Problem Description
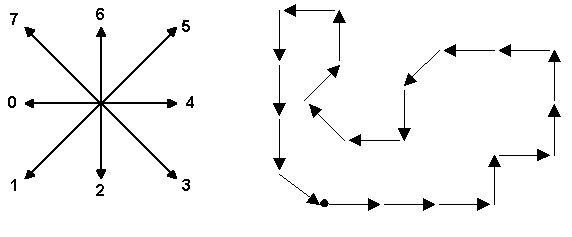
Two chain codes may represent the same shape if the shape has been rotated, or if a different starting point is chosen for the contour. To normalize the code for rotation, we can compute the first difference of the chain code instead. The first difference is obtained by counting the number of direction changes in counterclockwise direction between consecutive elements in the chain code (the last element is consecutive with the first one). In the above code, the first difference is
00110026202011676122
Finally, to normalize for the starting point, we consider all cyclic rotations of the first difference and choose among them the lexicographically smallest such code. The resulting code is called the shape number.
00110026202011676122
01100262020116761220
11002620201167612200
...
20011002620201167612
In this case, 00110026202011676122 is the shape number of the shape above.
00110026202011676122
分析:
(1)利用两个指针p1, p2。初始化时p1指向s[0], p2指向s[1]。
(2)k = 0开始,检验s[p1+k]与s[p2+k]对应的字符是否相等,如果相等则k++,一直下去,直到找到第一个不同,(若k试了一个字符串的长度也没找到不同,则那个位置就是最小表示位置,算法终止并返回)。则该过程中,s[p1+k]与s[p2+k]的大小关系,有三种情况:
(A).s[p1+k] > s[p2+k],则p1滑动到p1+k+1处---即s1[p1->p1+k]不会
是该循环字符串的“最小表示”的前缀。
(B). s[p1+k] > s[p2+k],则p1滑动到p1+k+1处,原因同上。
(C). s[p1+k] = s[p2+k],则k++;if (k == len)返回结果。
注:这里滑动方式有个小细节,若滑动后p1 == p2,将正在变化的那个指针再+1。直到p1、p2把整个字符串都检验完毕,返回两者中小于len的值。
(3) 如果k == len,则返回p1与p2中的最小值
如果p1 >= len 则返回p2
如果p2 >= len 则返回p1
(4) 进一步的优化,例如:p1要移到p1+k+1时,如果p1+k+1 <= p2的话,可以直接把p1移到p2之前,因为,p2到p2+k已经检验过了该前缀比以p1到p1+k之间任何一个位前缀都小;p2时的类似,移动到p1+1。
code:

 View Code
View Code
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#define min(a,b)((a)<(b))?(a):(b)
int Min(char s[],int len)
{
int i=0,j=1,k=0;
while(i<len&&j<len&&k<len)
{
if(s[(i+k)%len]==s[(j+k)%len])
k++;
else
{
if(s[(i+k)%len]>s[(j+k)%len])
i+=k+1;
else
j+=k+1;
if(i==j)
j++;
k=0;
}
}
return min(i,j);
}
char s[300001];
int main()
{
int i,len,k;
char tmp;
while(scanf("%s",s)!=EOF)
{
len=strlen(s);
tmp=s[0];
for(i=0;i<len-1;i++)
s[i]=(s[i+1]+8-s[i])%8+'0';
s[i]=(tmp+8-s[i])%8+'0';
k=Min(s,len);
for(i=k;i<len;i++)
printf("%c",s[i]);
for(i=0;i<k;i++)
printf("%c",s[i]);
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}




 本文介绍了一种用于标准化轮廓表示的方法——形状编号算法。通过计算链码的第一次差分,并选择字典序最小的循环旋转来规范化形状。文章还提供了详细的算法步骤及实现代码。
本文介绍了一种用于标准化轮廓表示的方法——形状编号算法。通过计算链码的第一次差分,并选择字典序最小的循环旋转来规范化形状。文章还提供了详细的算法步骤及实现代码。
















 3008
3008

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








