The L1 Median (Weber 1909) 链接网址
Derived from a transportation cost minimization problem, the L1 median is defined to be any point which minimizes the sum of Euclidean distances to all points in the data set (fig.2).
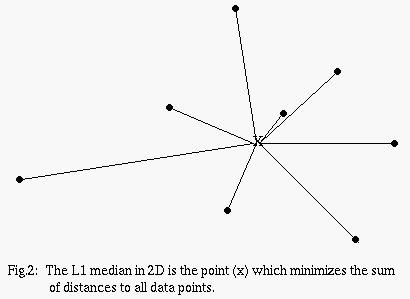
As with most median definitions, the L1 median need not be one of the data. However, it is known to be a unique point in 2D or higher. The L1 is well known to reduce to the standard univariate median. Another similarity is that any measurement X of the data set can be moved along the vector from L1 to X without changing the value of the median. The breakdown point of the L1 median has been found to be 1/2. This is evident by noticing that if we place just over 50% of the data at one point, then the median will always stay there (fig.3). This idea can be extended to any data set within a bounded region: when just under 50% of the data is moved to infinity, the median remains in the vicinity of the majority of the data, since the bounded region resembles a point from infinity.

At present I am not aware of any solutions for finding the L1 median.
http://cgm.cs.mcgill.ca/~athens/Geometric-Estimators/location.html























 4546
4546

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








