变量:
全局变量:只能在这一个脚本文件中可以使用,在其他的脚本文件中不可使用
环境变量:在所有的脚本文件中都可以使用(export)
建议:把所有的变量都放在脚本文件的开头,不失为一种良好的习惯
保留字read:
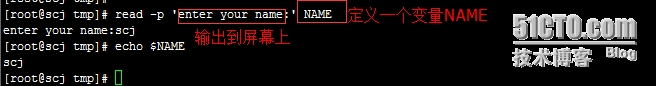
read name :定义一个变量name,并把键盘输入的数据作为name这个变量的值
判断语句:
id1=2
id2=3
test $id1 -eq $id2 (或 [ $id1 -eq $id2 ])
echo $?
注释:返回码0:命令执行成功 返回码非0:命令执行失败
定义函数:
function HELP
{
echo "enter your name:"
}
HELP
注释:定义一个函数:function 函数名
调用一个函数:直接输入函数名
花括号“{}”一定要单独一行
Hello() (建议用这种方法)
{
echo hello $1
}
Hello scj
while read LINE用法:
cat file | while read LINE #定义一个LINE变量
do
xxxxxxxxxx
done
或:
while read LINE ##以行来循环
do
xxxxxxxxxx
done < file
awk求和:
180.153.108.142 354k
180.153.108.143 45k
180.153.108.15 123k
180.153.108.142 875k
180.153.108.143 987k
180.153.108.15 765k
180.153.108.142 222k
如上:
对第二列进行求和:
awk '{print $2}' filename |awk -F'k' '{print $1}' |awk '{sum+=$1}END{print sum}'
3371
或者:
awk '{a[1]+=$2}END{print a[1]}' filename
3371
注释:第二种方法采用数组,更简单;首先创建一个数组a,在数组a里添加一个下标是1的元素(下标是任意的,只要没有冲突就可以),默认a[1]的值为0,$2是第二列,在求和时第二列的单位是被忽略的
对第一列分组后对第二列求和:
awk '{a[$1]+=$2}END{for(i in a)print i,a[i]}' filename
180.153.108.15 888
180.153.108.142 1451
180.153.108.143 1032
注释:$1是第一列,也就是ip;$2是第二列,也就是要求和的列;创建一个数组a,在数组a里添加下标是ip的元素,即:a[180.153.108.142],a[180.153.108.143],a[180.153.108.15]三个元素,默认初始值都为0;for (i in a):for循环逐次取出数组a里面的下标,也就是第一列的ip
从第三行开始对第一列分组后对第二列求和:
awk 'NR>2{a[$1]+=$2}END{for(i in a)print i,a[i]}' filename
注释:NR:行号 NF:每行的列数
#*的用法
[root@localhost scripts]# vi file2.sh
str1=/tmp/scripts/file1
str2=scripts
str3=${str1#*$str2}
echo $str3
str1=/tmp/scripts/file1
str2=scripts
str3=${str1#*scripts}
echo $str3
str1=tmp/scripts/file1
str2=/
str3=${str1#*$str2}
echo $str3
[root@localhost scripts]# bash file2.sh /file1 /file1 scripts/file1
用法:
${str1#*str2}:从str1中获取首次出现str2之后的所有内容
str1是一个变量,但是前面不加$,其实其$放在了{}外面
str2是一个字符串,可以用$str2去引用一个变量
for循环和while循环
for循环:对于文件来说,每次循环并不是以行来循环,而是以空格分割的来循环
while read:对于文件来说,以行来循环
例如:
[root@localhost sctipts]# cat failIP.txt 22368 43.229.53.55 20520 43.229.53.53 20235 221.203.142.72
用for来循环:
vi for.sh
#!/bin/bash
for failStatus in `cat failIP.txt`
do
faliTimes=`echo $failStatus | awk '{print $1}'`
done
##执行脚本
[root@localhost sctipts]# bash -x for.sh
++ cat failIP.txt
+ for failStatus in '`cat failIP.txt`'
++ awk '{print $1}'
++ echo 22368
+ faliTimes=22368
+ for failStatus in '`cat failIP.txt`'
++ awk '{print $1}'
++ echo 43.229.53.55
+ faliTimes=43.229.53.55
+ for failStatus in '`cat failIP.txt`'
++ awk '{print $1}'
++ echo 20520
+ faliTimes=20520
+ for failStatus in '`cat failIP.txt`'
++ awk '{print $1}'
++ echo 43.229.53.53
+ faliTimes=43.229.53.53
+ for failStatus in '`cat failIP.txt`'
++ awk '{print $1}'
++ echo 20235
+ faliTimes=20235
+ for failStatus in '`cat failIP.txt`'
++ awk '{print $1}'
++ echo 221.203.142.72
+ faliTimes=221.203.142.72
由结果来看,for循环,并没有以行来循环
用while read来循环
vi while.sh
#!/bin/bash
while read failStatus
do
failTimes=`echo $failStatus | awk '{print $1}'`
failIP=`echo $failStatus | awk '{print $2}'`
echo $failTimes
echo $failIP
done < failIP.txt
##执行脚本 [root@localhost sctipts]# bash while.sh 22368 43.229.53.55 20520 43.229.53.53 20235 221.203.142.72
转载于:https://blog.51cto.com/732233048/1617630






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








