1114. Boxes
Time Limit: 0.6 second
Memory Limit: 16 MB
Input
Output
Sample
| input | output |
|---|---|
| 2 1 1 | 9 |
解答如下(C#语言):
2
3 namespace Skyiv.Ben.Timus
4 {
5 // http://acm.timus.ru/problem.aspx?space=1 &num=1114
6 sealed class T1114
7 {
8 static void Main()
9 {
10 string [] ss = Console.ReadLine().Split();
11 ulong n = ushort .Parse(ss[ 0 ]);
12 ulong a = ushort .Parse(ss[ 1 ]);
13 ulong b = ushort .Parse(ss[ 2 ]);
14 Console.WriteLine(F(n, a) * F(n, b));
15 }
16
17 static ulong F( ulong n, ulong m)
18 {
19 ulong v = 1 ;
20 for ( ulong i = 1 ; i <= n; i ++ ) v = v * (m + i) / i;
21 return v;
22 }
23 }
24 }
这道题就是一个组合数学问题。题目说,你有 N (1 ≤ N ≤ 20) 个盒子,A (0 ≤ A ≤ 15) 个红色的球和 B (0 ≤ B ≤ 15) 个蓝色的球。这些球可以放到盒子里面,也可以不放到盒子里面,一个盒子可以放任意多个球。问总共有多少种不同情形。
由于球可以放到盒子里面,也可以不放到盒子里面,所以红球和盒子总共有 C( N + A, A ) 种不同的情形。同样,蓝球和盒子总共有 C( N + B, B ) 种不同的情形。所以,最终的答案就是 C( N + A, A) * C( N + B, B ) 。这里,C( n, m ) 表示从 n 个不同的物品中任意取出 m 个的组合数,公式是 C( n, m ) = n! / (n - m)! / m!。以上程序中的 F( n, m ) = C( n + m, m)。
要注意的是,当输入为 N = 20,A = 15,B = 15 时,输出是 10549134770590785600,这个数已经大于 263 - 1,所以要使用 ulong 数据类型。如果使用 C/C++ 语言,因为 Timus Online Judge 使用的是 Visual C++ 编译器,所以要使用 unsigned __int64 数据类型。如果 在 Sphere Online Judge 答题的话,因为其编译器是 gcc,所以要使用 unsigned long long 数据类型。C++ 语言的程序如下所示(如果是 gcc 编译器则去掉第 2 行开头的“//”):
2 // #define __int64 long long
3
4 unsigned __int64 f(unsigned __int64 n, unsigned __int64 m)
5 {
6 unsigned __int64 v = 1 ;
7 for (unsigned __int64 i = 1 ; i <= n; i ++ ) v = v * (m + i) / i;
8 return v;
9 }
10
11 int main()
12 {
13 unsigned __int64 n, a, b;
14 std::cin >> n >> a >> b;
15 std::cout << f(n, a) * f(n, b) << std::endl;
16 }
本程序的运行时间如下:
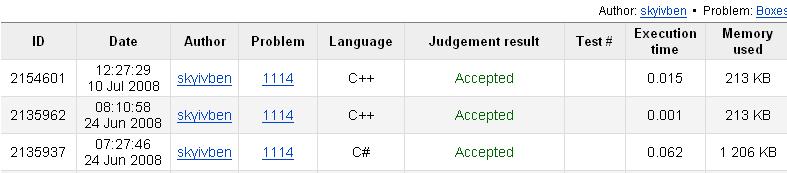
有点奇怪的是,Visual C++ 编译器也可以使用 unsigned long long,但是速度却比使用 unsinged __int64 慢了 15 倍。如上图所示,ID = 2154601 的记录就是使用 unsinged long long,运行时间为 0.015 秒。而 ID = 2135962 的记录使用 unsinged __int64,运行时间为 0.001 秒。不知是什么原因。照理说,__int64 应该和 long long 是一样的。




 解决Timus1114.Boxes问题,计算不同颜色球放入盒子的所有可能组合数。使用组合数学方法,给出C#及C++实现方案。
解决Timus1114.Boxes问题,计算不同颜色球放入盒子的所有可能组合数。使用组合数学方法,给出C#及C++实现方案。

















 109
109

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








