我们来看下IO的基本类图:
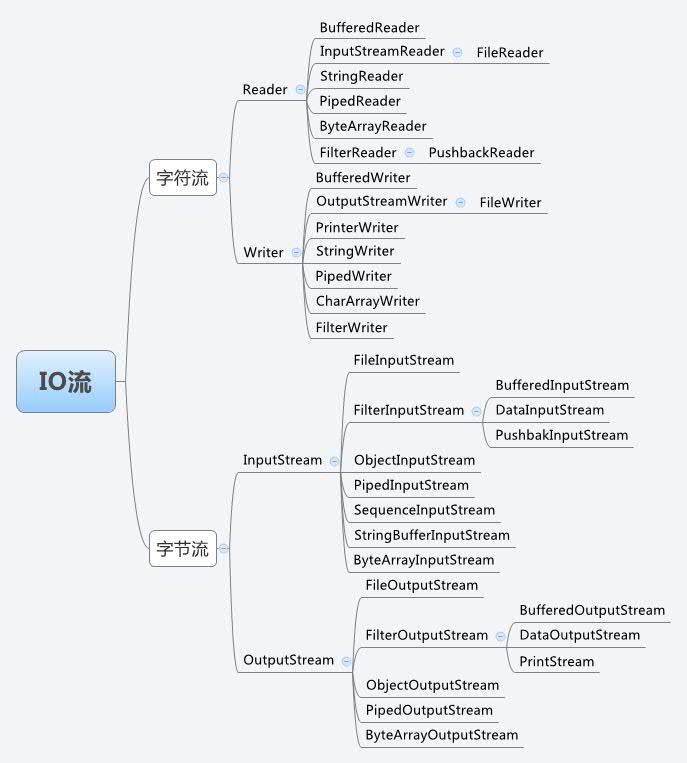
我需要牢牢抓住的就是4个主类:InputStream,OutputStream,Reader,Writer,这里我只学习下InputStream,这样OutputStream也可以解决了。
所有在InputStream下面的类都是为了配合一种流,也就可以理解为什么要衍生出这么多类了,毕竟数据流的类型太多了。
来看下InputStream的三个read方法源码:
有一点好记,所有的read方法返回-1就算读完啦。
InputStream 中的read()方法:一个抽象方法,让子类实现去了。
public abstract int read() throws IOException;
read(byte b[])方法:
public int read(byte b[]) throws IOException {
// 调用了read(byte b[], int off, int len)
return read(b, 0, b.length);
}
read(byte b[], int off, int len)方法:
看下它的API:
将输入流中最多 len 个数据字节读入字节数组。尝试读取多达 len 字节,但可能读取较少数量。以整数形式返回实际读取的字节数。
在输入数据可用、检测到流的末尾或者抛出异常前,此方法一直阻塞。
如果 b 为 null,则抛出 NullPointerException。
如果 off 为负,或 len 为负,或 off+len 大于数组 b 的长度,则抛出 IndexOutOfBoundsException。
如果 len 为 0,则没有字节可读且返回 0;否则,要尝试读取至少一个字节。如果因为流位于文件末尾而没有可用的字节,则返回值 -1;否则,至少可以读取一个字节并将其存储在 b 中。
将读取的第一个字节存储在元素 b[off] 中,下一个存储在 b[off+1] 中,依次类推。读取的字节数最多等于 len。让 k 为实际读取的字节数;这些字节将存储在元素 b[off] 至 b[off+k-1] 之间,其余元素 b[off+k] 至 b[off+len-1] 不受影响。
在任何情况下,元素 b[0] 至 b[off] 和元素 b[off+len] 至 b[b.length-1] 都不会受到影响。
如果不是因为流位于文件末尾而无法读取第一个字节,则抛出 IOException。特别是,如果输入流已关闭,则抛出 IOException。
FileInputStream类用来对付文件流的,可以这么想把它可以把一个文件变成InputStream。
来看下它的read()方法:
public native int read() throws IOException;
好吧,都到native了,(native方法是指本地方法,当在方法中调用一些不是由java语言写的代码或者在方法中用java语言,直接操纵计算机硬件时要声明为native方法,java中,通过JNI(Java Native Interface,java本地接口)来实现本地化)
据说是交给c库实现了...
关于它的使用比较常见吧:
以前写的拷贝的方法:
private void copyFile(String fromPath, String toPath) throws IOException {
// input
File fromFile = new File(fromPath);
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(fromFile);
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(is);
// output
File toFile = new File(toPath);
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(toFile);
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(os);
// transfer station
byte b[] = new byte[(int) fromFile.length()];
while (bis.read(b, 0, b.length) != -1) {
bos.write(b, 0, b.length);
}
bis.close();
bos.close();
}
DataInputStream类是来对付读取基本 Java 数据类型的。
它有:
|
|
ByteArrayInputStream是为了把内存中的数据读到字节数组中。
网上共享的代码:是DataInputStream结合ByteArrayInputStream的使用
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ByteArrayTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ByteArrayOutputStream bout = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
DataOutputStream dout = new DataOutputStream(bout);
String name = "dc";
int age = 94;
dout.writeUTF(name);
dout.writeInt(age);
byte[] buff = bout.toByteArray();// byte数组作为中间值了
ByteArrayInputStream bin = new ByteArrayInputStream(buff);
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(bin);
String newName = dis.readUTF();
int newAge = dis.readInt();
System.out.println(newName + ":" + newAge);
}
}
类似上面一层层包着的感觉提供张图更直观:
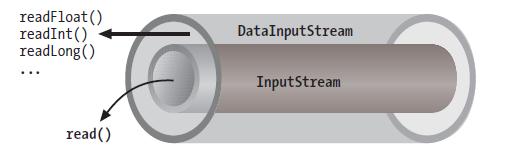
我们甚至可以一层层的装饰下去。







 本文详细介绍了 Java 中的 IO 流概念,重点讲解 InputStream 类及其子类 FileInputStream 和 DataInputStream 的使用方法。通过示例展示了如何利用这些类进行文件拷贝及从字节数组中读取基本 Java 数据类型。
本文详细介绍了 Java 中的 IO 流概念,重点讲解 InputStream 类及其子类 FileInputStream 和 DataInputStream 的使用方法。通过示例展示了如何利用这些类进行文件拷贝及从字节数组中读取基本 Java 数据类型。

















 2104
2104

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








