相似度度量(Similarity),即計算個體間的相似程度,相似度度量的值越小,說明個體間相似度越小,相似度的值越大說明個體差異越大。
對於多個不同的文本或者短文本對話消息要來計算他們之間的相似度如何,一個好的做法就是將這些文本中詞語,映射到向量空間,形成文本中文字和向量數據的映射關系,通過計算幾個或者多個不同的向量的差異的大小,來計算文本的相似度。下面介紹一個詳細成熟的向量空間余弦相似度方法計算相似度
向量空間余弦相似度(Cosine Similarity)
余弦相似度用向量空間中兩個向量夾角的余弦值作為衡量兩個個體間差異的大小。余弦值越接近1,就表明夾角越接近0度,也就是兩個向量越相似,這就叫"余弦相似性"。
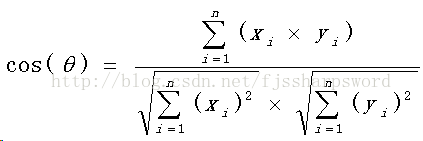
思路上就是:將文本中的詞匯映射到向量空間,來計算兩個向量的夾角余弦值,作為兩個文本相似度的判斷。
代碼參考如下:
package com.test;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
public class Cosine {
public static double getSimilarity(String doc1, String doc2) {
if (doc1 != null && doc1.trim().length() > 0 && doc2 != null&& doc2.trim().length() > 0) {
Map AlgorithmMap = new HashMap();
//將兩個字符串中的中文字符以及出現的總數封裝到,AlgorithmMap中
for (int i = 0; i < doc1.length(); i++) {
char d1 = doc1.charAt(i);
if(isHanZi(d1)){//標點和數字不處理
int charIndex = getGB2312Id(d1);//保存字符對應的GB2312編碼
if(charIndex != -1){
int[] fq = AlgorithmMap.get(charIndex);
if(fq != null && fq.length == 2){
fq[0]++;//已有該字符,加1
}else {
fq = new int[2];
fq[0] = 1;
fq[1] = 0;
AlgorithmMap.put(charIndex, fq);//新增字符入map
}
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < doc2.length(); i++) {
char d2 = doc2.charAt(i);
if(isHanZi(d2)){
int charIndex = getGB2312Id(d2);
if(charIndex != -1){
int[] fq = AlgorithmMap.get(charIndex);
if(fq != null && fq.length == 2){
fq[1]++;
}else {
fq = new int[2];
fq[0] = 0;
fq[1] = 1;
AlgorithmMap.put(charIndex, fq);
}
}
}
}
Iterator iterator = AlgorithmMap.keySet().iterator();
double sqdoc1 = 0;
double sqdoc2 = 0;
double denominator = 0;
while(iterator.hasNext()){
int[] c = AlgorithmMap.get(iterator.next());
denominator += c[0]*c[1];
sqdoc1 += c[0]*c[0];
sqdoc2 += c[1]*c[1];
}
return denominator / Math.sqrt(sqdoc1*sqdoc2);//余弦計算
} else {
throw new NullPointerException(" the Document is null or have not cahrs!!");
}
}
public static boolean isHanZi(char ch) {
// 判斷是否漢字
return (ch >= 0x4E00 && ch <= 0x9FA5);
/*if (ch >= 0x4E00 && ch <= 0x9FA5) {//漢字
return true;
}else{
String str = "" + ch;
boolean isNum = str.matches("[0-9]+");
return isNum;
}*/
/*if(Character.isLetterOrDigit(ch)){
String str = "" + ch;
if (str.matches("[0-9a-zA-Z\\u4e00-\\u9fa5]+")){//非亂碼
return true;
}else return false;
}else return false;*/
}
/**
* 根據輸入的Unicode字符,獲取它的GB2312編碼或者ascii編碼,
*
* @param ch 輸入的GB2312中文字符或者ASCII字符(128個)
* @return ch在GB2312中的位置,-1表示該字符不認識
*/
public static short getGB2312Id(char ch) {
try {
byte[] buffer = Character.toString(ch).getBytes("GB2312");
if (buffer.length != 2) {
// 正常情況下buffer應該是兩個字節,否則說明ch不屬於GB2312編碼,故返回'?',此時說明不認識該字符
return -1;
}
int b0 = (int) (buffer[0] & 0x0FF) - 161; // 編碼從A1開始,因此減去0xA1=161
int b1 = (int) (buffer[1] & 0x0FF) - 161;
return (short) (b0 * 94 + b1);// 第一個字符和最后一個字符沒有漢字,因此每個區只收16*6-2=94個漢字
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return -1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1="余弦定理算法:doc1 與 doc2 相似度為:0.9954971, 耗時:22mm";
String str2="余弦定理算法:doc1 和doc2 相似度為:0.99425095, 用時:33mm";
long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
double Similarity=Cosine.getSimilarity(str1, str2);
System.out.println("用時:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-start));
System.out.println(Similarity);
}
}
執行結果:
用時:16
0.8461538461538461







 本文介绍了一种通过计算向量空间中两个向量夹角的余弦值来判断文本相似度的方法——余弦相似度。该方法将文本词汇映射为向量,并通过计算向量之间的夹角余弦值来量化文本间的相似程度。
本文介绍了一种通过计算向量空间中两个向量夹角的余弦值来判断文本相似度的方法——余弦相似度。该方法将文本词汇映射为向量,并通过计算向量之间的夹角余弦值来量化文本间的相似程度。
















 352
352

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








