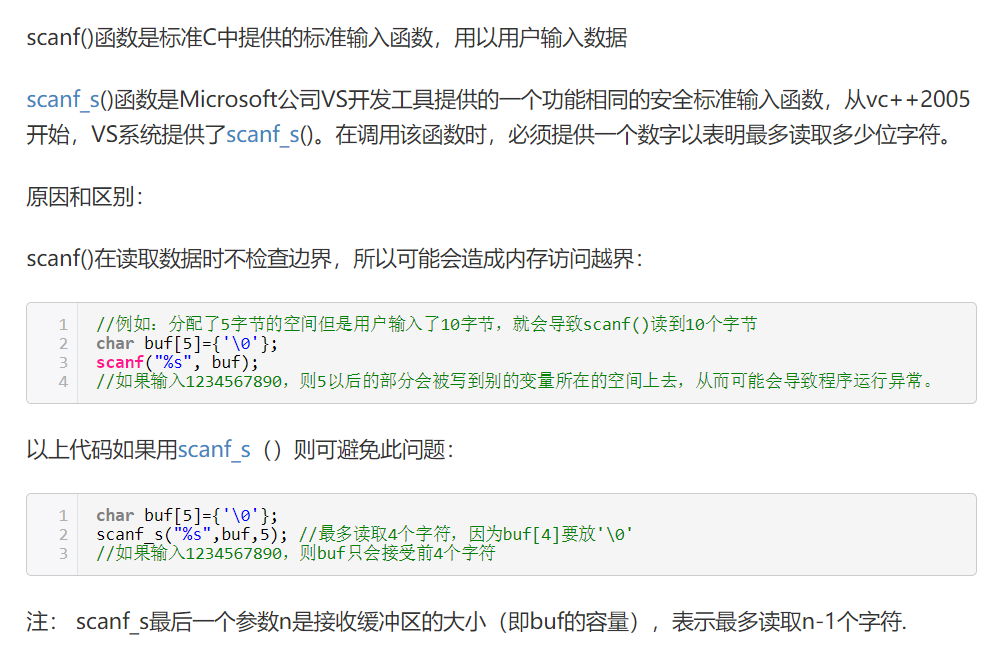
PS: 很多带“_s”后缀的函数是为了让原版函数更安全,传入一个和参数有关的大小值,避免引用到不存在的元素,防止hacker利用原版的不安全性(漏洞)黑掉系统。
 本文介绍了一种通过使用带有_s后缀的安全函数来提高软件安全性的方法,这些函数通过增加额外参数来验证内存操作的有效性,从而避免潜在的安全漏洞。
本文介绍了一种通过使用带有_s后缀的安全函数来提高软件安全性的方法,这些函数通过增加额外参数来验证内存操作的有效性,从而避免潜在的安全漏洞。

PS: 很多带“_s”后缀的函数是为了让原版函数更安全,传入一个和参数有关的大小值,避免引用到不存在的元素,防止hacker利用原版的不安全性(漏洞)黑掉系统。
转载于:https://www.cnblogs.com/Marigolci/p/9447651.html

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?


