1、 JDBC编程
JDBC的配置:
一、配置的内容主要有下载相关的数据库驱动,一般为JAR的格式文件,根据核心编程的说法,如果该JAR文件里面含有META-INF/services/java.sql.Driver的文件可以自动注册驱动,也就是不必使用手动方式进行注册:
1、驱动类方式进行注册:
Class.forName(“org.XXX.Driver”);
2、设置jdbc.drivers的属性
System.setProperty(“jdbc.drivers”,”org.XXX.Driver”)
我们翻查java的API文档,找到Class.forName,发现有两种方式:
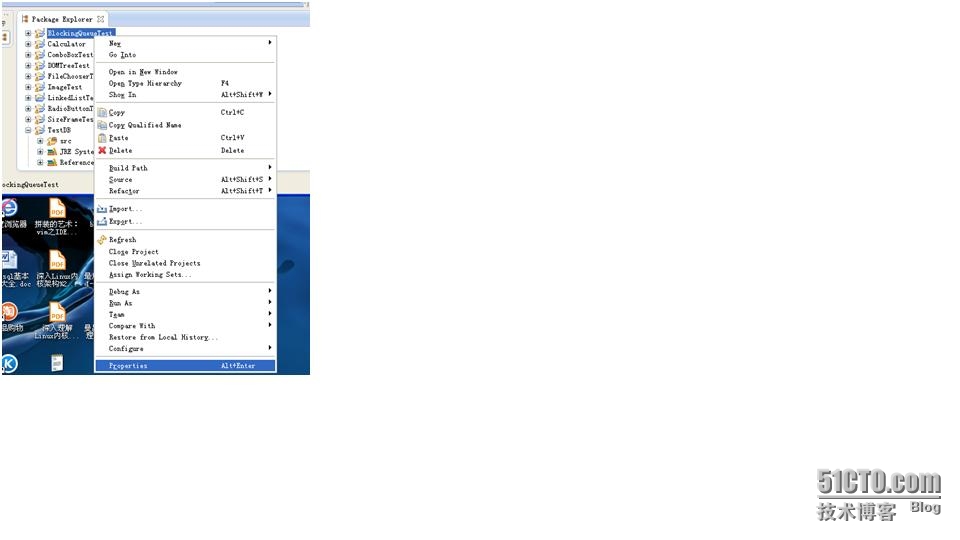
一、 forName publicstatic Class<?>forName(String className) throwsClassNotFoundException 二、 forName public static Class<?>forName(String name, boolean initialize, ClassLoader loader) throwsClassNotFoundException 文档上说明第一种方式其实是第二种方式的特殊情况 Invoking this method is equivalent to: Class.forName(className, true, currentLoader) wherecurrentLoader denotes the definingclass loader of the current class. 如果相关的驱动支持自动注册则不需要再进行手动注册。 我们刚开始使用eclipse进行JDBC编程的时候,下载了相关的驱动文件可能不会用,设置的方法如下: 选择相关的项目的属性
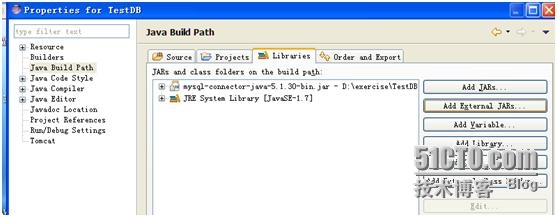
然后选择Java BuilderPath选择Add ExternalJARS,然后选择下载的相关数据库驱动JAR文件
下面说说相关的JDBC编程,这里使用了JAVA核心编程例子的部分代码:
runTest();Java核心编程最基本的sql语句的执行
storeim();存储相关的图片到mysql上面(该程序不能使用太大的图片,应该是Blob的类型设置的原因,否则会报一个数据过长的错误)
关于stroeimg主要是使用核心编程中的OLB的方式,不过发现书中有些错误,比如
longoff = 1;
OutputStream out = coverBlob.setBinaryStream(off);
书中off设置为0,然而跟进源码的时候发现,最小值不能小于1,否则抛出异
publicsynchronizedOutputStreamsetBinaryStream(longindexToWriteAt)throwsSQLException {
checkClosed();
if (indexToWriteAt< 1) {
throwSQLError.createSQLException(Messages.getString("Blob.0"),//$NON-NLS-1$
SQLError.SQL_STATE_ILLEGAL_ARGUMENT, this.exceptionInterceptor);
}
WatchableOutputStreambytesOut = newWatchableOutputStream();
bytesOut.setWatcher(this);
if (indexToWriteAt>0) {
bytesOut.write(this.binaryData, 0, (int) (indexToWriteAt- 1));
}
returnbytesOut;
}另外使用ImageIO.write(coverImage,"png", out);之后需要关闭out,在JAVA核心编程的流文件的章节提到过这个问题,如果不关闭out,那么out的数据可能永远也不会输出到coverBlob。
该语句的意思是把图片的写入相关的输出流
注意:测试发现,使用out.flush没作用。在OutputStream的API有这样一段话
If the intended destination of this stream is an abstraction provided bythe underlying operating system, for example a file, then flushing the streamguarantees only that bytes previously written to the stream are passed to theoperating system for writing; it does not guarantee that they are actuallywritten to a physical device such as a disk drive.
也就是说flush不保证传递的数据和硬盘读取的数据一样,它只是将当前拥有的数据传递过去。
**
* 存储图像数据到MYSQL
* @throwsSQLException
* @throwsIOException
*/
publicstaticvoidstorimg() throwsSQLException,IOException
{
Connection imconn = getConnect();
try
{
//创建Blob的对象用于存储图像的二进制数据
Blob coverBlob = imconn.createBlob();
long off = 1;
//创建一个输出流用于写Blob的对象,并设置开始写入的位置off
OutputStream out = coverBlob.setBinaryStream(off);
//从磁盘读取图像文件,并写入到相关的输出流
BufferedImagecoverImage = ImageIO.read(new File("12.png"));
ImageIO.write(coverImage, "png", out);
//关闭输出流,保证数据输出到Blob的对象
out.close();
//下面的是SQL的预执行语句,用于存储图像数据
PreparedStatement stat =imconn.prepareStatement("INSERT INTOimg VALUES(?,?)");
stat.setString(1,"isbn");
stat.setBlob(2, coverBlob);
stat.executeUpdate();
}
finally
{
imconn.close();
}
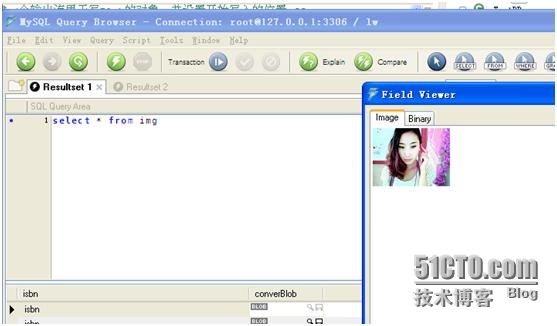
}最后效果如下
转载于:https://blog.51cto.com/9162220/1439978




 本文介绍了JDBC编程的基本配置及使用方法,包括数据库驱动的安装与注册,并详细讲解了如何通过JDBC将图片存储到MySQL数据库中。
本文介绍了JDBC编程的基本配置及使用方法,包括数据库驱动的安装与注册,并详细讲解了如何通过JDBC将图片存储到MySQL数据库中。
















 169
169

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








