1.头文件algorithm中有函数sort()用于排序,参数为:排序起始地址,排序结束地址,排序规则(返回bool型)
例如,要将array[] = {5,7,1,2,9}升序排列,则使用:
bool cmp(int a,int b);
int main()
{
int array[] = {5,7,1,2,9};
sort(array,array+5,cmp);
for(int i = 0;i < 5;i++)
cout << array[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
bool cmp(int a,int b)
{
if(a>b) return false;
else return true;
}注:1.在C语言中,使用qsort进行排序。
2.如果不指定排序方式,默认为升序。
2.对于有序映射关系,可以用巧妙的办法转化,例如:
ABC对应2,DEF对应3,GHI对应4,JKL对应5,MNO对应6,PRS对应7,TUV对应8,WXY对应9
要把一串字符按照这样的规则映射为数字,可以采用以下方法:
(*(p+i) - 'A' - (*(p+i)>'Q'))/3 + 2其中p为指向字符串的指针,因为每3个字母变化一次映射关系,因此只需要判断当前字符距离字符A的距离,然后除以三判断落在哪一组。需要注意的是字母Q不包含在映射关系当中,因此当字符在Q之后时,应该减去1个字符的距离再进行判断。
3.字典树是一种存放字符串的树形结构,又称为单词查找树,利用的是字符串的公共前缀来减少查询时间。需要注意的是字典树常常用于统计单词出现次数,而不是为了取出单词去存储单词。一般字典树的结构体如下:
struct DirectionTree{
int count;//计数到当前节点为止的单词个数
bool terminal;//记录此节点无子节点
DirectionTree* child[26];//该节点的子节点
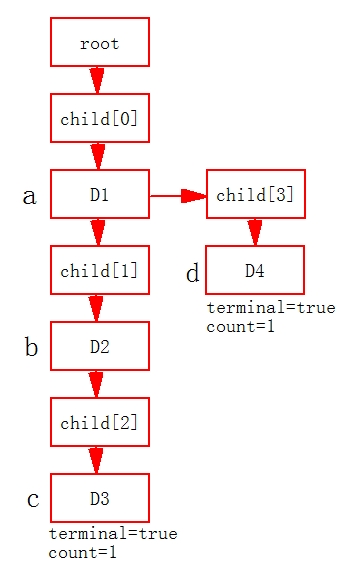
}*root;//字典树的根节点,根节点不包含任何字母字典树的存放方式为根连接子节点,子节点连接新的节点,一直连接到尾部。例如存储字符"abc","ad",则数据结构如下:
其中只有D3和D4两个节点的terminal值为true,count为1,其余的均为false,0。当再次添加同样的字符串时,不会创建新的节点,只会引起count加1。
完整代码如下(转):
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <assert.h>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 26 //the total number of alphabet is 26, a...z
struct Dictree
{
bool word;
int count;
struct Dictree *trie[MAX]; // the 26 child
} * a;
int init() // init the chained list
{
a = new Dictree;
for(int i = 0; i < MAX; i++)
{
a->trie[i] = NULL;
a->word = false;
}
return 0;
}
bool searchTrie(char *str)
{
int len, res;
Dictree *head = a;
assert(head);
len = strlen(str);
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
res = (int)(str[i] - 'a');
if(head->trie[res] == NULL)
return false;
head = head->trie[res];
}
if(head->word)
return true;
return false;
}
int insertTrie(char *str)
{
int len, res;
Dictree *head = a;
len = strlen(str);
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
res = int(str[i] - 'a');
if(head->trie[res] == NULL) //whether the node exist?
{
head->trie[res] = new Dictree;
head = head->trie[res];
head->count = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < MAX; j++)
{
head->trie[j] = NULL;
head->word = false;
}
}
else
head = head->trie[res];
}
head->count++;
head->word = true;
return head->count;
}
int main()
{
char str[20];
init();
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
scanf("%s", str);
printf("%d\n", insertTrie(str));
}
scanf("%s", str);
printf("%s\n", searchTrie(str) ? ("YES"):("NO"));
return 0;
}转载于:https://blog.51cto.com/570842253/1556652







 本文介绍如何使用C++实现字典树(单词查找树),并提供了简单的插入和查找操作示例。此外,还展示了如何将字符转换为特定的数字映射关系,以及如何使用字典树来统计不同映射关系下的字符数量。
本文介绍如何使用C++实现字典树(单词查找树),并提供了简单的插入和查找操作示例。此外,还展示了如何将字符转换为特定的数字映射关系,以及如何使用字典树来统计不同映射关系下的字符数量。
















 664
664

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








