Channel(通道)是专用于IO请求的独立处理器。用于在数据源与目标节点之间建立连接。负责缓冲区中数据的传输。
Java NIO的通道类似流,但又有些不同:
既可以从通道中读取数据,又可以写数据到通道。但流的读写通常是单向的。
通道可以异步地读写。
通道中的数据总是要先读到一个Buffer,或者总是要从一个Buffer中写入。
Channel可以看做是铁路,Buffer可以看作是列车,而Data数据可以看做是旅客。
1、Channel的实现
以下是Java NIO中最重要的通道的实现:
FileChannel:用于从文件中读写数据
DatagramChannel:能通过UDP读写网络中的数据
SocketChannel:能通过TCP读写网络中的数据(客户端)
ServerSocketChannel:可以监听新进来的TCP连接(服务端,像Web服务器那样)对每一个新进来的连接都会创建一个SocketChannel
2、Channel UML图
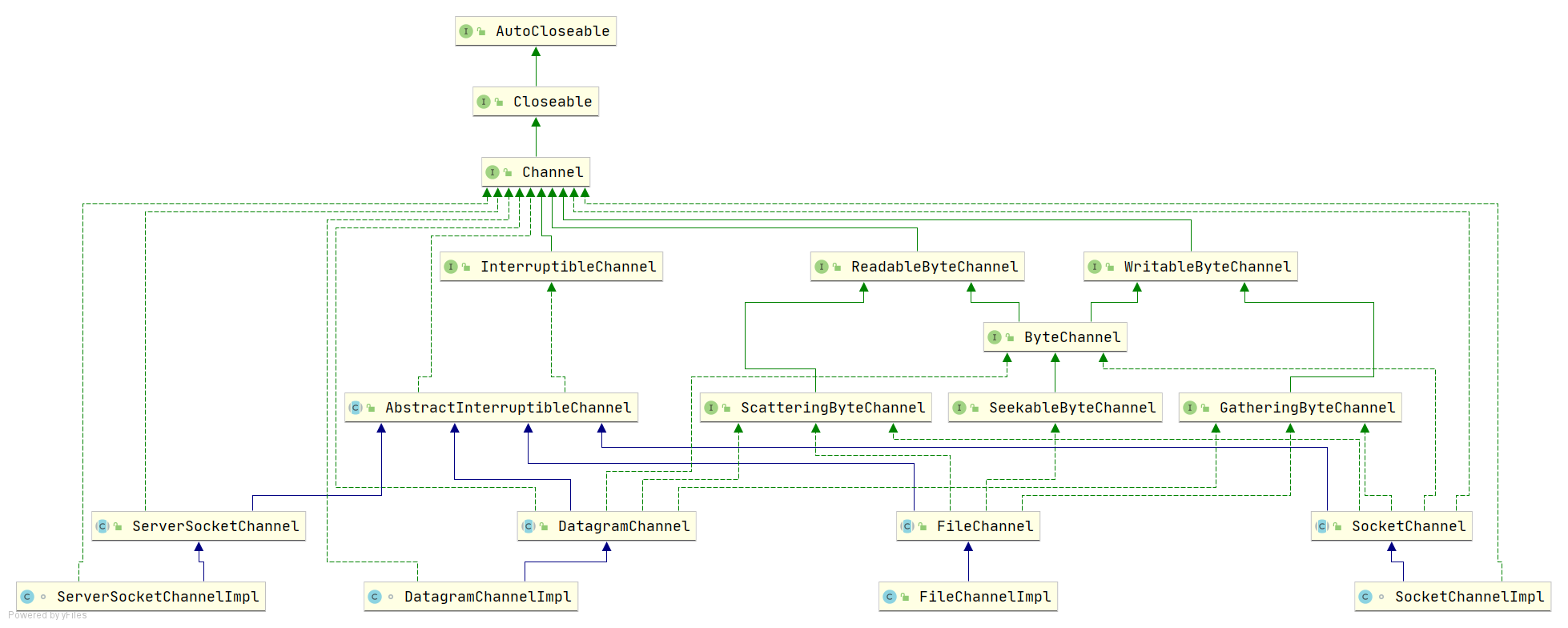
3、Channel使用示例(FileChannel)
3.1、JDK1.7之前
3.1.1、RandomAccessFile
FileChannel readChannel = null;
FileChannel writeChannel = null;
try {
RandomAccessFile sourceFile = new RandomAccessFile("demo.txt", "rw");//指定源文件及操作方式
RandomAccessFile dstFile = new RandomAccessFile("demo2.txt", "rw");//指定目标文件及操作方式
//获取读写通道
readChannel = sourceFile.getChannel();
writeChannel = dstFile.getChannel();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
while (-1 != readChannel.read(byteBuffer)) {
byteBuffer.flip();
writeChannel.write(byteBuffer);
byteBuffer.clear();
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
readChannel.close();
writeChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
3.1.2、FileInputStream/FileOutputStream
FileInputStream fips = null;
FileOutputStream fops = null;
FileChannel fipsChannel = null;
FileChannel fopsChannel = null;
try {
fips = new FileInputStream(new File("demo.txt"));
fops = new FileOutputStream(new File("demo2.txt"));
fipsChannel = fips.getChannel();
fopsChannel = fops.getChannel();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
while (-1 != fipsChannel.read(byteBuffer)) {
byteBuffer.flip();
fopsChannel.write(byteBuffer);
byteBuffer.clear();
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fips.close();
fops.flush();
fops.close();
fipsChannel.close();
fopsChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
3.2、JDK1.7开始
通过FileChannel的public static FileChannel open(Path path, OpenOption... options) 静态方法
try {
//获取读写通道 StandardOpenOption.CREATE表示——不存在则创建,存在则覆盖
FileChannel inChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("demo.txt"), StandardOpenOption.READ);
FileChannel outChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("demo2.txt"), StandardOpenOption.WRITE,StandardOpenOption.READ,StandardOpenOption.CREATE);
//使用内存映射文件方式读写数据(只有ByteBuffer支持)
MappedByteBuffer inBuffer = inChannel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_ONLY, 0, inChannel.size());
MappedByteBuffer outBuffer = outChannel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, inChannel.size());
//读写数据
byte[] dst = new byte[inBuffer.limit()];
inBuffer.get(dst);
outBuffer.put(dst);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
4、Channel通信
采用的是直接缓冲区的方式实现
public abstract long transferFrom(ReadableByteChannel src, long position, long count)
public abstract long transferTo(long position, long count, WritableByteChannel target)
try {
FileChannel inChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("demo.txt"), StandardOpenOption.READ);
FileChannel outChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("demo4.txt"), StandardOpenOption.WRITE,StandardOpenOption.READ,StandardOpenOption.CREATE);
//inChannel.transferTo(0, inChannel.size(), outChannel);
outChannel.transferFrom(inChannel,0,inChannel.size());
inChannel.close();
outChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}




















 591
591

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








