supervisor 管理进程简明教程
有些服务不能存放在后台执行,保证不被异常中断,之前都是通过nohup、&、screen来实现。
现在通过supervisor进程管理工具可以实现进程管理,自带start/stop/restart/reload功能
一、安装
1:easy_install 安装: easy_install supervisor 2:pip 安装: pip install supervisor 3:Debian / Ubuntu可以直接通过apt安装: apt-get install supervisor
二、配置文件
1、使用说明
使用supervisor很简单。只需要修改一些配置文件,就可以使用了。
1.1 配置文件
通过apt-get install supervisor安装后,supervisor配置文件在:
/etc/supervisor/supervisord.conf
即可看到默认配置情况,但是一般情况下,我们都不要去修改默认的配置,其管理的子进程配置文件在:
/etc/supervisor/conf.d/*.conf然后
开始给自己需要的脚本程序编写进配置文件,让supervisor来管理它。放在/etc/supervisor/conf.d/目录下,以.conf作为扩展名(每个进程的配置文件都可以单独分拆也可以把相关的脚本放一起)。如任意定义一个和脚本相关的项目名称的选项组(/etc/supervisor/conf.d/test.conf):
#项目名
[program:blog]
#脚本目录
directory=/opt/bin
#脚本执行命令
command=/usr/bin/python /opt/bin/test.py
#supervisor启动的时候是否随着同时启动,默认True
autostart=true
#当程序exit的时候,这个program不会自动重启,默认unexpected
#设置子进程挂掉后自动重启的情况,有三个选项,false,unexpected和true。如果为false的时候,无论什么情况下,都不会被重新启动,如果为unexpected,只有当进程的退出码不在下面的exitcodes里面定义的
autorestart=false
#这个选项是子进程启动多少秒之后,此时状态如果是running,则我们认为启动成功了。默认值为1
startsecs=1
#日志输出
stderr_logfile=/tmp/blog_stderr.log
stdout_logfile=/tmp/blog_stdout.log
#脚本运行的用户身份
user = zhoujy
#把 stderr 重定向到 stdout,默认 false
redirect_stderr = true
#stdout 日志文件大小,默认 50MB
stdout_logfile_maxbytes = 20M
#stdout 日志文件备份数
stdout_logfile_backups = 20
[program:zhoujy] #说明同上
directory=/opt/bin
command=/usr/bin/python /opt/bin/zhoujy.py
autostart=true
autorestart=false
stderr_logfile=/tmp/zhoujy_stderr.log
stdout_logfile=/tmp/zhoujy_stdout.log
#user = zhoujy1.2 启动服务端
现在,让我们来启动supervisor服务。
/etc/init.d/supervisor start
查看supervisord 是否运行:
ps -ef | grep superviosrd
1.3 项目配置与运行:
在/etc/supervisor/conf.d/目录下,添加个CGHTTPServer.conf
[program:CGIHTTPServer] directory=/data/CGIHTTPServer command=nohup python2.7 -m CGIHTTPServer 8480 & user=root autostart=true autorestart=true redirect_stderr = true stdout_logfile = /var/log/supervisor/CGIHTTPServer.log stderr_logfile = /var/log/supervisor/CGIHTTPServer_error.log loglevel = error stdout_logfile_maxbytes = 200MB stdout_logfile_backups = 7
重启supervisor
/etc/init.d/supervisor restart
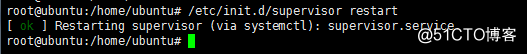
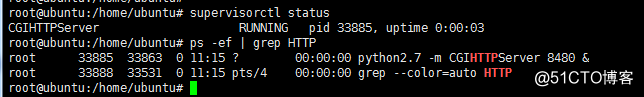
查看supervisorctl的进程管理
supervisorctl status
常用命令:
$ supervisorctl status
$ supervisorctl stop usercenter
$ supervisorctl start usercenter
$ supervisorctl restart usercenter
$ supervisorctl reread
$ supervisorctl update
参考地址:
https://www.cnblogs.com/zhoujinyi/p/6073705.html
https://www.jianshu.com/p/bf2b3f4dec73
centos:
http://www.eryajf.net/1903.html
转载于:https://blog.51cto.com/hellvenus/2389899























 1560
1560

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








