John Doe, a skilled pilot, enjoys traveling. While on vacation, he rents a small plane and starts visiting beautiful places. To save money, John must determine the shortest closed tour that connects his destinations. Each destination is represented by a point in the plane pi =< xi , yi >. John uses the following strategy: he starts from the leftmost point, then he goes strictly left to right to the rightmost point, and then he goes strictly right back to the starting point. It is known that the points have distinct x-coordinates. Write a program that, given a set of n points in the plane, computes the shortest closed tour that connects the points according to John’s strategy. Input The program input is from a text file. Each data set in the file stands for a particular set of points. For each set of points the data set contains the number of points, and the point coordinates in ascending order of the x coordinate. White spaces can occur freely in input. The input data are correct. Output For each set of data, your program should print the result to the standard output from the beginning of a line. The tour length, a floating-point number with two fractional digits, represents the result. Note: An input/output sample is in the table below. Here there are two data sets. The first one contains 3 points specified by their x and y coordinates. The second point, for example, has the x coordinate 2, and the y coordinate 3. The result for each data set is the tour length, (6.47 for the first data set in the given example). Sample Input 3 1 1 2 3 3 1 4 1 1 2 3 3 1 4 2 Sample Output 6.47 7.89
【分析】:
首先按横坐标递增给所有点排序。
定义状态dp[i][j]表示从点i向n走一条路L1,从点j向n走另一条路L2(如下图,两条路互不相交,并且L1在L2上面),L1 + L2的最小值。程序中用distance(i, j)表示点i到点j的距离。
如何计算dp[i, j]呢?
我们考虑k = max(i, j) + 1这个点,这个点肯定在L1或者L2上。
k在L1上时,k在L2上时,如图
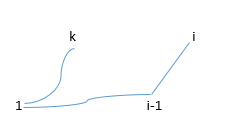
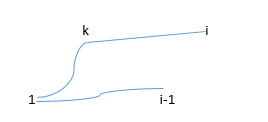
dp[i][j]取这两者最小值即可。
可能还是有点抽象,举个实际的例子吧。
假如i = 5, j = 4。在计算dp[5][4]的时候,考虑6这个点。6只有两种选择,要么在L1上(上面的路),这时候的代价为dp[6][4] + distance(5, 6)。要么在L2上(下面的路),这时候的代价为dp[5][6] + distance(4, 6)。
所以状态转移方程为:dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][k] + distance(j, k),dp[k][j] + distance(i, k))
一、临界情况
1. i = n: dp[i][j] = distance(j, n)
2. j = n: dp[i][j] = distance(i, n)
二、其余情况
k = max(i, j) + 1
dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][k] + distance(j, k), dp[k][j] + distance(i,k))
【讲解】:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_51cea4040100gkcq.html
【代码】:
#include <bits/stdc++.h> #include <cmath> #include <ctime> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <cstdlib> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; const int N = 205; double dp[N][N]; struct node { double x, y; bool operator < (const node& a) { return x < a.x; //按横坐标递增给所有点排序 } }a[N]; //bool cmp(node a,node b) //{ // return a.x > b.x; //} double dis(int i, int j) { return sqrt((a[i].x-a[j].x)*(a[i].x-a[j].x)+(a[i].y-a[j].y)*(a[i].y-a[j].y)); } int main() { int n; while(cin >> n) { for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) cin >> a[i].x >> a[i].y; sort(a+1, a+n+1); memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp)); for(int i=n; i>=1; i--){ for(int j=n; j>=1; j--){ if(i==n && j==n) dp[i][j]=0; else if(j==n) dp[i][j]=dis(i,n); else if(i==n) dp[i][j]=dis(j,n); else{ int k=max(i,j)+1; dp[i][j]=min(dp[i][k]+dis(j,k), dp[k][j]+dis(i,k)); } } } printf("%.2f\n", dp[1][1]); } }




 本文介绍了一种计算平面中给定点集的最短封闭旅行路径的方法。该算法首先按横坐标对点进行排序,然后使用动态规划求解从左至右再返回起点的最短路径。适用于希望节省旅行费用并遍访特定地点的应用场景。
本文介绍了一种计算平面中给定点集的最短封闭旅行路径的方法。该算法首先按横坐标对点进行排序,然后使用动态规划求解从左至右再返回起点的最短路径。适用于希望节省旅行费用并遍访特定地点的应用场景。
















 245
245

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








