第8章Enterprise integration patterns是core Camel的最后一章了,第二章已经介绍了一部分camel在eip中的应用。这一章全部都是讲eip.
看来eip确实是camel的核心,camel确实是基于eip的。
这一章包含了5方面的EIP问题:
■ The Aggregator EIP 消息合并
■ The Splitter EIP 消息分拆
■ The Routing Slip EIP 根据消息标签进行路由(也是一种路由)
■ The Dynamic Router EIP 动态路由
■ The Load Balancer EIP 负载均衡
The Aggregator EIP
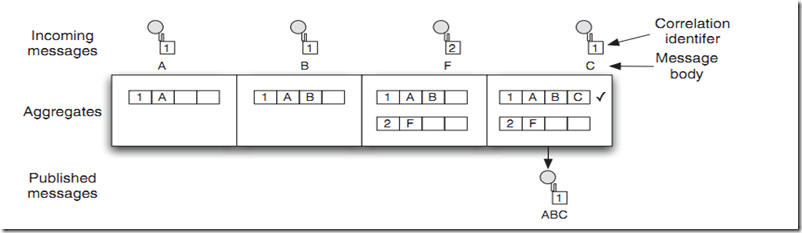
消息合并模式,如下图所示,只有当接收到三个标识相同的消息合并完成后再发送出去。1为消息标识,ABC为消息内容。
关于消息合并我们需要关注三个方面:
1.Correlation identifier
消息合并的标识,即如何确定这几个消息是一组的。如上图标识的1,2
2.Completion condition
消息合并完成的条件,即多少个消息,多长时间内的消息合并。如上图3个消息合并完成。
3.Aggregation strategy
消息合并的策略,即消息是如何合并的。这个需要自己实现接口AggregationStrategy。
public void configure() throws Exception {
from("direct:start")
.log("Sending ${body}")
.aggregate(xpath(/order/@customer), new MyAggregationStrategy()) //定义合并标示
.completionSize(2).completionTimeout(5000) //定义合并完成条件消息数量为2,等待时间为5s
.log("Sending out ${body}")
.to("mock:result");
}
消息合并的是需要等待的,默认情况下Camel是将收到的消息缓存在内存中,在生产中为了消息的安全,可能需要将收到的消息持久化。
Camel提供了接口AggregationRepository帮助我们实现消息持久化,如下。
AggregationRepository myRepo = new
HawtDBAggregationRepository("myrepo", "data/myrepo.dat");
from("file://target/inbox")
.log("Consuming ${file:name}")
.aggregate(constant(true), new MyAggregationStrategy())
.aggregationRepository(myRepo)
.completionSize(3)
.log("Sending out ${body}")
.to("mock:result");
HawtDB是Camel自带的一个嵌入式数据库。
The Splitter EIP
消息分拆模式与前一种模式刚好相反,是将接收到的消息按一定的规则分拆成多个消息发出去,如下图所示。
Camel对消息的分拆也提供了多种方法:
如果消息本身就是一个集合,可以用DSL中的split对消息分拆,示例如下:
public class SplitterABCTest extends CamelTestSupport {
public void testSplitABC() throws Exception {
MockEndpoint mock = getMockEndpoint("mock:split");
mock.expectedBodiesReceived("A", "B", "C");
List<String> body = new ArrayList<String>();
body.add("A");
body.add("B");
body.add("C");
template.sendBody("direct:start", body);
assertMockEndpointsSatisfied();
}
protected RouteBuilder createRouteBuilder() throws Exception {
return new RouteBuilder() {
public void configure() throws Exception {
from("direct:start")
.split(body())
.log("Split line ${body}")
.to("mock:split");
}
};
}
}
如果消息本身是一个对象我们也可能通过bean的形式对消息分拆,示例如下:
public void configure() throws Exception {
from("direct:start")
.split().method(CustomerService.class, "splitDepartments")
.to("log:split")
.to("mock:split");
}
最后对大消息的分拆可能采用流的形式如.split(body().tokenize("\n")).streaming()
The Routing Slip EIP
有些特殊的消息我们需要根据消息来动态的路由到一个多个结点。这是我们可以采用routing Slip的模式,示例如下:
public void testRoutingSlip() throws Exception {
getMockEndpoint("mock:a").expectedMessageCount(1);
getMockEndpoint("mock:b").expectedMessageCount(0);
getMockEndpoint("mock:c").expectedMessageCount(1);
template.sendBodyAndHeader("direct:start", "Hello World",
"mySlip", "mock:a,mock:c");
assertMockEndpointsSatisfied();
}
路由定义为:from("direct:start").routingSlip("mySlip", ";");
关于Routing Slip的形式也有多种方式:
各split一样可以采用dsl的形式,bean的形式同时camel还是提供了注解@RoutingSlip。
The Dynamic Router EIP
动态路由和Routing Slip一样也是不同的消息路由到不同的节点,如下。
public class DynamicRouterBean {
public String route(String body,
@Header(Exchange.SLIP_ENDPOINT) String previous) {
return whereToGo(body, previous);
}
private String whereToGo(String body, String previous) {
if (previous == null) {
return "mock://a";
} else if ("mock://a".equals(previous)) {
return "language://simple:Bye ${body}";
} else {
return null;
}
}
基本可以同上,也提供了注解的形式@DynamicRouter。
The Load Balancer EIP
负载均衡就不用细说了,Camel提供了对负载均衡的支持,示例如下:
from("direct:start")
.loadBalance().roundRobin()
.to("seda:a").to("seda:b")
.end();
关于负载均衡的策略Camel也提供了6种策略:Random,Round robin,Sticky,Topic,Failover,Custom。
更详细的信息请查询手册。
小结:至此Camel 的核心部分已经介绍完了,后面会再写一篇关于Camel的事务控制(第9章),额外介绍下Camel关于路由质量的监控BAM组件的使用,
其他的章节就不再介绍了。







 本文深入探讨了Apache Camel中企业集成模式(EIP)的核心概念,包括消息合并(Aggregator)、消息分拆(Splitter)、路由单(Routing Slip)、动态路由(Dynamic Router)及负载均衡(Load Balancer)等五大关键模式,并通过实例展示了这些模式的具体应用。
本文深入探讨了Apache Camel中企业集成模式(EIP)的核心概念,包括消息合并(Aggregator)、消息分拆(Splitter)、路由单(Routing Slip)、动态路由(Dynamic Router)及负载均衡(Load Balancer)等五大关键模式,并通过实例展示了这些模式的具体应用。


















 660
660

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








