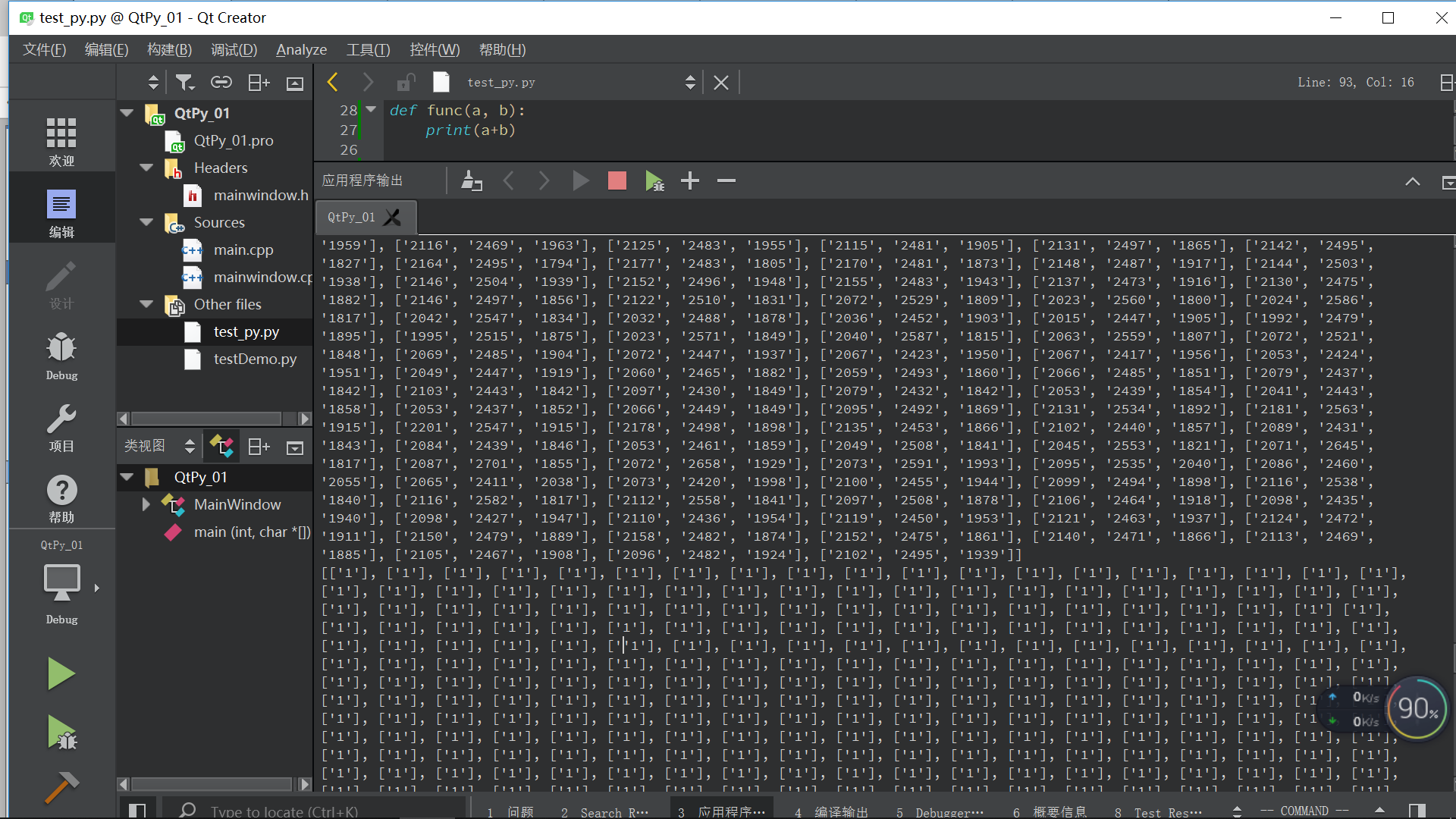




 本文介绍如何在Qt中调用Python读取CSV文件,用于K近邻算法的预处理。作者避免使用pandas,提供了一种读取和切片CSV数据的方法,为后续的K近邻算法做准备。博客内容包括相关配置、遇到的问题以及读取和处理CSV数据的代码示例。
本文介绍如何在Qt中调用Python读取CSV文件,用于K近邻算法的预处理。作者避免使用pandas,提供了一种读取和切片CSV数据的方法,为后续的K近邻算法做准备。博客内容包括相关配置、遇到的问题以及读取和处理CSV数据的代码示例。
















 1295
1295

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








