一.集合概念
Java中的集合是工具类,可以存储任意数量具有共同属性的对象。
1.使用场景:
无法预测存储数据的数量;
同时存储具有一对一关系的数据;
需要进行数据的增删;
数据重复问题。
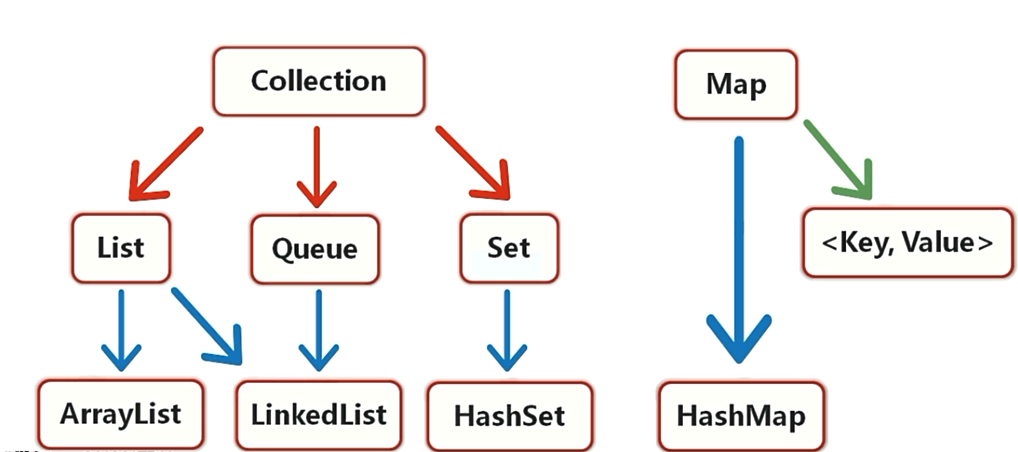
2.集合框架的体系结构:
二.List(列表)
1.List相关概念:
List是元素有序并且可以重复的集合,称为序列;
List可以精确的控制每个元素的插入位置,或删除某个位置的元素;
List的两个主要实现类是ArrayList(和数组相似,内存上连续的存储空间)和LinkedList(链表)。
2.ArrayList和LinkedList:
2.1ArrayList:
ArrayList底层是由数组实现的;动态增长,以满足应用程序的需求;在列表尾部插入或删除数据非常有效;更适合查找和更新元素;ArrayList中的元素可以为null。
| 方法摘要 | ||
|---|---|---|
boolean | add(E e) 将指定的元素添加到此列表的尾部。 | |
void | add(int index, E element) 将指定的元素插入此列表中的指定位置。 | |
boolean | addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) 按照指定 collection 的迭代器所返回的元素顺序,将该 collection 中的所有元素添加到此列表的尾部。 | |
boolean | addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) 从指定的位置开始,将指定 collection 中的所有元素插入到此列表中。 | |
void | clear() 移除此列表中的所有元素。 | |
Object | clone() 返回此 ArrayList 实例的浅表副本。 | |
boolean | contains(Object o) 如果此列表中包含指定的元素,则返回 true。 | |
void | ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) 如有必要,增加此 ArrayList 实例的容量,以确保它至少能够容纳最小容量参数所指定的元素数。 | |
E | get(int index) 返回此列表中指定位置上的元素。 | |
int | indexOf(Object o) 返回此列表中首次出现的指定元素的索引,或如果此列表不包含元素,则返回 -1。 | |
boolean | isEmpty() 如果此列表中没有元素,则返回 true | |
int | lastIndexOf(Object o) 返回此列表中最后一次出现的指定元素的索引,或如果此列表不包含索引,则返回 -1。 | |
E | remove(int index) 移除此列表中指定位置上的元素。 | |
boolean | remove(Object o) 移除此列表中首次出现的指定元素(如果存在)。 | |
protected void | removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) 移除列表中索引在 fromIndex(包括)和 toIndex(不包括)之间的所有元素。 | |
E | set(int index, E element) 用指定的元素替代此列表中指定位置上的元素。 | |
int | size() 返回此列表中的元素数。 | |
Object[] | toArray() 按适当顺序(从第一个到最后一个元素)返回包含此列表中所有元素的数组。 | |
| toArray(T[] a) 按适当顺序(从第一个到最后一个元素)返回包含此列表中所有元素的数组;返回数组的运行时类型是指定数组的运行时类型。 | |
void | trimToSize() 将此 ArrayList 实例的容量调整为列表的当前大小。 | |


1 package com.swpu; 2 3 import java.util.Date; 4 5 public class Notice { 6 private int id; 7 private String title; 8 private String ctrator; 9 private Date createTime; 10 public Notice(int id, String title, String ctrator, Date createTime) { 11 super(); 12 this.id = id; 13 this.title = title; 14 this.ctrator = ctrator; 15 this.createTime = createTime; 16 } 17 public int getId() { 18 return id; 19 } 20 public void setId(int id) { 21 this.id = id; 22 } 23 public String getTitle() { 24 return title; 25 } 26 public void setTitle(String title) { 27 this.title = title; 28 } 29 public String getCtrator() { 30 return ctrator; 31 } 32 public void setCtrator(String ctrator) { 33 this.ctrator = ctrator; 34 } 35 public Date getCreateTime() { 36 return createTime; 37 } 38 public void setCreateTime(Date createTime) { 39 this.createTime = createTime; 40 } 41 42 43 }


1 package com.swpu.test; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Date; 5 6 import com.swpu.Notice; 7 8 public class NoticeTest { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 Notice notice1 = new Notice(1, "哈哈1", "LYQ1", new Date()); 11 Notice notice2 = new Notice(2, "哈哈2", "LYQ2", new Date()); 12 Notice notice3 = new Notice(3, "哈哈3", "LYQ3", new Date()); 13 ArrayList arraylist=new ArrayList(); 14 //添加 15 arraylist.add(notice1); 16 arraylist.add(notice2); 17 arraylist.add(notice3); 18 System.out.println("公告内容:"); 19 for(int i=0;i<arraylist.size();i++){ 20 System.out.println(i+1+":"+((Notice)(arraylist.get(i))).getTitle()); 21 } 22 Notice notice4 = new Notice(4, "哈哈4", "LYQ4", new Date()); 23 //指定位置添加 24 arraylist.add(1,notice4); 25 System.out.println("**********"); 26 for(int i=0;i<arraylist.size();i++){ 27 System.out.println(i+1+":"+((Notice)(arraylist.get(i))).getTitle()); 28 } 29 //移除 30 arraylist.remove(1); 31 //修改 32 notice4.setTitle("新哈哈4"); 33 arraylist.set(2, notice4); 34 35 36 37 } 38 39 }
2.2LinkedList:
与ArrayList一样,LinkedList也按照索引位置排序,但它的元素z之间是双向链接的;
适合快速的插入和删除元素;
LinkdList实现List和Queue两个接口。
| 方法摘要 | ||
|---|---|---|
boolean | add(E e) 将指定元素添加到此列表的结尾。 | |
void | add(int index, E element) 在此列表中指定的位置插入指定的元素。 | |
boolean | addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) 添加指定 collection 中的所有元素到此列表的结尾,顺序是指定 collection 的迭代器返回这些元素的顺序。 | |
boolean | addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) 将指定 collection 中的所有元素从指定位置开始插入此列表。 | |
void | addFirst(E e) 将指定元素插入此列表的开头。 | |
void | addLast(E e) 将指定元素添加到此列表的结尾。 | |
void | clear() 从此列表中移除所有元素。 | |
Object | clone() 返回此 LinkedList 的浅表副本。 | |
boolean | contains(Object o) 如果此列表包含指定元素,则返回 true。 | |
Iterator<E> | descendingIterator() 返回以逆向顺序在此双端队列的元素上进行迭代的迭代器。 | |
E | element() 获取但不移除此列表的头(第一个元素)。 | |
E | get(int index) 返回此列表中指定位置处的元素。 | |
E | getFirst() 返回此列表的第一个元素。 | |
E | getLast() 返回此列表的最后一个元素。 | |
int | indexOf(Object o) 返回此列表中首次出现的指定元素的索引,如果此列表中不包含该元素,则返回 -1。 | |
int | lastIndexOf(Object o) 返回此列表中最后出现的指定元素的索引,如果此列表中不包含该元素,则返回 -1。 | |
ListIterator<E> | listIterator(int index) 返回此列表中的元素的列表迭代器(按适当顺序),从列表中指定位置开始。 | |
boolean | offer(E e) 将指定元素添加到此列表的末尾(最后一个元素)。 | |
boolean | offerFirst(E e) 在此列表的开头插入指定的元素。 | |
boolean | offerLast(E e) 在此列表末尾插入指定的元素。 | |
E | peek() 获取但不移除此列表的头(第一个元素)。 | |
E | peekFirst() 获取但不移除此列表的第一个元素;如果此列表为空,则返回 null。 | |
E | peekLast() 获取但不移除此列表的最后一个元素;如果此列表为空,则返回 null。 | |
E | poll() 获取并移除此列表的头(第一个元素) | |
E | pollFirst() 获取并移除此列表的第一个元素;如果此列表为空,则返回 null。 | |
E | pollLast() 获取并移除此列表的最后一个元素;如果此列表为空,则返回 null。 | |
E | pop() 从此列表所表示的堆栈处弹出一个元素。 | |
void | push(E e) 将元素推入此列表所表示的堆栈。 | |
E | remove() 获取并移除此列表的头(第一个元素)。 | |
E | remove(int index) 移除此列表中指定位置处的元素。 | |
boolean | remove(Object o) 从此列表中移除首次出现的指定元素(如果存在)。 | |
E | removeFirst() 移除并返回此列表的第一个元素。 | |
boolean | removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) 从此列表中移除第一次出现的指定元素(从头部到尾部遍历列表时)。 | |
E | removeLast() 移除并返回此列表的最后一个元素。 | |
boolean | removeLastOccurrence(Object o) 从此列表中移除最后一次出现的指定元素(从头部到尾部遍历列表时)。 | |
E | set(int index, E element) 将此列表中指定位置的元素替换为指定的元素。 | |
int | size() 返回此列表的元素数。 | |
Object[] | toArray() 返回以适当顺序(从第一个元素到最后一个元素)包含此列表中所有元素的数组。 | |
| toArray(T[] a) 返回以适当顺序(从第一个元素到最后一个元素)包含此列表中所有元素的数组;返回数组的运行时类型为指定数组的类型。 | |
三.Set
Set是元素无序并且不可以重复的集合,简称为集。
1.HashSet(底层是HashMap):
HashSet是Set的一个重要实现类,成为哈希集;
HashSet中的元素无序并且不可以重复;
HashSet中允许一个null元素;
具有良好的存储和查找功能。
迭代器(Iterator):
Iterator接口可以以统一的方式对各种集合元素进行遍历;hasNext()方法检测集合是否还有下一个元素;next()方法返回集合中的下一个元素。
例1:


1 package com.swpu; 2 3 import java.util.HashSet; 4 import java.util.Iterator; 5 import java.util.Set; 6 7 public class WordDemo { 8 public static void main(String[] args){ 9 Set set=new HashSet(); 10 set.add("哈哈1"); 11 set.add("哈哈2"); 12 set.add("哈哈3"); 13 Iterator it=set.iterator(); 14 //遍历迭代器 15 while(it.hasNext()){ 16 System.out.print(it.next()+" "); 17 } 18 } 19 20 }
例2:


1 package com.swpu; 2 3 public class Cat { 4 private String name; 5 private int month; 6 private String species; 7 public Cat(String name, int month, String species) { 8 super(); 9 this.name = name; 10 this.month = month; 11 this.species = species; 12 } 13 public String getName() { 14 return name; 15 } 16 public void setName(String name) { 17 this.name = name; 18 } 19 public int getMonth() { 20 return month; 21 } 22 public void setMonth(int month) { 23 this.month = month; 24 } 25 public String getSpecies() { 26 return species; 27 } 28 public void setSpecies(String species) { 29 this.species = species; 30 } 31 //重写toString方法 32 @Override 33 public String toString() { 34 return "Cat [name=" + name + ", month=" + month + ", species=" + species + "]"; 35 } 36 //重写hashCode()方法 37 @Override 38 public int hashCode() { 39 final int prime = 31; 40 int result = 1; 41 result = prime * result + month; 42 result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode()); 43 result = prime * result + ((species == null) ? 0 : species.hashCode()); 44 return result; 45 } 46 //重写提高查询速度 47 @Override 48 public boolean equals(Object obj) { 49 //判断对象是否相等,相等则返回true,不用继续比较属性了 50 if (this==obj){ 51 return true; 52 } 53 //判断obj是否是Cat类的对象 54 if(obj.getClass()==Cat.class){ 55 Cat cat=(Cat) obj; 56 return (cat.getName().equals(name))&&(cat.getMonth()==month)&&cat.getSpecies().equals(species); 57 } 58 return false; 59 60 /* 61 * if (this == obj) 62 return true; 63 if (obj == null) 64 return false; 65 if (getClass() != obj.getClass()) 66 return false; 67 Cat other = (Cat) obj; 68 if (month != other.month) 69 return false; 70 if (name == null) { 71 if (other.name != null) 72 return false; 73 } else if (!name.equals(other.name)) 74 return false; 75 if (species == null) { 76 if (other.species != null) 77 return false; 78 } else if (!species.equals(other.species)) 79 return false; 80 return true; 81 */ 82 } 83 84 85 86 }


1 package com.swpu.test; 2 3 import java.util.HashSet; 4 import java.util.Iterator; 5 import java.util.Set; 6 7 import com.swpu.Cat; 8 9 public class CatTest { 10 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 Cat cat1=new Cat("花花",12,"英国短毛猫"); 13 Cat cat2 =new Cat("凡凡",10,"中国田园猫"); 14 //<>泛型,限定类型 15 Set<Cat> set=new HashSet<Cat>(); 16 set.add(cat1); 17 set.add(cat2); 18 Iterator<Cat> it=set.iterator(); 19 while(it.hasNext()){ 20 System.out.println(it.next()); 21 } 22 //添加一个猫(对象属性一样,但是是两个不同的对象) 23 System.out.println("**************"); 24 Cat cat3 =new Cat("凡凡",10,"中国田园猫"); 25 set.add(cat3); 26 it=set.iterator(); 27 while(it.hasNext()){ 28 System.out.println(it.next()); 29 } 30 //重新插入一个猫 31 System.out.println("**************"); 32 Cat cat4 =new Cat("凡凡二代",10,"中国田园猫"); 33 set.add(cat4); 34 it=set.iterator(); 35 while(it.hasNext()){ 36 System.out.println(it.next()); 37 } 38 //在集合中查找花花的信息 39 if(set.contains(cat1)){ 40 System.out.println("找到了花花"); 41 System.out.println(cat1); 42 } 43 else{ 44 System.out.println("未找到!!!"); 45 } 46 System.out.println("**************"); 47 //在集合中使用名字查找花花的信息 48 System.out.println("通过名字查找"); 49 boolean flag=false; 50 Cat c=null; 51 it=set.iterator(); 52 while(it.hasNext()){ 53 c=it.next(); 54 if (c.getName().equals("花花")){ 55 flag=true;// 56 break; 57 } 58 } 59 if(flag=true){ 60 System.out.println("找到了"); 61 System.out.println(c); 62 63 } 64 else{ 65 System.out.println("未找到"); 66 } 67 System.out.println("**************"); 68 //删除凡凡二代 69 for(Cat cat:set){ 70 if ("凡凡二代".equals(cat.getName())){ 71 set.remove(cat); 72 } 73 } 74 for(Cat cat:set){ 75 System.out.println(cat); 76 } 77 //删除所有 78 boolean flag1=set.removeAll(set); 79 if(set.isEmpty()){ 80 System.out.println("删除了"); 81 } 82 else{ 83 System.out.println("删除失败"); 84 85 } 86 87 } 88 89 } 90
Python中实现:


1 class Cat(object): 2 def __init__(self, name, month, species): 3 self.name = name 4 self.month = month 5 self.species = species 6 7 # 重写__repr__魔法函数指定返回值 8 def __repr__(self): 9 return "name:" + self.name + " 年龄: " + str(self.month) 10 11 # 重写__eq__和__hash__魔法函数,判断是否相等 12 def __eq__(self, other): 13 if self is other: 14 return True 15 if self.__class__ == self.__class__: 16 if self.name == other.name and self.month == other.month and self.species == other.species: 17 return True 18 return False 19 20 def __hash__(self): 21 prime = 31 22 result = 1 23 result = prime * result + self.month 24 return result 25 26 if __name__=="__main__": 27 28 cat1 = Cat("花花", 12, "英国短毛猫") 29 cat2 = Cat("凡凡", 12, "中华田园猫") 30 cat3 = Cat("花花", 12, "英国短毛猫") 31 cat3 = Cat("花花二代", 12, "英国短毛猫") 32 33 myset = set() 34 myset.add(cat1) 35 myset.add(cat2) 36 for i in myset: 37 print(i) 38 print("*"*10) 39 #判断cat1是否在myset中 40 if (cat1 in myset): 41 print("找到了") 42 print("*"*10) 43 #通过name判断 44 for i in myset: 45 if i.name=="花花": 46 print("找到了") 47 print(i) 48 break 49 #删除花花二代 50 for i in myset: 51 if i.name=="花花二代": 52 myset.remove(i) 53 break 54 #移除所有 55 myset.clear() 56 print(myset)
四.Map
注:
Map的数据是以键值对(key-value)的形式存储;
key-value以Entry类型的实例对象存在;
可以通过key值快速查找value;
一个映射不能包含重复的键;
每个键最多只能映射到一个值。
HashMap:
基于哈希表的Map接口的实现;
允许使用null值和null键;
key值不允许重复;
HashMap中的Entry对象是无序排列的。
| 方法摘要 | |
|---|---|
void | clear() 从此映射中移除所有映射关系。 |
Object | clone() 返回此 HashMap 实例的浅表副本:并不复制键和值本身。 |
boolean | containsKey(Object key) 如果此映射包含对于指定键的映射关系,则返回 true。 |
boolean | containsValue(Object value) 如果此映射将一个或多个键映射到指定值,则返回 true。 |
Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> | entrySet() 返回此映射所包含的映射关系的 Set 视图。 |
V | get(Object key) 返回指定键所映射的值;如果对于该键来说,此映射不包含任何映射关系,则返回 null。 |
boolean | isEmpty() 如果此映射不包含键-值映射关系,则返回 true。 |
Set<K> | keySet() 返回此映射中所包含的键的 Set 视图。 |
V | put(K key, V value) 在此映射中关联指定值与指定键。 |
void | putAll(Map<? extends K,? extends V> m) 将指定映射的所有映射关系复制到此映射中,这些映射关系将替换此映射目前针对指定映射中所有键的所有映射关系。 |
V | remove(Object key) 从此映射中移除指定键的映射关系(如果存在)。 |
int | size() 返回此映射中的键-值映射关系数。 |
Collection<V> | values() 返回此映射所包含的值的 Collection 视图。 |
例1:


1 package com.swpu.test; 2 3 import java.awt.datatransfer.StringSelection; 4 import java.util.HashMap; 5 import java.util.Iterator; 6 import java.util.Map; 7 import java.util.Map.Entry; 8 import java.util.Scanner; 9 import java.util.Set; 10 11 public class MapTest { 12 13 public static void main(String[] args) { 14 15 Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>(); 16 System.out.println("请输入三组单词存入HashMap:"); 17 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); 18 int i = 0; 19 while (i < 3) { 20 System.out.print("请输入键:"); 21 String key = sc.next(); 22 System.out.print("请输入值:"); 23 String value = sc.next(); 24 map.put(key, value); 25 i++; 26 27 } 28 // 打印输出value值 29 System.out.println("*************"); 30 System.out.println("使用迭代器输出values:"); 31 Iterator<String> it = map.values().iterator(); 32 while (it.hasNext()) { 33 System.out.print(it.next() + " "); 34 } 35 // 使用entrySet打印key,value 36 System.out.println("\n使用entrySet打印key,value:"); 37 Set<Entry<String, String>> entrySet = map.entrySet(); 38 for(Entry<String,String> entry:entrySet){ 39 System.out.println(entry.getKey()+"-"+entry.getValue()); 40 } 41 //通过key找到value 42 //使用KeySet方法 43 String stringSearch=it.next(); 44 Set<String> keySet=map.keySet(); 45 //2.遍历KeySet 46 for(String key:keySet){ 47 if (stringSearch.equals(key)){ 48 System.out.println("找到了为:"+key+":"+map.get(key)); 49 break; 50 } 51 } 52 53 54 } 55 56 }
例2:


1 package com.swpu; 2 3 public class Good { 4 private String id; 5 private String name; 6 @Override 7 public String toString() { 8 return "Good [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", price=" + price + "]"; 9 } 10 private double price; 11 public Good(String id, String name, double price) { 12 super(); 13 this.id = id; 14 this.name = name; 15 this.price = price; 16 } 17 public String getId() { 18 return id; 19 } 20 public void setId(String id) { 21 this.id = id; 22 } 23 public String getName() { 24 return name; 25 } 26 public void setName(String name) { 27 this.name = name; 28 } 29 public double getPrice() { 30 return price; 31 } 32 public void setPrice(double price) { 33 this.price = price; 34 } 35 36 }


1 package com.swpu.test; 2 3 import java.util.HashMap; 4 import java.util.Iterator; 5 import java.util.Map; 6 import java.util.Scanner; 7 8 import com.swpu.Good; 9 10 public class GoodTest { 11 12 public static void main(String[] args) { 13 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 14 Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); 15 Map<String,Good> goodMap=new HashMap<String,Good>(); 16 System.out.println("请输入商品信息"); 17 int i=0; 18 while(i<3){ 19 System.out.println("请输入第"+(i+1)+"条商品"); 20 System.out.println("请输入商品编号:"); 21 String goodId=sc.next(); 22 //判断商品编号是否存在 23 if(goodMap.containsKey(goodId)){ 24 System.out.println("该商品id已经存在,请从新输入"); 25 continue; 26 } 27 System.out.println("请输入商品名称:"); 28 String goodName=sc.next(); 29 System.out.println("请输入商品价格:"); 30 double goodPrice=0; 31 try{ 32 goodPrice=sc.nextDouble(); 33 } 34 catch(java.util.InputMismatchException e){ 35 System.out.println("价格格式输入不正确!!请从新输入!!"); 36 sc.next(); 37 continue; 38 } 39 Good good=new Good(goodId,goodName,goodPrice); 40 //将商品信息添加 41 goodMap.put(goodId, good); 42 i++; 43 } 44 Iterator <Good> it=goodMap.values().iterator(); 45 while(it.hasNext()){ 46 System.out.println(it.next()); 47 } 48 49 } 50 51 }























 7775
7775

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








