原型模式
原型模式是一种创建型设计模式,Prototype模式允许一个对象再创建另外一个可定制的对象,根本无需知道任何如何创建的细节,工作原理是:通过将一个原型对象传给那个要发动创建的对象,这个要发动创建的对象通过请求原型对象拷贝它们自己来实施创建。
浅拷贝
应用场景:项目中经常用到的地方,例如PO转VO
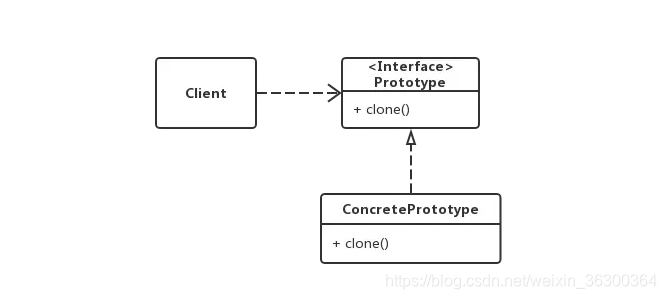
角色:
- Client:使用者
- Prototype:接口(抽象类),声明具备clone能力,例如java中得Cloneable接口
- ConcretePrototype:具体的原型类
代码实现:
public interface Prototype {
Object clone();
}
import java.util.List;
public class ConcretePrototype implements Prototype {
private String name;
private int age;
private List<String> hobbies;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "ConcretePrototype{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", hobbies=" + hobbies +
'}';
}
public ConcretePrototype() {
}
public ConcretePrototype(String name, int age, List<String> hobbies) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.hobbies = hobbies;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public List<String> getHobbies() {
return hobbies;
}
public void setHobbies(List<String> hobbies) {
this.hobbies = hobbies;
}
@Override
public Object clone() {
return new ConcretePrototype(this.name, this.age, this.hobbies);
}
}
public class Client {
private Prototype prototype;
public Client(Prototype prototype) {
this.prototype = prototype;
}
public Prototype startClone() {
return (Prototype)prototype.clone();
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConcretePrototype concretePrototype =new ConcretePrototype();
concretePrototype.setAge(11);
concretePrototype.setName("哈哈哈");
concretePrototype.setHobbies(Arrays.asList(new String[]{"sport", "drink"}));
System.out.println(concretePrototype);
ConcretePrototype clone = (ConcretePrototype)concretePrototype.clone();
System.out.println(clone);
System.out.println(concretePrototype.getName() == clone.getName());
System.out.println(concretePrototype.getHobbies() == clone.getHobbies());
}
}
输出结果:
ConcretePrototype{name='哈哈哈', age=11, hobbies=[sport, drink]}
ConcretePrototype{name='哈哈哈', age=11, hobbies=[sport, drink]}
true
true
通过这个结果我们可以看出,hobbies拷贝后他们的引用地址是相同的,也就是并没用再堆中重新分配空间,创建对象,这种拷贝也称为浅拷贝。
深拷贝
把上面的代码修改一下,创建一个ConcretePrototype1
public class ConcretePrototype1 implements Prototype,Serializable {
private String name;
private int age;
private List<String> hobbies;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "ConcretePrototype{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", hobbies=" + hobbies +
'}';
}
public ConcretePrototype1() {
}
public ConcretePrototype1(String name, int age, List<String> hobbies) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.hobbies = hobbies;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public List<String> getHobbies() {
return hobbies;
}
public void setHobbies(List<String> hobbies) {
this.hobbies = hobbies;
}
@Override
public Object clone() {
return deepClone();
}
private Object deepClone() {
try {
ByteArrayOutputStream outputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(outputStream);
oos.writeObject(this);
oos.close();
oos.flush();
ByteArrayInputStream inputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(outputStream.toByteArray());
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(inputStream);
Object object = objectInputStream.readObject();
return object;
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConcretePrototype1 concretePrototype =new ConcretePrototype1();
concretePrototype.setAge(11);
concretePrototype.setName("哈哈哈");
concretePrototype.setHobbies(Arrays.asList(new String[]{"sport", "drink"}));
System.out.println(concretePrototype);
ConcretePrototype1 clone = (ConcretePrototype1)concretePrototype.clone();
System.out.println(clone);
System.out.println(concretePrototype.getName() == clone.getName());
System.out.println(concretePrototype.getHobbies() == clone.getHobbies());
}
}
打印结果
ConcretePrototype{name='哈哈哈', age=11, hobbies=[sport, drink]}
ConcretePrototype{name='哈哈哈', age=11, hobbies=[sport, drink]}
false
false
克隆破坏单例模式
如果我们克隆的对象是单例对象,那么,深克隆会破坏单例模式。解决方案有两种,要么禁止克隆,要么重写clone方法,返回单例对象。





















 884
884

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








