Dependency Scope
Dependency scope is used to limit the transitivity of a dependency, and also to affect the classpath used for various build tasks.
依赖范围用于限制依赖项的传递性,也影响用于各种构建任务的类路径。
There are 6 scopes available:
compile
This is the default scope, used if none is specified. Compile dependencies are available in all classpaths of a project. Furthermore, those dependencies are propagated to dependent projects.
默认的 scope。编译依赖项可在项目的所有类路径中使用。此外,这些依赖关系被传播到依赖项目。
provided
This is much like compile, but indicates you expect the JDK or a container to provide the dependency at runtime. For example, when building a web application for the Java Enterprise Edition, you would set the dependency on the Servlet API and related Java EE APIs to scope provided because the web container provides those classes. This scope is only available on the compilation and test classpath, and is not transitive.
provided scope 很像 compile scope,但表示您希望JDK或容器在运行时提供依赖性。例如,当为Java企业版构建Web应用程序时,您会将servlet API和相关的JavaEE API的依赖项设置为提供的作用域,因为Web容器提供了这些类。此范围仅在编译和测试类路径上可用,并且不是传递性的。
runtime
This scope indicates that the dependency is not required for compilation, but is for execution. It is in the runtime and test classpaths, but not the compile classpath.
此范围指示编译不需要依赖项,而是用于执行。它在运行时和测试类中,而不是编译类路径。
test
This scope indicates that the dependency is not required for normal use of the application, and is only available for the test compilation and execution phases. This scope is not transitive.
此范围指示应用程序的正常使用不需要依赖项,并且仅可用于测试编译和执行阶段。这个范围不是传递的。
system
This scope is similar to provided except that you have to provide the JAR which contains it explicitly. The artifact is always available and is not looked up in a repository.
此范围与 provided 类似,只是必须显式地提供包含它的jar。工件总是可用的,而不是在存储库中查找的。
import
This scope is only supported on a dependency of type pom in the <dependencyManagement> section. It indicates the dependency to be replaced with the effective list of dependencies in the specified POM's <dependencyManagement> section. Since they are replaced, dependencies with a scope of import do not actually participate in limiting the transitivity of a dependency.
此范围仅支持在“依赖关系管理>节”中的类型POM的依赖项中。它指示要在指定的POM的<dependencyManagement>部分中用有效的依赖项列表替换的依赖项。由于它们被替换,具有导入范围的依赖项实际上并不参与限制依赖项的传递性。
备注
Each of the scopes (except for import) affects transitive dependencies in different ways, as is demonstrated in the table below. If a dependency is set to the scope in the left column, transitive dependencies of that dependency with the scope across the top row will result in a dependency in the main project with the scope listed at the intersection. If no scope is listed, it means the dependency will be omitted. 每个scope(除了导入)都会以不同的方式影响传递依赖关系,如下面的表所示。如果将依赖项设置为左列中的范围,则该依赖项与跨顶行的范围的传递依赖项将导致主项目中的依赖项与交叉点列出的范围。如果没有列出范围,则表示依赖项将被省略。
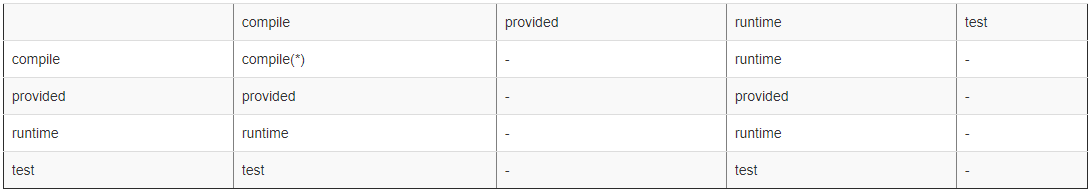
it is intended that this should be runtime scope instead, so that all compile dependencies must be explicitly listed - however, there is the case where the library you depend on extends a class from another library, forcing you to have available at compile time. For this reason, compile time dependencies remain as compile scope even when they are transitive. 这应该是运行时范围,因此必须显式列出所有编译依赖项-但是,您所依赖的库从另一个库扩展了一个类,迫使您在编译时可用。由于这个原因,编译时依赖关系即使在传递时仍然保留为编译范围。
以上内容取自maven官网资料
案例
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.4</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
其他关于scope的资料
https://www.jianshu.com/p/a4fc54b5a6bf
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/kimylrong/article/details/50353161
https://howtodoinjava.com/maven/maven-dependency-scopes/
https://www.baeldung.com/maven-dependency-scopes
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/maven/maven_manage_dependencies.htm





















 643
643

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








