Introduction
In questions related to linked list, fast and slow pointer solution is very common. Fast pointer step two and Slow pointer step one. Always we can the regular through draw a picture and mathematical derivation, we can find:
- middle of the linked list
- interaction pointer to assert if there is a cycle
leetcode 141 Linked List Cycle
Question
Given a linked list, determine if it has a cycle in it.
Follow up:
Can you solve it without using extra space?
Solution
Only if there is a cycle, fast will catch up with the slow pointer.
class Solution(object):
def hasCycle(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: bool
"""
fast = head
slow = head
while fast != None and fast.next != None:
fast = fast.next.next
slow = slow.next
if fast == slow:
return True
return Falseleetcode 142 Linked List Cycle II
Question

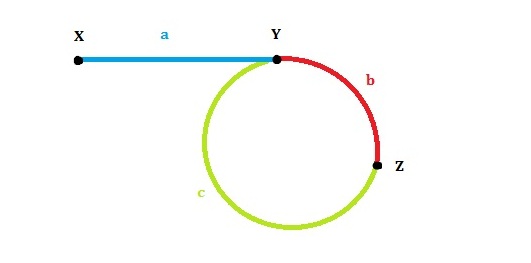
Fast pointer catch up slow when slow is on the first cycle. so:
- slowLen = a + b
- fastLen = (a + b) + n*r
- fastLen = 2 * slowLen
- a + b + n*r = a +b +b +c + (n-1)r = 2 (a + b)
- c = a +( n - 1) * r
When they come across, slow from the head and fast from the meeting point, they will finally meet at the begin point of the cycle.
class Solution(object):
def detectCycle(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
fast = head
slow = head
while fast and fast.next:
fast = fast.next.next
slow = slow.next
if fast == slow:
slow = head
while fast != slow:
fast = fast.next
slow = slow.next
return slow
return None



 本文详细介绍了快慢指针法在解决链表问题中的应用,包括判断链表是否有环、寻找环的入口点等。通过数学推导和代码实现,深入浅出地解释了这一经典算法。
本文详细介绍了快慢指针法在解决链表问题中的应用,包括判断链表是否有环、寻找环的入口点等。通过数学推导和代码实现,深入浅出地解释了这一经典算法。
















 1047
1047

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








