As far as I know, SharedPreferences allow us to store some simple data in a named area in our phone. Introduction to the uses of SharedPreferences is very clear at Android SDK website. I just copied here(I divided the contents into four parts):
Introduction
The SharedPreferences class provides a general framework that allows you to save and retrieve persistent key-value pairs of primitive data types. You can use SharedPreferences to save any primitive data: booleans, floats, ints, longs, and strings. This data will persist across user sessions (even if your application is killed).
Get SharedPreferences object
To get a SharedPreferences object for your application, use one of two methods:
getSharedPreferences()- Use this if you need multiple preferences files identified by name, which you specify with the first parameter.getPreferences()- Use this if you need only one preferences file for your Activity. Because this will be the only preferences file for your Activity, you don't supply a name.
Write the values
To write values:
- Call
edit()to get aSharedPreferences.Editor. - Add values with methods such as
putBoolean()andputString(). - Commit the new values with
commit()
Read the values
To read values, use SharedPreferences methods such as getBoolean() and getString().
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Now let's get into example time:
First, take a look at AndroidManifest.xml file to get to know it.
<!-- part of AndroidManifest.xml -->
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >
<activity
android:name="com.example.sharedpreferences.MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<activity
android:name="com.example.sharedpreferences.Display"
android:label="Display" >
</activity>
</application>
Two Activities exist in this example,
MainActivity.java which uses activity_main.xml as the content view;
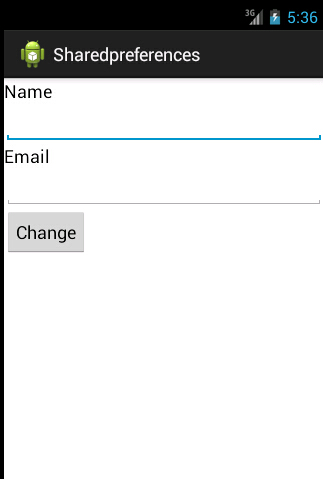
Display.java which uses main.xml as the content view:

//MainActivity.java
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private static final String MY_PREF="firstpreferencefile";
private Button change;
private EditText ed1;
private EditText ed2;
private SharedPreferences sp;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
change=(Button)findViewById(R.id.change);
ed1=(EditText)findViewById(R.id.editText1);
ed2=(EditText)findViewById(R.id.editText2);
sp=getSharedPreferences(MY_PREF, 0);
System.out.println("hello"+sp.getString("name", "null"));
change.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Editor editor=sp.edit();
editor.putString("name", ed1.getText().toString());
editor.putString("email", ed2.getText().toString());
editor.commit();
Intent intent=new Intent(getApplicationContext(),Display.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
});
}
}
//Display.java
public class Display extends Activity {
private static final String MY_PREF="firstpreferencefile";
private TextView tv1;
private TextView tv2;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
SharedPreferences sp=getSharedPreferences(MY_PREF, 0);
tv1=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.textView1);
tv2=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.textView2);
tv1.setText(sp.getString("name", "song"));
tv2.setText(sp.getString("email", "jies.2408@gmail.com"));
}
}
We set up two values and store them in SharedPreferences object. These two values can be changed in MainActivity.java, and would be displayed in main.java.







 本文介绍SharedPreferences类的基本用法,包括获取SharedPreferences对象、写入和读取数据等,并通过一个具体示例展示了如何在两个Activity间传递数据。
本文介绍SharedPreferences类的基本用法,包括获取SharedPreferences对象、写入和读取数据等,并通过一个具体示例展示了如何在两个Activity间传递数据。
















 695
695

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








