#Spring AOP Spring本身提供了两种AOP的实现
- @AspectJ annotation-based AOP
通过整合AspectJ的annotation来提供AOP的功能 - XML schema-based AOP Spring通过XML在配置文件声明
我们后续定义AOP几个重要的功能Aspect是定义到底是什么功能:日志、安全等。Pointcut匹配对应的函数。Advice定义到具体某个点执行函数。
##@AspectJ AOP
- 添加aspectweaver.jar
本身是在aspectJ的jar包,应当在Maven中进行管理。
###Maven
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.aspectj/aspectjweaver -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.8.9</version>
</dependency>
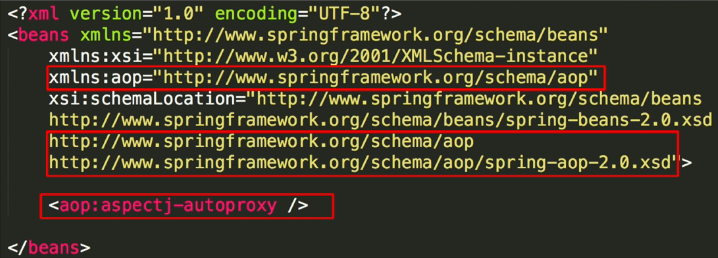
###Spring @AspectJ AOP配置 然后我们需要在Spring的配置文件中,添加xmlns:aop并添加xsi:schemaLocation。
最后在配置文件中添加
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy />
就完成了AOP的配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy />
</beans>
###xmlns xmlns是XML NameSpace的缩写,作用类似Java代码中引用不同的package,例如类名相同,但是由于存放在不同的package当中,则在程序运行时,对应不同的类。xmlns和该功能类似,避免出现类似的标签,导致的重名。通过namespace来区分不同的xml文件。这里xmlns定义了一个tag,这里tag的名称使用的是url来定义的。这里我们要使用aop的功能就是使用<aop:xxx />的tag,这里会有不同的属性与标签。 ###schema 但是我们并不知道用户所填写的标签是否合法,xsd文件是xml schema definition。定义了有哪些元素、哪些属性。当我应用程序去使用schema时,程序在验证xml文件时,就可以使用shema进行验证元素属性正确。
##定义Aspect 首先我们需要定义Aspect的Bean对象
<bean id="loggingAspect" class="com.netease.course.LoggingAspect"></bean>
需要我们在类级别添加@Aspect的annotation
package com.netease.course;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
@Aspect
public class LoggingAspect {
}
这里的Apect并没有Pointcut,不能知道匹配的函数是什么,来执行这个功能。
##定义Pointcut
@Pointcut("execution(* com.netease.course.Caaculator.*(..))")
private void arithmetic(){
}
这里我们可以看到两部分,上面的@Pointcut是表达式,这里这个表达式的意思是:我们要去匹配com.netease.course.Caculator这个类下面的所有函数,例如这个Caculator这个类下面有许多方法,比如加减乘除,上面的表达式匹配了所有方法。下面的部分为这个表达式的名称arithmetic,后续的使用我们可以直接通过这个名称去使用Pointcut的表达式。
###Pointcut表达式
designator(modifier? return-type declaring-type? name(param) throw?)
- designator
代表标签的功能,execution,within,主要介绍execution标签,代表匹配函数执行过程,within在某个包或者某个类运行。 - modifiers
这个是可有可无的,代表的是public还是private。可选的。 - return-type
函数的返回类型,通过*来表示匹配所有返回类型 - declaring-type
声明类型,包名、类名,为可选的。 - name
最终要的是我们的函数名称,name代表着函数的名称,可以通过*的方式匹配所有的函数名称。也可以通过表达式的方式匹配。 - param
代表函数的参数,()代表无参函数,(..)代表任意参数 - throws
代表抛出的异常类型,是可选的配置。
##Pointcut示例
- 匹配所有public函数
execution(public * *(..))
private void publicMethod(){
}
- 匹配所有DAO模块中的public函数
execution(public * com.netease.dao.*.*(..))
private void publicDaoMethod(){
}
- 匹配所哟以save开头的函数
execution(* save*(..))
private void saveMethod()
- 所有以save开发的public函数
AspectJ是支持两个不同表达式的组合的
execution(publicMethod() && saveMethod())
private void publicSaveMethod()
##定义Advice ###在函数运行之前定义Advice 定义Advice在特定的点做哪些事情,比如像函数执行之前执行日志。在函数的级别添加@Before annotation。@Before里面的参数是pointcut表达式,如下示例并不是pointcut表达式,而是pointcut名称。可以通过pointcut名称的方式
@Before("com.netease.course.LoggingAspect.arithmetic")
public void doLog(){
}
也可以用pointcut表达式的方式
@Before("execution(* com.netease.course.Caculator.*(..))")
public void doLog(){
}
以上是在函数运行之前定义Advice
###在函数返回之后
@AfterReturning("com.netease.course.LoggingAspect.arithmetic()")
public void doLog(){
}
###在函数抛出异常后
@AfterThrowing("com.netease.course.LoggingAspect.arithmetic()")
public void doLog(){
}
###在函数运行之后
@After("com.netease.course.LoggingAspect.arithmetic()")
public void doLog(){
}
##Advice参数
- 函数上下文信息
可以通过在Advice函数的入口添加JoinPoint来获取函数上下文信息
@Before("com.netease.course.LoggingAspect.arithmetic()")
public void doLog(JoinPoint jp){
System.out.println(jp.getSignature() + ", " + jp.getArgs());
}
通过JoinPoint获取函数的签名,函数的参数,joinPoint.getArgs()能够拿到参数,但是拿到的参数都是无类型的。如果需要进行处理,则需要知道对应类型。
但是@Around和其他几类Advice是不一致的,必须使用ProceedingJoinPoint,@Around需要调用函数的具体执行,如下示例首先,在函数开始时运行println,然后通过pjp.proceed()来执行被切函数所执行的操作。最后在函数结束后,打印日志。
@Around("com.netease.course.LoggingAspect.arithmetic()")
public void doLog(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp){
System.out.println("start method: " + pjp.toString());
Object retVal = pjp.proceed();
System.out.println("stop method: " + pjp.toString());
return retVal;
}
- 返回值
我们还希望拿到运行时调用函数的返回值,我们通过在定义时添加returning定义成retVal变量,然后我们就可以在Advice函数里面的参数添加retVal,来匹配对应返回值。函数体内部就可以对返回值进行进一步处理。
@AfterReturning(pointcut="com.netease.course.LoggingAspect.arithmetic()",returning="retVal")
public void doLog(Object retVal){
}
- 异常
注意:这里要接收什么异常的类型,则就要填写什么类型如下例子并不能直接使用
我们通过throwing定义的ex的参数,来捕获函数返回的异常,并在Advice函数体参数,进行对应。这里我们需要注意的是,异常是有IllegalArgumentException的类型的。而并不是通用的Exception。
@AfterThrowing(pointcut="com.netease.course.LoggingAspect.arithmetic()",throwing="ex")
public void doLog(IllegalArgumentException ex){
}
- 目标函数参数
我们通过pointcut里面需要args这样的方式,按照如下方式,可以匹配一个或者多个参数内容。之后再函数体内添加参数
@Before("com.netease.course.LoggingAspect.arithmetic() && args(a, ..)")
public void doLog(JoinPoint jp,int a){
}
#Schema-based AOP ##Spring配置文件
##定义Aspcet
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect id="loggingAspect" ref="loggingBean">
...
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
<bean id="loggingBean" class="com.netease.course.LoggingAspect" />
##定义Pointcut
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="arithmetic" expression="execution(* com.netease.course.Caculator.*(..))" />
</aop:config>
或者使用
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="arithmetic" expression="com.netease.course.LoggingAspect.arithmetic()" />
</aop:config>
或者一定Pointcut到aspect内部
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect id="loggingAspect" ref="loggingBean">
<aop:pointcut id="arithmetic" expression="execution(* com.netease.course.Caculator.*(..))" />
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
##定义Advice
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect id="loggingAspect" ref="loggingBean">
<aop:pointcut id="arithmetic_pointcut" expression="execution(* com.netease.course.Caculator.*(..))" />
<aop:before pointcut-ref="arithmetic_pointcut" method="doLog" />
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
我们也可以把pointcut写入到aop:before当中
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect id="loggingAspect" ref="loggingBean">
<aop:before pointcut="execution(* com.netease.course.Caculator.*(..))" method="doLog" />
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
###其他类型的的定义 ###after-returning
<aop:aspect id="loggingAspect" ref="loggingBean">
<aop:after-returning pointcut-rf="arithmetic" returning="retVal" method="doLog" />
</aop:aspect>
###after-throwing
<aop:aspect id="loggingAspect" ref="loggingBean">
<aop:after-throwing pointcut-rf="arithmetic" returning="ex" method="doLog" />
</aop:aspect>
###around
<aop:aspect id="loggingAspect" ref="loggingBean">
<aop:after-returning pointcut-rf="arithmetic" method="doLog" />
</aop:aspect>
#Schema与AspectJ Schema的方式配置集中,AspectJ方式配置分散,但是兼容AspectJ。建议使用AspectJ





 本文深入解析Spring中的两种AOP实现方式:@AspectJ注解式AOP与XML Schema配置式AOP。详细介绍如何通过这两种方式定义Aspect、Pointcut、Advice等核心概念,以及它们的应用场景。
本文深入解析Spring中的两种AOP实现方式:@AspectJ注解式AOP与XML Schema配置式AOP。详细介绍如何通过这两种方式定义Aspect、Pointcut、Advice等核心概念,以及它们的应用场景。

















 1398
1398

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








