Transmitters
描述
In a wireless network with multiple transmitters sending on the same frequencies, it is often a requirement that signals don't overlap, or at least that they don't conflict. One way of accomplishing this is to restrict a transmitter's coverage area. This problem uses a shielded transmitter that only broadcasts in a semicircle.
A transmitter T is located somewhere on a 1,000 square meter grid. It broadcasts in a semicircular area of radius r. The transmitter may be rotated any amount, but not moved. Given N points anywhere on the grid, compute the maximum number of points that can be simultaneously reached by the transmitter's signal. Figure 1 shows the same data points with two different transmitter rotations. 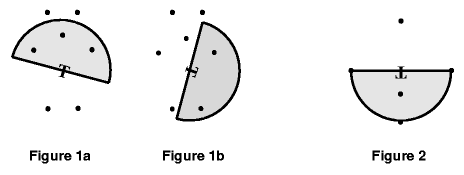
输入
输出
For each transmitter, the output contains a single line with the maximum number of points that can be contained in some semicircle.
样例输入
样例输出
#include<iostream> #include<cmath> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; double n,m,r; struct Node { double x; double y; } p[1003]; int main() { int T; double x,y,temp; while(~scanf("%lf%lf%lf",&n,&m,&r)) { if(r<0) break; scanf("%d",&T); int k=0; for(int i=0; i<T; i++) { scanf("%lf%lf",&x,&y); temp = sqrt((x-n)*(x-n)+(y-m)*(y-m)); if(temp<=r) { p[k].x = x-n; p[k++].y = y-m; } } int ans , Max = 0; for(int i=0; i<k; i++) { ans = 0; for(int j=0; j<k; j++) { if(p[j].x*p[i].y-p[j].y*p[i].x<=0) ans ++; } if(ans>Max) Max = ans; } printf("%d\n",Max); } return 0; }




 本文介绍了一个无线网络中信号覆盖的问题,通过使用一个可以旋转但不能移动的半圆形发射器,来计算其最大能覆盖的点数。文章提供了解决方案,并通过C++代码实现了这一算法。
本文介绍了一个无线网络中信号覆盖的问题,通过使用一个可以旋转但不能移动的半圆形发射器,来计算其最大能覆盖的点数。文章提供了解决方案,并通过C++代码实现了这一算法。
















 302
302

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








