好久之前面试遇到了一个路径问题, 由于某些原因, 不能直接原题贴出来, 只能描述一下,并提出我的解决思路和方法.
问题:
给一个图AB5, BC4, CD8, DC8, DE6, AD5, CE2, EB3, AE7
找出:
①从C->C, 最多经过3个顶点的所有路径
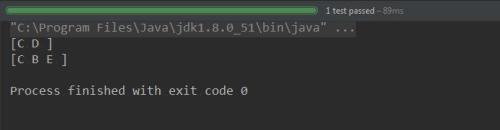
: C->D->C (2 个顶点). C->E->B->C (3 个顶点).
②从A->C, 只经过4个顶点的所有路径
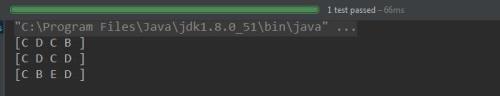
: A ->C (经过 B,C,D); A -> C (经过 D,C,D); and A-> C (经过 D,E,B).
③从C->C, 消耗资源不超过30的所有路径
: CDC, CEBC, CEBCDC, CDCEBC, CDEBC, CEBCEBC, CEBCEBCEBC.
从全局考虑需要创建的类和方法
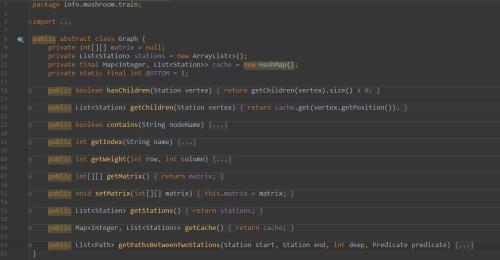
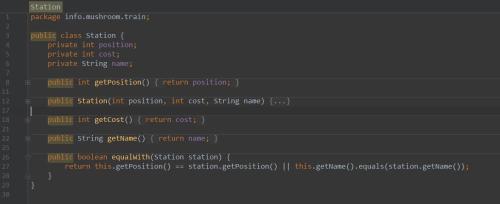
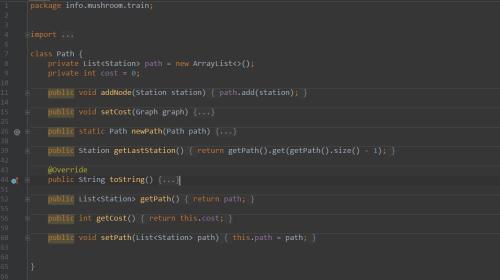
1, 需要创建一个图Graph.java, 顶点Station.java, 路径Path.java作为基本数据类型
1)Graph是图的抽象,包含了对图的必要操作
2)Station是顶点抽象,包含了对图的必要操作
3)Path是路径的抽象,包含了对图的必要操作
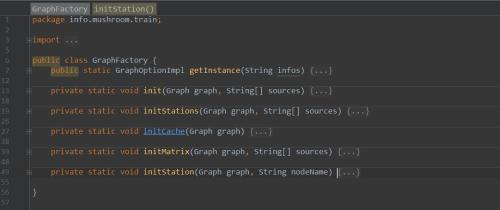
2, 从字符串读取并创建一个图Graph对象,考虑使用工厂模式, 所以创建一个GraphFactory.java
3, 对于图的算法,单独写一个接口GraphOptions.java和实现GraphOptionsImpl.java
思考问题①:
画一个树图分析可知,它从C为根root node, 开始遍历子children nodes, 直到某个child node
为C, 这时创建一个Path, 将当前节点添加到Path中,并且返回给上一层,然后需要添加上一层的节点到Path,
............,最后的Path中其实是倒序排列的节点也就是从end->xx->xx...->Start
递归条件: 从root开始递归子节点, 如果子节点是C,且当前路径经过的顶点不大于3,
返回条件: 当前点是C点或者当前路径顶点大于3
结束条件: 当前路径经过的顶点大于3
递归参数: 当前点current node, 需要递归的子节点 children node, 当前遍历深度,
还需要一个Predicate(它是后期重构使用的)
注意:为了解决①②我重构了代码将共同的部分抽取出来, 不同的部分使用lambda表达式, ①②问题的单元测试中都包含了lambda表达式
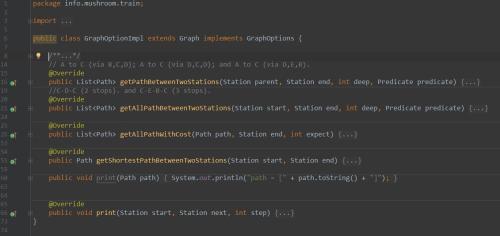
代码:Graph.java
public List<Path> getPathsBetweenTwoStations(Station start, Station end,
int deep, Predicate predicate) {
List<Path> parentPath = new ArrayList<>();
// if the deep reaches the bottom, an empty collection will be returned
if (deep < BOTTOM) {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
if (hasChildren(start)) {
List<Station> children = getChildren(start);
for (Station currentStation : children) {
// print(start, child, step);
// if the current node is equal with the end node and predicate
// is true. So the current is the end for current path.
// Creating a new path. and It will be a child path for the parent
// node;
if (currentStation.equalWith(end) && predicate.predicate(BOTTOM, deep)) {
final Path childPath = new Path();
childPath.addNode(currentStation);
parentPath.add(childPath);
}
// Going on iteration. Then Iterating the return collection. It contains the child paths.
// If the collection is empty , the iterator will not be executed.
// If the collection is not empty , it should have a path at least.
// Then the paths should be merged to the parent path one by one.
// Don't forget add the current node before merge.
getPathsBetweenTwoStations(currentStation, end, deep - 1, predicate).stream().forEach((childPath) -> {
childPath.addNode(currentStation);
parentPath.add(childPath);
});
}
}
return parentPath;
}GraphOptionsImpl.java
//C-D-C (2 stops). and C-E-B-C (3 stops).
@Override
public List<Path> getAllPathBetweenTwoStations(Station start, Station end, int deep) {
// Watching out,: here is a lambda expression. it will be the parameter of
// the {@link GraphOptionImpl#getAllPathBetweenTwoStations}.
// and will be called by the super method {@link Graph#getPathsBetweenTwoStations}
return super.getPathsBetweenTwoStations(start, end, deep, (actual, expect) -> {
return actual <= expect;
});
}单元测试UT:Junit4
// cdc cebc cebcdc cdcebccdebc cebcebc cebcebcebc
// cdcebccdebc cebcebc cebcebcebc
// @Ignore
@Test
public void testGetAllPathWithCost() {
Station station = new Station(2, 0, "C");
Path path = new Path();
path.addNode(station);
GraphOptions context = GraphFactory.getInstance(sources);
List<Path> nodes = context.getAllPathWithCost(path, station, 30);
Assert.assertEquals(7, nodes.size());
for (Path node : nodes) {
System.out.println(node.toString());
}
}
控制台输出
思考问题②:
通过①的分析可知,其实只需要修改一下①的判断条件
if (currentStation.equalWith(end) && predicate.predicate(BOTTOM, deep)) {
final Path childPath = new Path();
childPath.addNode(currentStation);
parentPath.add(childPath);
}就可以了,所以在这里我直接进行了重构,将这些不同的地方拿出来,放在子方法中
代码:GraphOptionsImpl.java
/**
* p [2C 3D 2C 3D 2C]
* p [2C 1B 4E 3D 2C]
* p [2C 1B 4E 2C]
* p [2C 3D 2c]
*/
// A to C (via B,C,D); A to C (via D,C,D); and A to C (via D,E,B).
@Override
public List<Path> getPathBetweenTwoStations(Station parent, Station end, int deep) {
// Watching out,: here is a lambda expression. it will be the parameter of
// the {@link GraphOptionImpl#getAllPathBetweenTwoStations}.
// and will be called by the super method {@link Graph#getPathsBetweenTwoStations}
return super.getPathsBetweenTwoStations(parent, end, deep, (actual, expect) -> {
return actual == expect;
});
}单元测试UT:junit4
// AB5,BC4,CD8,DC8,DE6,AD5,CE2,EB3,AE7
// @Ignore
@Test
public void testGetPathBetweenTwoStations() {
GraphOptions context = GraphFactory.getInstance(sources);
Station start = new Station(0, -1, "A");
Station end = new Station(2, -1, "C");
List<Path> nodes = context.getPathBetweenTwoStations(start, end, 4);
// expect is 3, actual is node.size
Assert.assertEquals(3, nodes.size());
for (Path node : nodes) {
String s = "[";
for (Station n : node.getPath()) {
s += n.getName() + " ";
}
s += "]";
System.out.println(s);
}
}控制台输出:
思考问题③:
这个问题不像①②通过从最后的end node创建Path来完成, 而是直接通过从顶层创建Path,并且在某一层的迭代中clone一个新的路径来承载接下来满足要求的Path
递归方式:传入一个Path, 通过判断当前点是否满足条件,如果满足则添加当前点,并且clone一个包含当前点的新路径,以便于递归当前点的子节点;
递归参数:一个Path, 结束点end, 期望的条件expect
结束条件: path的cost大于期望值expect;
注意:这里仍然有很多代码和①②类似,但是我觉得不需要重构, 如果你是代码控,可以接着重构,
@Override
public List<Path> getAllPathWithCost(Path path, Station end, int expect) {
List<Path> parentPath = new ArrayList<>();
if (path.getCost() > expect) {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
// The last node is the parent of the next node
if (hasChildren(path.getLastStation())) {
List<Station> children = getChildren(path.getLastStation());
for (Station child : children) {
//print(path);
// Creating a new path at first.
Path newPath = Path.newPath(path);
newPath.setCost(this);
// Getting the weight of the path, expect for the end node, because the end will be processing next.
int pathWeight = getWeight(path.getLastStation().getPosition(),
child.getPosition());
// Getting the weight of the end node.
int endWeight = getWeight(child.getPosition(), child.getPosition());
// If the total is less than the expected, the end node will be added
if (newPath.getCost() + pathWeight + endWeight < expect) {
newPath.addNode(child);
newPath.setCost(this);
// If the end path is the expected, add it.
if (child.equalWith(end)) {
parentPath.add(newPath);
}
// Going on iteration. The left nodes and their children nodes will be iterated here.
// The return collection contains all of the child paths.
// If the collection is empty , the iterator will not be executed.
// If the collection is not empty , it should have a path at least.
// Then the paths should be merged to the parent path one by one.
// Don't add the current node again before merge.
getAllPathWithCost(newPath, end, expect).stream().forEach((childPath) -> {
parentPath.add(childPath);
});
}
}
}
return parentPath;
}单元测试UT :
// cdc cebc cebcdc cdcebccdebc cebcebc cebcebcebc
// cdcebccdebc cebcebc cebcebcebc
// @Ignore
@Test
public void testGetAllPathWithCost() {
Station station = new Station(2, 0, "C");
Path path = new Path();
path.addNode(station);
GraphOptions context = GraphFactory.getInstance(sources);
List<Path> nodes = context.getAllPathWithCost(path, station, 30);
Assert.assertEquals(7, nodes.size());
for (Path node : nodes) {
System.out.println(node.toString());
}
}控制台输出:
总结: 关于路径问题的递归深度
1: 有关上述问题以及上述问题的变种,都可以使用递归解决,.但是重要的是分析递归表达式、递归参数,、递归结束条件, 以及满足当前条件后的递归处理
① 如果涉及最大如何如何,可以考虑将当前的递归深度actual和期望的递归深度expect都传入函数,根据实际需要进行判断. 还有一种就是给定一个递归的限度,递增或者递减递归深度,然后在写其他代码
②如何递归:
一般来说就是从全局出发找出抽象的递归规律, 建立一个可靠抽象模型,比如树模型, 比如二分模型.然后找出触发递归的临界条件, 接下来就是进一步的确定下一次递归的参数问题, 参数可能能会包含了需要本次递归处理的数据对象current 以及待下次处理的数据对象next ,以及两次递归之间的条件数据对象condition,结合两次的参数来选择最终合适的参数.
③路径的递归可以使用树模型作为分析模型, 因为树的自顶向下的层次结构方便分析递归深度
④如果碰到可以建立树模型,但是又不知道如何分析的情况,
可以想象树从地里吸收水分,和雨水从枝叶最终汇聚到树根,两种解析水的方式.
建议画一个树图, 结果集元素可以从根root 通过clone 传到到子节点, 也可以从目标子节点出发,最终汇聚到根节点. 即就是自顶向下汇聚,和从下到顶的汇聚方式.
如果发现文中有问题可以直接联系@我,也可以提交你的代码到我的github.
详细代码可以参考我的github,
欢迎访问 https://github.com/kiksh710000/train.git
转载于:https://blog.51cto.com/smallmushroom/1871937





















 1326
1326

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








