二叉树(Binary Tree)是将数据按一定的分支关系组织起来的结构,保存数据的基本节点(Node)最多有两个子树,通常子树的根被称之为“左子树”(Left subtree)和“右子树”(Right subtree)。
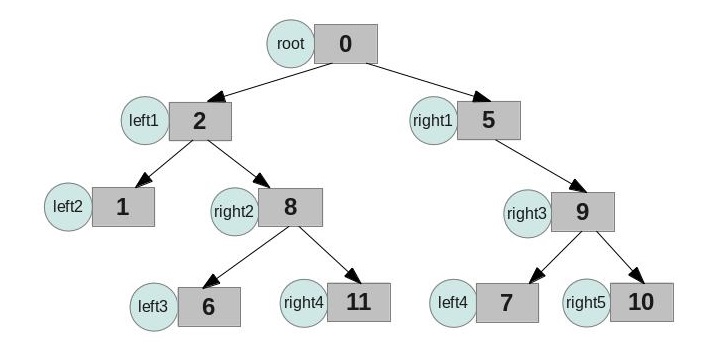
图1 一个简单的二叉树
由二叉树的性质可知,一个节点最基本的三要素为:保存节点的值以及指向左右子树的指针。


1 typedef struct binTree{ 2 int data; 3 struct binTree* left; 4 struct binTree* right; 5 }BinNode, *BinTree;
构造如图1所示的二叉树,如下代码。


1 /* 2 * root 3 * left1 right1 4 * left2 right2 right3 5 * left3 right4 left4 right5 6 */ 7 8 void createBinTree(BinTree& root){ 9 BinTree left1 = new BinNode; 10 BinTree right1 = new BinNode; 11 left1->data = 2; 12 right1->data = 5; 13 root->left = left1; 14 root->right = right1; //Construct the first layer. 15 16 BinTree left2 = new BinNode; 17 BinTree right2 = new BinNode; 18 left2->data = 1; 19 right2->data = 8; 20 left1->left = left2; 21 left1->right = right2; 22 BinTree right3 = new BinNode; 23 right3->data = 9; 24 right1->right = right3; //Construct the second layer 25 26 BinTree left3 = new BinNode; 27 left3->data = 6; 28 right2->left = left3; 29 BinTree right4 = new BinNode; 30 right4->data = 11; 31 right2->right = right4; 32 33 BinTree left4 = new BinNode; 34 left4->data = 7; 35 right3->left = left4; 36 BinTree right5 = new BinNode; 37 right5->data = 10; 38 right3->right = right5; 39 }
完整代码:


1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 typedef struct binTree{ 5 int data; 6 struct binTree* left; 7 struct binTree* right; 8 }BinNode, *BinTree; 9 10 /* 11 * root 12 * left1 right1 13 * left2 right2 right3 14 * left3 right4 left4 right5 15 */ 16 17 void createBinTree(BinTree& root){ 18 BinTree left1 = new BinNode; 19 BinTree right1 = new BinNode; 20 left1->data = 2; 21 right1->data = 5; 22 root->left = left1; 23 root->right = right1; //Construct the first layer. 24 25 BinTree left2 = new BinNode; 26 BinTree right2 = new BinNode; 27 left2->data = 1; 28 right2->data = 8; 29 left1->left = left2; 30 left1->right = right2; 31 BinTree right3 = new BinNode; 32 right3->data = 9; 33 right1->right = right3; //Construct the second layer 34 35 BinTree left3 = new BinNode; 36 left3->data = 6; 37 right2->left = left3; 38 BinTree right4 = new BinNode; 39 right4->data = 11; 40 right2->right = right4; 41 42 BinTree left4 = new BinNode; 43 left4->data = 7; 44 right3->left = left4; 45 BinTree right5 = new BinNode; 46 right5->data = 10; 47 right3->right = right5; 48 } 49 50 int main(void){ 51 BinTree root = new BinNode; 52 root->data = 0; 53 createBinTree(root); 54 return 0; 55 }




 本文详细介绍了如何使用C++语言构建一个简单的二叉树,包括节点定义、构造函数实现及树的构建过程。
本文详细介绍了如何使用C++语言构建一个简单的二叉树,包括节点定义、构造函数实现及树的构建过程。
















 1053
1053

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








