An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, the heights of the two child subtrees of any node differ by at most one; if at any time they differ by more than one, rebalancing is done to restore this property. Figures 1-4 illustrate the rotation rules.
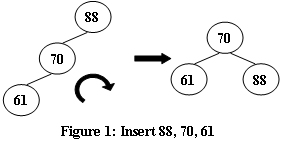
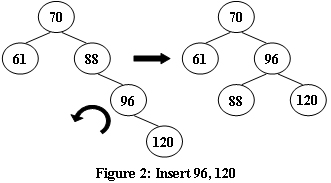


Now given a sequence of insertions, you are supposed to tell the root of the resulting AVL tree.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤20) which is the total number of keys to be inserted. Then N distinct integer keys are given in the next line. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the root of the resulting AVL tree in one line.
Sample Input 1:
5
88 70 61 96 120
Sample Output 1:
70
Sample Input 2:
7
88 70 61 96 120 90 65
Sample Output 2:
88
题意:
给出N个正整数,将他们依次插入一颗初始为空的AVL树上,求插入后根结点的值
思路:
对于AVL树的操作,非常麻烦而且复杂,有标准步骤
但本题只是输出中位数,也可得到许多分数,如下为中位数代码
得分:17(有两个case不能通过)
方法一:建平衡二叉树
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int v, height;
node *lchild, *rchild;
}*root;
node* newnode(int v) {
node* Node = new node;
Node->v = v;
Node->height = 1;
Node->lchild = Node->rchild = NULL;
return Node;
}
int getHeight(node* root) {
if(root == NULL) {
return 0;
}
return root->height;
}
void updatahegiht(node* root) {
root->height = max(getHeight(root->lchild), getHeight(root->rchild)) + 1;
}
int getbalancefac(node* root) {
return getHeight(root->lchild) - getHeight(root->rchild);
}
//左旋
void L(node* &root) {
node* temp = root->rchild;
root->rchild = temp->lchild;
temp->lchild = root;
updatahegiht(root);
updatahegiht(temp);
root = temp;
}
//右旋
void R(node* &root) {
node* temp = root->lchild;
root->lchild = temp->rchild;
temp->rchild = root;
updatahegiht(root);
updatahegiht(temp);
root = temp;
}
void insert(node* &root, int v) {
if(root == NULL) {
root = newnode(v);
return ;
}
if(v < root->v) {
insert(root->lchild, v);
updatahegiht(root);
if(getbalancefac(root) == 2) {
if(getbalancefac(root->lchild) == 1) { //LL
R(root);
} else if(getbalancefac(root->lchild) == -1) { //LR
L(root->lchild);
R(root);
}
}
} else {
insert(root->rchild, v);
updatahegiht(root);
if(getbalancefac(root) == -2) {
if(getbalancefac(root->rchild) == -1) { //RR
L(root);
} else if(getbalancefac(root->rchild) == 1) { //RL
R(root->rchild);
L(root);
}
}
}
}
int main() {
int n, v;
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &v);
insert(root, v);
}
printf("%d\n", root->v);
return 0;
}
方法二:中位数
得分:17(有两个case不能通过)
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 25;
int num[maxn];
int main(){
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
scanf("%d", &num[i]);
}
sort(num, num + n);
printf("%d", num[n / 2]);
return 0;
}










 本文介绍AVL树的构建过程及其自平衡特性。通过两个方法实现:一是构建平衡二叉树,详细展示了节点插入及旋转操作;二是直接求解中位数,适用于快速获取AVL树根节点值。
本文介绍AVL树的构建过程及其自平衡特性。通过两个方法实现:一是构建平衡二叉树,详细展示了节点插入及旋转操作;二是直接求解中位数,适用于快速获取AVL树根节点值。
















 3983
3983

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








