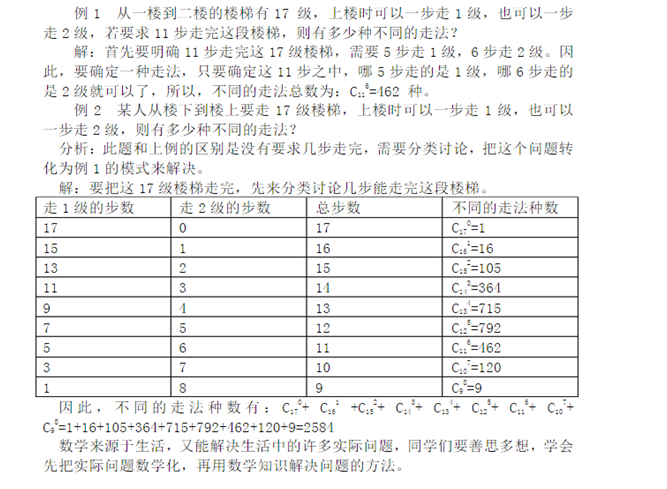
例3:一共有10级,每次可走一步也可以走两步.必须要8步走完10级楼梯. 问:一共有多少种走法?
分析:走一步的需要6次,走两步的需要2次。因此,本题是6个1、2个2的组合问题。在6个一步中,插入2个两步的,因可放在第一个1步之前,也可以放在最后一个1步之后,所以6个1步有7个空.因此,如果两个两步在一起有c(7,1)种;如果两个两步的分开来插有C(7,2)种,因此共有 c(7,1)+c(7,2)=7+21=28(种)=C(8,2)=C(8,6)
总数=8步中选2中走两步的=8步中选6个走一步的
Java编程实现:(数组迭代,动态规划,递归)
package com.test;
public classzoutaijie {
// 梯有N阶,上楼可以一步上一阶,也可以一次上二阶。编一个程序,计算共有多少种不同的走法。如果上20阶会有几种走法
public staticlongresult[]=new long[100];
public staticvoidmain(String[] args) {
result[0]=result[1]=1;
for(inti=2;i<</span>result.length;i++)
result[i]=-1;
//s不能太大,否则int溢出
int s =60;
//动态规划
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("动态规划解决:"+fun1(s));
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("动态规划解决-程序运行时间:"+(endTime-startTime)+"ms");
//数组叠加
long startTime2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("数组叠加实现:"+fun2(s));
long endTime2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("数组叠加实现-程序运行时间:"+(endTime2-startTime2)+"ms");
//递归方法
long startTime1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("递归方法解决:"+fun(s));
long endTime1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("递归方法解决-程序运行时间:"+(endTime1-startTime1)+"ms");
}
public staticlongfun(ints){
if(s==0 || s==1)
return 1;
else{
return fun(s-1)+fun(s-2);
}
}
public staticlongfun1(ints){
if(result[s]>=0) {
return result[s];
}else{
result[s]=(fun1(s-1)+fun1(s-2));
return result[s];
}
}
public staticlongfun2(ints){
long result_1[]=newlong[s+1];//注意这个要大一个,多了个第0个
result_1[0]=result_1[1]=1;
for(inti=2;i<=s;i++)
result_1[i]=result_1[i-1]+result_1[i-2];
return result_1[s];//s就是第s+1个
}
}
分析:
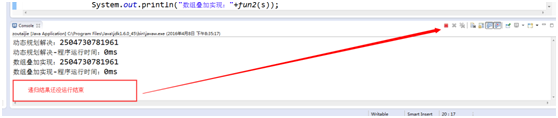
(1) int s=48时候的运行效果:
(2). int s=60时候的运行效果
显然数组叠加和动态规划效率高很多很多,不是一个数量级的!
/**
* 功能:有个小孩正在上楼梯,楼梯有n阶台阶,小孩一次可以上1阶、2阶或3阶。计算小孩上楼梯的方式有多少种。
*/
三种方法:
方法一:
//递归法
/**
* 思路:自上而下的方式。
* 最后一步可能是从第n-1阶往上走1阶、从第n-2阶往上走2阶或从第n-3阶往上走3阶。
* 因此,抵达最后一阶的走法,抵达这最后三阶的方式的综合。
* @param n
* @return
*/
public static int countWays(int n){
if(n<0)
return 0;
else if(n==0)//注意此处条件
return 1;
else{
return countWays(n-1)+countWays(n-2)+countWays(n-3);
}
}
方法二:
//动态规划
/**
* 思路:每次调用都会分支出三次调用。予以动态规划加以修正。
* @param n
* @param map
* @return
*/
public static int countWaysDP(int n,int[] map){
if(n<0)
return 0;
else if(n==0)
return 1;
else if(map[n]>-1)
return map[n];
else{
map[n]=countWaysDP(n-1,map)+countWaysDP(n-2,map)+countWaysDP(n-3, map);
return map[n];
}
}
方法三:
- package com.tian;
- import java.util.TreeMap;
- /**
- * 爬楼梯的算法(有一个人要爬楼梯,楼梯有N个台阶,此人最多可以爬M个台阶
- * 问这个人上楼有多少中上法)
- * @author Administrator
- *
- */
- public class Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(new Test().suanfa(3,1));
- }
- /**
- * 得到所有能相加等于这个数的2个非自然正数
- * @param n
- */
- public void fenjie(final int n){
- for (int i = 1; i <=n; i++) {
- System.out.println(i+","+(n-i));
- }
- }
- /**
- *
- * @param n 总台阶数
- * @param m 最多能走的步数
- * @return 返回能走方法数
- */
- public int suanfa(final int n,final int m){
- switch (n) {
- case 1:
- return 1;
- case 2:
- if(m>=2){
- return 2;
- }
- else{
- return 1;
- }
- }
- int result=0;
- for (int i = 1; i <n; i++) {
- int a=i;
- int b=n-i;
- System.out.println(i+","+(n-i));
- result+=suanfa(a, m)*suanfa(b, m);
- }
- return result;
- }
- }

























 882
882

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








