对象 序列 运算 回顾
[注]所有的序列都是一个可迭代对象。
类: 数据+方法
实例的调用接口,或支持的操作。
3+5
3.add()
列表和字典
变量名:没有类型,存储在一个位置,指向对象的引用。
对象:存储在另一个位置。
python是动态语言,在python中引用是可以临时修改的。因此一个变量名引用的是整形对象,下一步可以任意指向其他一种对象,如列表对象,字典对象等等。如果某个对象不被引用,或引用计数为零时,那么这个对象就可被称为垃圾回收器所回收的对象。但事实上,python虚拟机可能在内部使用时可能不会立即回收,因为后续的引用有可能还会指向它。
a=3
a={}
x=3
点号运算符:
1属性:调用对象里面变量名 数据 返回一个数据,显示则要使用print语句
2方法:调用操作() 执行方法内部的一段代码
可调用对象: callable()
1 函数
2方法
3类
字串:‘ ’, “” ,‘’‘ ’‘‘,”“” “”“
列表:[]
元组:()
操作:
list
list.append()
list.insert()
list.count()
list.index()
list.extend()
list.pop()
list.remove()
list.sort()
list.reverse()
dict.has_key() 字典中的键是否存在
dict.get()
dict.iteritems() 返回一个迭代器对象 可以使用next 返回元素的对象使用next()返回元素的值
dict.keys()
dict.items()
python3中所有的dict的内置方法
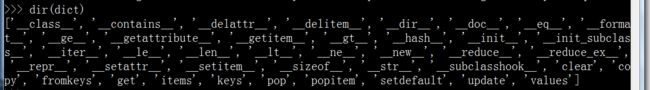
如何获取使用帮助:
获取对象支持使用的属性和方法:dir()
某方法的具体使用帮助: help()
获取可调用对象的文档字符串:print(obj.doc)
集合
集合:是一组无序排列、可哈希对象的值。
支持数学中的关系测试
也支持成员关系测试: in not in 迭代
不支持:索引、元素获取、切片
集合的类型:set(),frozenset() 这两个就是工厂函数
没有特定语法格式,只能通过工厂函数创建
python3 help(set)
class set(object)
| set() -> new empty set object
| set(iterable) -> new set object
|
| Build an unordered collection of unique elements.
|
| Methods defined here:
|
| and(self, value, /)
| Return self&value.
|
| contains(…)
| x.contains(y) <> y in x.
|
| eq(self, value, /)
| Return selfvalue.
|
| ge(self, value, /)
| Return self>=value.
|
| getattribute(self, name, /)
| Return getattr(self, name).
|
| gt(self, value, /)
| Return self>value.
|
| iand(self, value, /)
| Return self&=value.
|
| init(self, /, *args, **kwargs)
| Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature.
|
| ior(self, value, /)
| Return self|=value.
|
| isub(self, value, /)
| Return self-=value.
|
| iter(self, /)
| Implement iter(self).
|
| ixor(self, value, /)
| Return self^=value.
|
| le(self, value, /)
| Return self<=value.
|
| len(self, /)
| Return len(self).
|
| lt(self, value, /)
| Return self|
| ne(self, value, /)
| Return self!=value.
|
| new(*args, **kwargs) from builtins.type
| Create and return a new object. See help(type) for accurate signature.
|
| or(self, value, /)
| Return self|value.
|
| rand(self, value, /)
| Return value&self.
|
| reduce(…)
| Return state information for pickling.
|
| repr(self, /)
| Return repr(self).
|
| ror(self, value, /)
| Return value|self.
|
| rsub(self, value, /)
| Return value-self.
|
| rxor(self, value, /)
| Return value^self.
|
| sizeof(…)
| S.sizeof() -> size of S in memory, in bytes
|
| sub(self, value, /)
| Return self-value.
|
| xor(self, value, /)
| Return self^value.
|
| add(…)
| Add an element to a set.
|
| This has no effect if the element is already present.
|
| clear(…)
| Remove all elements from this set.
|
| copy(…)
| Return a shallow copy of a set.
|
| difference(…)
| Return the difference of two or more sets as a new set.
|
| (i.e. all elements that are in this set but not the others.)
|
| difference_update(…)
| Remove all elements of another set from this set.
|
| discard(…)
| Remove an element from a set if it is a member.
|
| If the element is not a member, do nothing.
|
| intersection(…)
| Return the intersection of two sets as a new set.
|
| (i.e. all elements that are in both sets.)
|
| intersection_update(…)
| Update a set with the intersection of itself and another.
|
| isdisjoint(…)
| Return True if two sets have a null intersection.
|
| issubset(…)
| Report whether another set contains this set.
|
| issuperset(…)
| Report whether this set contains another set.
|
| pop(…)
| Remove and return an arbitrary set element.
| Raises KeyError if the set is empty.
|
| remove(…)
| Remove an element from a set; it must be a member.
|
| If the element is not a member, raise a KeyError.
|
| symmetric_difference(…)
| Return the symmetric difference of two sets as a new set.
|
| (i.e. all elements that are in exactly one of the sets.)
|
| symmetric_difference_update(…)
| Update a set with the symmetric difference of itself and another.
|
| union(…)
| Return the union of sets as a new set.
|
| (i.e. all elements that are in either set.)
|
| update(…)
| Update a set with the union of itself and others.
Data and other attributes defined here:
hash = None
python3中set支持的方法:


#创建set集合 参数必须是可迭代的对象 Iterator
>>> s1=set([1,2,3,4])
>>> print(s1)
{1, 2, 3, 4}
>>> s2=set([2,3,4,5])
#取集合的交集的两种方法 & 内置方法: intersection()
>>> s1&s2
{2, 3, 4}
>>> s1.intersection(s2)
{2, 3, 4}
#取两个序列的并集 两种方法 | 内置方法:symmetric_difference()
>>> s1.symmetric_difference(s2)
{1, 5}
>>> s1|s2
{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
>>> s3=set("xyz")
>>> print(s3)
{'y', 'z', 'x'}
#取出集合中的值并在集合中删除掉
>>> s3.pop()
'y'
>>> print(s3)
{'z', 'x'}
`>>> id(s1)
49969416
>>> print(s1,s3)
{1, 2, 3, 4} {'z', 'x'}
#在原集合的基础初上加上一个集合 对象的引用没有变 相当于合并集合
>>> s1.update(s3)
>>> id(s1)
49969416
>>> print(s1)
{1, 2, 3, 4, 'z', 'x'}
#添加新的元素到集合当中去
>>> s1.add(7)
>>> s1.add("jerry")
>>> print(s1)
{1, 2, 3, 4, 'z', 'x', 7, 'jerry'}
>>> s4=set(["xiaopang","like","home"])
>>> print(s4)
{'home', 'like', 'xiaopang'}
容器、类型、对象 小结
1:列表、元组,字典可以在不使用换行符的情况下直接分布的写于多个行上,另外最后一个元素后面允许使用逗号,如果没有元素时不允许使用逗号的。
2:所有对象都有引用计数,为某个对象指定一个新的变量名称或者将某个对象放入一个容器当中时,都会导致其引用计数增加,当引用计数为0时,都会导致垃圾回收机制的回收此对象。另外使用del()语句执行删除操作或者是某次引用的修改超出当前对象的作用域时,那么对象的引用计数就会减少。sys.getrefcount(a)可以计数当前变量的引用次数。
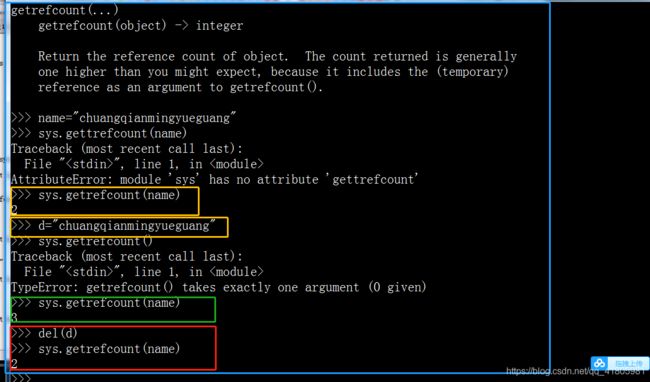
3.列表和字典都支持两种类型的复制操作;潜复制和深复制。潜复制会创建一个新对象,但是它是对原始对象中中所包含对象的引用,因此它们指向的是同样的内存地址。深复制则创建一个新对象,并且递归复制它所包含的所有对象。深复制就是原来的对象的修改并不会导致复制后的新的对象的修改。深复制的方法可使用 copy模块中deepcopy()来使用。
4:python中的所有对象都是"第一类的”,这意味着使用标示符命名的所有对象都具有相同状态,于是能够命名所有对象都可以直接当数据进行处理。
5:序列表示为索引为非负整数的有序对象集合,包括字符串、列表、元组,字符串是字符的序列,而列表和元组则是任意python对象的序列。字符串和元组不可变,列表和字典则是可变的。列表支持元素的插入,替换等操作。所有序列都支持迭代。
6:所有序列都支持的操作方法:
1:s[i] 索引
2: s[i:j] 切片
3:s[i:j:stride] 扩展切片
4:len()求长度
5:max()最大值
6:min()最小值
7:sum() 数值序列的求和
8:all()判断序列中是否存在False
9:any() 判断任意为True
10:s1+s2 连接
11:s1*N 重复
12:obj in s1:成员关系判断
13:obj not in s1 :非成员关系判断
7.可变序列的操作:
1.s1[index]=value 元素赋值
2.s1[i:j]=t 切片赋值
3.del s1[index] 删除序列中指定索引位置的元素
4.del s1[i:j] 删除序列中的某个切片
5:del s1[i:j:stride] 删除序列中的扩展切片
完结
下一篇 python表达式和语句




 本文回顾了Python中的序列、对象和运算,强调了Python作为动态语言的特性,如变量名无类型、引用可修改。详细介绍了集合的特性和方法,如交集、并集、差集操作,并探讨了集合的创建、更新和删除元素的方法。同时,总结了Python序列的基本操作,包括索引、切片、迭代和常用方法。
本文回顾了Python中的序列、对象和运算,强调了Python作为动态语言的特性,如变量名无类型、引用可修改。详细介绍了集合的特性和方法,如交集、并集、差集操作,并探讨了集合的创建、更新和删除元素的方法。同时,总结了Python序列的基本操作,包括索引、切片、迭代和常用方法。
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








