Spring MVC的Control主要由HandlerMapping和HandlerAdapter两个组件提供。
HandlerMapping负责映射用户的URL和对应的处理类,HandlerMapping并没有规定这个URL与应用的处理类如何映射,在HandlerMapping接口中只定义了根据一个URL必须返回一个由HandlerExecutionChain代表的处理链,我们可以在这个处理链中添加任意的HandlerAdapter实例来处理这个URL的对应的请求。
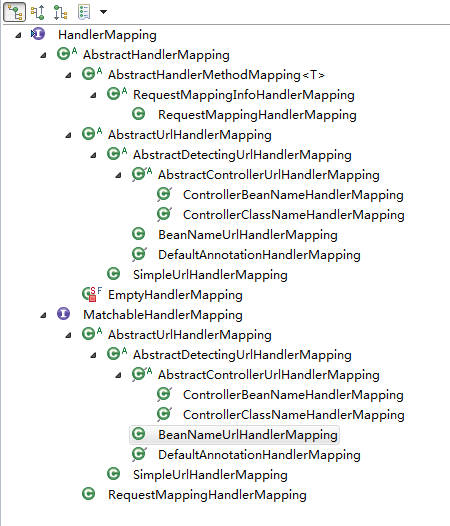
HandlerMapping的继承关系如下:
HandlerMapping中只定义了一个getHandler的api:
1 /** 2 * Return a handler and any interceptors for this request. The choice may be made 3 * on request URL, session state, or any factor the implementing class chooses. 4 * <p>The returned HandlerExecutionChain contains a handler Object, rather than 5 * even a tag interface, so that handlers are not constrained in any way. 6 * For example, a HandlerAdapter could be written to allow another framework's 7 * handler objects to be used. 8 * <p>Returns {@code null} if no match was found. This is not an error. 9 * The DispatcherServlet will query all registered HandlerMapping beans to find 10 * a match, and only decide there is an error if none can find a handler. 11 * @param request current HTTP request 12 * @return a HandlerExecutionChain instance containing handler object and 13 * any interceptors, or {@code null} if no mapping found 14 * @throws Exception if there is an internal error 15 */ 16 HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception;
AbstractHandlerMapping继承了WebApplicationObjectSupport,其主要方法有:
setServletContext()
initApplicationContext()
initServletContext()
getWebApplicationContext()
getServletContext()
即WebApplicationObjectSupport主要用来提供上下文ApplicationContext和ServletContext.
AbstractHandlerMapping中实现了getHandler(),查找给定请求的handler,如果没有找到特定的请求,则返回到默认处理程序,源代码如下:
1 /** 2 * Look up a handler for the given request, falling back to the default 3 * handler if no specific one is found. 4 * @param request current HTTP request 5 * @return the corresponding handler instance, or the default handler 6 * @see #getHandlerInternal 7 */ 8 @Override 9 public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { 10 Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request); 11 if (handler == null) { 12 handler = getDefaultHandler(); 13 } 14 if (handler == null) { 15 return null; 16 } 17 // Bean name or resolved handler? 18 if (handler instanceof String) { 19 String handlerName = (String) handler; 20 handler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName); 21 } 22 23 HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request); 24 if (CorsUtils.isCorsRequest(request)) { 25 CorsConfiguration globalConfig = this.globalCorsConfigSource.getCorsConfiguration(request); 26 CorsConfiguration handlerConfig = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request); 27 CorsConfiguration config = (globalConfig != null ? globalConfig.combine(handlerConfig) : handlerConfig); 28 executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config); 29 } 30 return executionChain; 31 }
预留了getHandlerInternal()方法给子类实现。
getHandlerExecutionChain()方法是封装拦截器到HandlerExecutionChain,其源码为:
1 /** 2 * Build a {@link HandlerExecutionChain} for the given handler, including 3 * applicable interceptors. 4 * <p>The default implementation builds a standard {@link HandlerExecutionChain} 5 * with the given handler, the handler mapping's common interceptors, and any 6 * {@link MappedInterceptor}s matching to the current request URL. Interceptors 7 * are added in the order they were registered. Subclasses may override this 8 * in order to extend/rearrange the list of interceptors. 9 * <p><b>NOTE:</b> The passed-in handler object may be a raw handler or a 10 * pre-built {@link HandlerExecutionChain}. This method should handle those 11 * two cases explicitly, either building a new {@link HandlerExecutionChain} 12 * or extending the existing chain. 13 * <p>For simply adding an interceptor in a custom subclass, consider calling 14 * {@code super.getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request)} and invoking 15 * {@link HandlerExecutionChain#addInterceptor} on the returned chain object. 16 * @param handler the resolved handler instance (never {@code null}) 17 * @param request current HTTP request 18 * @return the HandlerExecutionChain (never {@code null}) 19 * @see #getAdaptedInterceptors() 20 */ 21 protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) { 22 HandlerExecutionChain chain = (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain ? 23 (HandlerExecutionChain) handler : new HandlerExecutionChain(handler)); 24 25 String lookupPath = this.urlPathHelper.getLookupPathForRequest(request); 26 for (HandlerInterceptor interceptor : this.adaptedInterceptors) { 27 if (interceptor instanceof MappedInterceptor) { 28 MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor = (MappedInterceptor) interceptor; 29 if (mappedInterceptor.matches(lookupPath, this.pathMatcher)) { 30 chain.addInterceptor(mappedInterceptor.getInterceptor()); 31 } 32 } 33 else { 34 chain.addInterceptor(interceptor); 35 } 36 } 37 return chain; 38 }




 本文深入探讨SpringMVC框架中的HandlerMapping和HandlerAdapter组件作用及其实现原理,重点介绍了HandlerMapping接口及其getHandler方法的功能,包括如何通过该方法获取处理器实例并构建处理链。
本文深入探讨SpringMVC框架中的HandlerMapping和HandlerAdapter组件作用及其实现原理,重点介绍了HandlerMapping接口及其getHandler方法的功能,包括如何通过该方法获取处理器实例并构建处理链。
















 1549
1549

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








