CLOSE_WAIT连接过多的现象分析与处理
未分类
1. CLOSE_WAIT的机制和原理一.
来自参考资料:从问题看本质: 研究TCP close_wait的内幕
客户端主动发起 socket.close时
假设我们有一个client, 一个server.
当client主动发起一个socket.close()这个时候对应TCP来说,会发生什么事情呢?如下图所示.
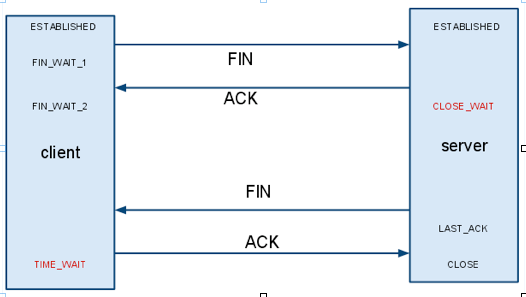
client首先发送一个FIN信号给server, 这个时候client变成了FIN_WAIT_1的状态, server端收到FIN之后,返回ACK,然后server端的状态变成了CLOSE_WAIT.
接着server端需要发送一个FIN给client,然后server端的状态变成了LAST_ACK,接着client返回一个ACK,然后server端的socket就被成功的关闭了.
从这里可以看到,如果由客户端主动关闭一链接,那么客户端是不会出现CLOSE_WAIT状态的.客户端主动关闭链接,那么Server端将会出现CLOSE_WAIT的状态.
服务器端主动发起 socket.close 时
那么当server主动发起一个socket.close(),这个时候又发生了一些什么事情呢.

从图中我们可以看到,如果是server主动关闭链接,那么Client则有可能进入CLOSE_WAIT,如果Client不发送FIN包,那么client就一直会处在CLOSE_WAIT状态(后面我们可以看到有参数可以调整这个时间).
结论
谁主动关闭链接,则对方则可能进入CLOSE_WAIT状态,除非对方达到超时时间,主动关闭。
服务器端的设置
如果我们的tomcat既服务于浏览器,又服务于其他的APP,而且我们把connection的keep-alive时间设置为10分钟,那么带来的后果是浏览器打开一个页面,然后这个页面一直不关闭,那么服务器上的socket也不能关闭,它所占用的FD也不能服务于其他请求.如果并发一高,很快服务器的资源将会被耗尽.新的请求再也进不来. 那么如果把keep-alive的时间设置的短一点呢,比如15s? 那么其他的APP来访问这个服务器的时候,一旦这个socket, 15s之内没有新的请求,那么客户端APP的socket将出现大量的CLOSE_WAIT状态.
所以如果出现这种情况,建议将你的server分开部署,服务于browser的部署到单独的JVM实例上,保持keep-alive为15s,而服务于架构中其他应用的功能部署到另外的JVM实例中,并且将keep-alive的时间设置的更
长,比如说1个小时.这样客户端APP建立的connection,如果在一个小时之内都没有重用这条connection,那么客户端的socket才会进入CLOSE_WAIT的状态.针对不同的应用场景来设置不同的keep-alive时间,可以帮助我们提高程序的性能.
2. CLOSE_WAIT的机制和原理二(附实例代码)
来自参考资料:
This is strictly a violation of the TCP specification
TCP: About FIN_WAIT_2, TIME_WAIT and CLOSE_WAIT
产生机制


Time to raise the curtain of doubt. Here is what happens.
The listening application leaks sockets, they are stuck in CLOSE_WAIT TCP state forever. These sockets look like (127.0.0.1:5000, 127.0.0.1:some-port). The client socket at the other end of the connection is (127.0.0.1:some-port, 127.0.0.1:5000), and is properly closed and cleaned up.
When the client application quits, the (127.0.0.1:some-port, 127.0.0.1:5000) socket enters the FIN_WAIT_1 state and then quickly transitions to FIN_WAIT_2. The FIN_WAIT_2 state should move on to TIME_WAIT if the client received FIN packet, but this never happens. The FIN_WAIT_2 eventually times out. On Linux this is 60 seconds, controlled by net.ipv4.tcp_fin_timeout sysctl.
This is where the problem starts. The (127.0.0.1:5000, 127.0.0.1:some-port) socket is still in CLOSE_WAIT state, while (127.0.0.1:some-port, 127.0.0.1:5000) has been cleaned up and is ready to be reused. When this happens the result is a total mess. One part of the socket won't be able to advance from the SYN_SENT state, while the other part is stuck in CLOSE_WAIT. The SYN_SENT socket will eventually give up failing with ETIMEDOUT.
sysctl-a|grep ipv4|grep timeout
kernel.hung_task_timeout_secs=120
net.ipv4.route.gc_timeout=300
net.ipv4.tcp_fin_timeout=60
net.ipv4.tcp_thin_linear_timeouts=0
实例问题代码
// This is a trivial TCP server leaking sockets.
packagemain
import(
"fmt"
"net"
"time"
)
func handle(conn net.Conn){
defer conn.Close()
for{
time.Sleep(time.Second)
}
}
func main(){
IP:=""
Port:=5000
listener,err:=net.Listen("tcp4",fmt.Sprintf("%s:%d",IP,Port))
iferr!=nil{
panic(err)
}
i:=0
for{
ifconn,err:=listener.Accept();err==nil{
i+=1
ifi<800{
go handle(conn)
}else{
conn.Close()
}
}else{
panic(err)
}
}
}
重现CLOSE_WAIT
启动服务端
# go build listener.go && ./listener &
# ss -n4tpl 'sport = :5000'
StateRecv-QSend-QLocalAddress:PortPeerAddress:Port
LISTEN0128*:5000*:*users:(("listener",pid=15158,fd=3))
启动客户端,用nc
ss-n4tpl'sport = :5000'
StateRecv-QSend-QLocalAddress:PortPeerAddress:Port
LISTEN0128*:5000*:*users:(("listener",pid=15158,fd=3))
ESTAB00127.0.0.1:5000127.0.0.1:47810users:(("listener",pid=15158,fd=5))
可以看到启动了一个socket连接,客户端端口是47810.
杀死客户端
kill`pidof nc`
服务端连接进入CLOSE_WAIT.
ss-n4tp|grep5000
CLOSE-WAIT10127.0.0.1:5000127.0.0.1:47810users:(("listener",pid=15158,fd=5))
TCP设计说明
It seems that the design decisions made by the BSD Socket API have unexpected long lasting consequences. If you think about it - why exactly the socket can automatically expire the FIN_WAIT state, but can't move off from CLOSE_WAIT after some grace time. This is very confusing... And it should be! The original TCP specification does not allow automatic state transition after FIN_WAIT_2 state! According to the spec FIN_WAIT_2 is supposed to stay running until the application on the other side cleans up.
Let me leave you with the tcp(7) manpage describing the tcp_fin_timeout setting:
tcp_fin_timeout(integer;default:60)
Thisspecifies how many seconds to waitforafinalFIN packet before the socketisforcibly closed.Thisisstrictly a violation of the TCP specification,but required to prevent
denial-of-service attacks.
I think now we understand why automatically closing FIN_WAIT_2 is strictly speaking a violation of the TCP specification.
3. CLOSE_WAIT 处理说明
如果您发现与给定进程相关的连接往往总是处于CLOSE_WAIT状态,则意味着此进程在被动关闭后不执行活动关闭。编写通过TCP进行通信的程序时,应检测远程主机何时关闭连接并正确关闭套接字。如果您未能执行此操作,则套接字将保留在CLOSE_WAIT中,直到进程本身消失。
所以基本上,CLOSE_WAIT意味着操作系统知道远程应用程序已关闭连接并等待本地应用程序也这样做。因此,您不应尝试调整TCP参数来解决此问题,但请检查拥有本地主机上的连接的应用程序。由于没有CLOSE_WAIT超时,连接可以永远保持这种状态(或者至少在程序最终关闭连接或进程存在或被杀死之前)。
如果您无法修复应用程序或修复它,解决方案是终止打开连接的进程。当然,由于本地端点仍然可以在缓冲区中发送数据,因此仍然存在丢失数据的风险。此外,如果许多应用程序在同一进程中运行(就像Java Enterprise应用程序的情况一样),那么终止拥有进程并不总是一种选择。
我没有尝试使用tcpkill,killcx或者cutter强制关闭CLOSE_WAIT连接但是如果你不能杀死或重启持有连接的进程,那么它可能是一个选项。
4. 查看CLOSE_WAIT的ip与端口连接对
netstat-tulnap|grep CLOSE_WAIT|sed-e's/::ffff://g'|awk'{print $4,$5}'|sed's/:/ /g'
结果举例:
172.26.59.197808854.241.136.3444690
172.26.59.1978088171.48.17.7747220
172.26.59.197808854.241.136.3457828
172.26.59.1978088157.230.119.23955920
172.26.59.1978088157.230.119.23959650
172.26.59.1978088157.230.119.23944418
172.26.59.1978088157.230.119.23947634
172.26.59.1978088157.230.119.23934940
每一行是一对CLOSE_WAIT的socket连接。示例是服务器端的连接。
5. 杀死 CLOSE_WAIT的perl代码
apt-getinstall libnet-rawip-perl libnet-pcap-perl libnetpacket-perl
git clone https://github.com/rghose/kill-close-wait-connections.git
cd kill-close-wait-connections
mv kill_close_wait_connections.pl/usr/bin/kill_close_wait_connections
chmod+x/usr/bin/kill_close_wait_connections
ubuntu 准备
apt-getinstall libnet-rawip-perl libnet-pcap-perl libnetpacket-perl
CentOS准备
yum-y install perl-Net-Pcaplibpcap-devel perl-NetPacket
curl-L http://cpanmin.us | perl - --sudo App::cpanminus
cpanmNet::RawIP
cpanmNet::Pcap
cpanmNetPacket
安装
wget http://39.106.122.67/ctorrent/kill_close_wait_connections.pl
mv kill_close_wait_connections.pl/usr/bin/kill_close_wait_connections
chmod+x/usr/bin/kill_close_wait_connections
执行
kill_close_wait_connections
6. 杀死tcp 的其他命令与说明
资料1来源
Kill an active TCP connection内容
Some notes on killing a TCP connection...
Info gathering
(remember to be root!)lsof | awk '{ print $2; }' | sort -rn | uniq -c | sort -rn | head
lsof | grep
netstat -tonp
Killcx deps: libnet-rawip-perl libnet-pcap-perl libnetpacket-perl
tcpkill deps: dsniff
Motivations
CLOSE_WAIT related
资料2来源
Kill tcp connection with tcpkill on CentOS 内容
Install tcpkill
yum-y install dsniff--enablerepo=epel
View connections
netstat-tnpa|grep ESTABLISHED.*sshd.
Block with ip tables
iptables-A INPUT-s IP-ADDRESS-j DROP
Kill connection
tcpkill-i eth0-9port50185
Block brute forcing - iptables rules
iptables-L-n
iptables-I INPUT-p tcp--dport22-i eth0-m state--state NEW-m recent--set
iptables-I INPUT-p tcp--dport22-i eth0-m state--state NEW-m recent--update--seconds600--hitcount3-j DROP
iptables-A INPUT-p tcp--dport22-m state--state NEW-m recent--set--name ssh--rsource
iptables-A INPUT-p tcp--dport22-m state--state NEW-m recent!--rcheck--seconds600--hitcount3--name ssh--rsource-j ACCEPT
service iptables save
service iptables restart
7. 参考资料







 当服务器出现CLOSE_WAIT过多时,可能导致资源耗尽,影响服务响应。分析表明,客户端主动关闭连接时,服务器端会出现CLOSE_WAIT状态。服务器配置,如Tomcat的keep-alive时间设置,对CLOSE_WAIT数量有直接影响。解决方案包括检查应用代码以正确关闭连接,或者通过特定工具如kill_close_wait_connections.pl脚本清理CLOSE_WAIT状态的连接。
当服务器出现CLOSE_WAIT过多时,可能导致资源耗尽,影响服务响应。分析表明,客户端主动关闭连接时,服务器端会出现CLOSE_WAIT状态。服务器配置,如Tomcat的keep-alive时间设置,对CLOSE_WAIT数量有直接影响。解决方案包括检查应用代码以正确关闭连接,或者通过特定工具如kill_close_wait_connections.pl脚本清理CLOSE_WAIT状态的连接。
















 1700
1700

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








