1. Different types of neurons
- Linear neurons
- Binary threshold neurons
- Recitified linear neurons
- sigmoid neurons
- Stochastic binary neurons
2. Reinforcement learning
Learn to select an action to maximize payoff.
– The goal in selecting each action is to maximize the expected sum
of the future rewards.
– We usually use a discount factor for delayed rewards so that we
don’t have to look too far into the future.
Reinforcement learning is difficult:
– The rewards are typically delayed so its hard to know where we
went wrong (or right).
– A scalar reward does not supply much information.
3. Main types of neural networks architecture
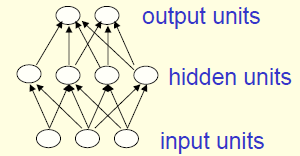
- Feed-forward
- The first layer is the input and the last layer is the output
- They compute a series of transformations that change the similarities between cases
- The activities of the neurons in each layer are a non-linear function of the activities in the layer below
- Recurrent
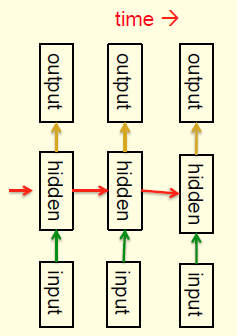
- They have directed cycles in their connection graph
- They have complicated dynamics
- It is a very natural way to model sequential data
- They are equivalent to very deep nets with one hidden layer per time slice
- They use the same weights at every time slice and they get input at every time slice.
- They have the ability to remember information in their hidden state
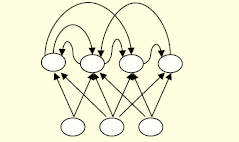

- Symmetrically connected networks
- They are like recurrent networks but the connections between units are symmetrical(same weights in both directions)
4. Perceptrons
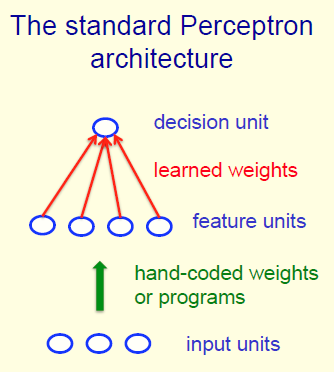
- Add an extra component with value 1 to each input vector. The “bias” weight on this component is minus the threshold. Now we can forget the threshold.
- Pick training cases using any policy that ensures that every training case willkeep getting picked.
- If the output unit is correct, leave its weights alone
- If the output unit incorrectly outputs a 1, subtract the input vector from the weight vector
- If the output unit incorrectly outputs a zero, add the input vector to the weight vector.
- This is guaranteed to find a set of weights that gets the right answer for all the
training cases if any such set exists.
5. The limitations of Perceptrons
- once the hand-coded features have been determined, there are very strong limitations on what a perceptron can learn
-
the part of a Perceptron that learns cannot learn to do this if the transformations form a group





















 1618
1618

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








