一:基础篇
MYSQL概述,SQL, 函数,约束,多表查询,事务
二:进阶篇
存储引擎,索引,SQL优化,视图/存储过程/触发器, 锁, InnoDB引擎, MYSQL管理
三:运维篇
日志,主从复制,分库分表,读写分离
四:其他
基础篇: MYSQL概述,SQL, 函数,约束,多表查询, 事务
1. mysql概述
关系型数据库管理系统,开源,企业版,社区版
版本: 5.x 、 6.x 、 7.x 、 8.x
常用工具:sqlyog navicat datagrip dbeaver
2. DDL语句
2.1 常用语句:
mysql -u root -p -- 使用root用户登录mysql
select version(); -- 查询mysql版本号 5.7.44-log
show databases; -- 查询数据库
create database my_db; -- 创建数据库
drop database my_db; -- 删除数据库
show databases; -- 查询所有数据库
show tables; -- 查询当前数据库所有表
show create table myuser2; -- 查询表创建sql
select database() -- 查询当前数据库
desc my_db1.myuser -- 查询当前表结构相关信息
alert table emp add nickname varchar(64) comment '昵称'; -- 给表添加字段
alert table emp modify nickname varchar(128) comment '昵称1' -- 修改表字段类型.
alert table mep change nickname username varchar(256) comment '昵称' -- 修改表字段名称及类型.
alert table emp drop username; -- 删除字段
alert table emp rename to employee; -- 修改表名
drop table emp; -- 删除表
drop table if exists emp;
truncate table emp; -- 删除指定表,并重新创建该表
set global validate_password_policy = 0; -- 设置mysql密码校验规则等级 0-low 1-middle 2-high
set global validate_password_length = 4; -- 设置密码长度为>=4位
2.2 数据类型
数值类型 2.字符串类型 3.日期时间类型
2.2.1 数值类型
id int
age tinyint unsigned 无符号的数字类型
score double(4,2) 4代表整体长度,2代表小数点后2位
2.2.2 字符串类型
char(10) (定长字符串-性能较高)10个字符 gender char(1) 性别 idcard char(18)
varchar(128) (变长字符串-性能较差) 128个字符串 username varchar(64) 姓名
2.2.3 日期时间类型
DATE - YYYY-MM-DD 日期值 birthday (生日)- date entrydate(入职时间) date
TIME - HH:MM:SS 时间值或持续时间
year - YYYY 年份值
*** DATETIME - YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS 日期+时间,这个用的多些
TIMESTAMP - YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS 日期+时间 只能到 2023-01-19 03:14:07
3. DML语句:
insert update delete
4. DQL语句:
4.1 逻辑运算符
> >= < <= = <>或!=
between . and. (左小右大,含最小最大值)
in(...)
ike 占位符 _ 匹配单个字符 % 匹配任意字符
is null
4.2 逻辑运算符
and 或 &&
or 或 ||
not 或 !
4.3 聚合函数
4.3.1
null值是不参与所有聚合函数运算的
count -统计数量
max - 最大值
min - 最小值
avg - 平均值
sum - 求和
SELECT * FROM my_db1.myuser;
select count(1) from my_db1.myuser;
select max(age) from my_db1.myuser;
select min(age) from my_db1.myuser;
select avg(age) from my_db1.myuser;
select sum(age) from my_db1.myuser;
4.3.2 分组 group by
select gender, count(1) from myuser group by gender;
select gender, avg(age) from myuser where age < 10 group by gender;
select gender, count(1) from myuser group by gender having count(1) > 2;
4.3.3 排序查询
select * from myuser order by age asc ; -- 按照年龄升序 asc 默认值,可以不写
select * from myuser order by age desc ; -- 按照年假进行降序
select * from myuser order by age desc , gender desc; -- 按照年假进行降序,如果年龄相同,在按照性别进行降序排序
4.3.4 分页查询
方言: limit (mysql) rownum (oracle嵌套)
select * from myuser limit 0, 2; -- 第1页,每页展示2条
select * from myuser limit 2 -- 上面可以省略为此,如果从第1页开始的
4.3.5 DQL执行顺序
SELECT
字段列表 ⑦
FROM
表名称列表 ①
WHERE
条件列表 ②
GROUP BY
分组字段列表 ③
HAVING
分组后条件列表 ④
ORDER BY
排序字段列表 ⑤
LIMIT
分页参数 ⑥
5. DCL语句
SELECT USER(); -- 查询当前用户
CREATE USER 'username'@'localhost' identified by 'password'; -- 创建用户 username,只能够在当前主机localhost访问,密码为password
CREATE USER 'username'@'%' identified by 'password'; -- 创建用户 username,可以在任意主机访问数据库, 密码是 password
ALTER USER 'username'@'%' identified with mysql_native_password by 'password1'; -- 修改用户 'username'@'%'的访问密码为 password1
create user 'chenzhen'@'%' identified with mysql_native_password by 'password'; -- 创建用户chenzhen,密码为password,可以在任意主机访问该数据库
grant all on *.* to 'chenzhen'@'%'; -- 分配所有权限
DROP USER 'username'@'localhost'; -- 删除 'username'@'localhost' 用户
-- 权限控制
ALL,ALL PRIVILEGES -- 所有权限
SELECT -- 查询权限
INSERT -- 插入权限
UPDATE -- 修改权限
DELETE -- 删除权限
ALTER -- 修改表
DROP -- 删除数据库/表/视图
CREATE -- 创建数据库/表
show grants for 'root'@'%'; -- 查询权限
grant all on itcast.* to 'root'@'%'; -- 授予权限
revoke all on itcast.* from 'root'@'%'; -- 撤销权限
6. 函数
字符串函数,数值函数,日期函数,流程函数
6.1 字符串函数
concat(s1, s2,... sn) 字符串拼接,将s1,s2,...sn拼接成一个字符串
lower(str) 将字符串str全部转为小写
upper(str) 将字符串str全部转为大写
trim(str) 去除字符串头部和尾部的空格
substring(str,start,len) 返回从字符串str从start位置起的len个长度的字符串
lpad(str, n, pad) 左填充,用字符串pad对str的左边进行填充,达到n个字符串长度
rpad(str, n, pad) 右填充,用字符串pad对str的右边进行填充,达到n个字符串长度
select concat('hello',' mysql'); hello mysql
select lower('HELLOW'); hellow
select upper('hello'); HELLO
select lpad('01',5,'-'); ---01
select rpad('01',5,'-'); 01---
select trim( ' hell o '); hell o
select substring('Hello mysql', 1,5); Hello
update myuser set worknum = lpad(worknum, 5, '0'); -- 把所有员工 工号补充为5位数,不足5位的前面加0
6.2 数字函数
ceil(x) 向上取整
floor(x) 向下取整
mod(x,y) 返回 x/y的模
rand() 返回0~1内的随机数
round(x,y) 求参数x的四舍五入的值,保留y位小数
select ceil(1.5); 2
select ceil(1.0); 1
select ceil(1.1); 2
select floor(1.5); 1
select floor(1.0); 1
select floor(1.1); 1
select mod(7,4); 3
select rand(); 0.583896713875138
select round(2.344,2); 2.34
select round(2.345,2); 2.35
select lpad(round(rand()*1000000,0),6,'0'); 806416 086895 -- 生成一个随机的6位数验证码
6.3 日期函数
curdate() 返回当前的日期
curtime() 返回当前时间
now() 返回当前日期+时间
year(date) 获取指定date的年份
month(date) 获取指定date的年份
day(date) 获取指定date的日期
date_add(date,interval expr type) 返回一个日期/时间值加上一个时间间隔expr后的时间值
datediff(date1, date2) 返回起始时间date1和结束时间date2之间的天数 date1 - date2
select curdate(); 2024-12-10
select curtime(); 10:32:34
select now(); 2024-12-10 10:32:51
select year(now()); 2024
select month(now()); 12
select day(now()); 10
select date_add(now(), INTERVAL 10 day ); 2024-10-20 10:35:50 往后推10天
select date_add(now(), INTERVAL -10 day ); 2024-11-30 10:36:25 往前推10天
select datediff('2021-11-11','2021-11-12 10:35:50'); -1 -- date1 -date2
查询所有员工的入职天数,并根据入职天数倒叙排序
select username,datediff(curdate(), entrydate) as entrydays from myuser order by entrydays desc;
6.4 流程控制函数
if(value, t, f) 如果value为true,则返回t,否则返回f
ifnull(value1,value2) 如果value1不为null,返回value1, 否则返回value2
case when [val1] then [res1] ... else[default] end 如果val1为true,返回res1,...否则返回default默认值
case [expr] when [val1] then [res1]...else [default] end 如果expr的值等于val1,返回res1,...否则返回default默认值
select if(true, 'ok','error'); ok
select ifnull('ok','error'); ok
select ifnull('','default'); 空
select ifnull(null, 'default'); default
-- 查询员工的工作地址, (北京,上海)展示为 ‘一线城市’, 其他城市 展示为 ‘二线城市’
select username,
(case address
when '北京' then '一线城市'
when '上海' then '一线城市'
else '二线城市'
end ) as ‘工作地址’
from myuser;
-- 针对学员成绩: >= 85 展示 ‘优秀’ >= 60展示 ‘及格’ 否则展示 ‘不及格’
select id, name,
( case when math >= 85 then '优秀' when math >= 60 then '及格' else ‘不及格’ end ) as '数学成绩',
( case when english >= 85 then '优秀' when english >= 60 then '及格' else ‘不及格’ end ) as '英语成绩'
from score;
7. 约束
约束作用于表中字段上的规则,用于限制存储在表中的数据。 目的: 保证数据库中数据的正确性,有效性和完整性
非空约束: NOT NULL 限制该字段的数据不能为null
唯一约束: UNIQUE 保证该字段的所有数据都是唯一,不能重复的
主键约束: PRIMARY KEY 主键是一行数据的唯一标识,要求非空且唯一
默认约束: DEFAULT 保存数据时,如果未指定该字段的值,则采用默认值
外键约束: FOREIGN KEY 用来让2张表的数据之间建立联系,保证数据的一致性和完整性
检查约束(8.0.16版本之后) CHECK 保证字段值满足某一个条件
create table myuser2 (
id int primary key auto_increment comment '主键',
name varchar(10) not null unique comment '姓名',
age int comment '年龄', -- 检查约束 8.0.16版本之后
-- age int check ( age > 0 && age <= 120 ) comment '年龄', -- 检查约束 8.0.16版本之后
status char(1) default '1' comment '状态,默认1',
gender char(1) comment '性别'
) comment '用户表';
添加外键 2张表, 删除/更新行为 级联操作
删除/更新行为以下:
1. NO ACTION 和 RESTRICT 在父表中删除/更新记录时, 首先检查该记录是否有外键, 有则不允许删除/更新
2. CASCADE 级联操作 --------------------------------------------有则也更新/删除外键在子表中的记录。
3。SET NULL ---------------------------------------------有则设置子表中该外键为值为null (这就要求该外键允许为null)
4. SET DEFAULT ---------------------------------------------有则子表将外键列设置为一个默认值(Innodb不支持)
alter table myuser2 add constraint fk_emp_dept_id foreign key (dept_id) references dept(id) on update CASCADE on delete cascade ;
alter table myuser2 drop foreign key fk_emp_dept_id; -- 删除外键
insert into myuser2(name, age, status, gender) values ('陈振',32,'1','男');
insert into myuser2(name, age, gender) values ('陈振2',32,'男');
insert into myuser2(name, age, status, gender) values ('陈振3',32,'','女');
insert into myuser2(name, age, status, gender) values ('陈振4',32,null,'女');
8. 多表查询
多表关系,多表查询概述,内连接,外连接,自连接,子查询,多表查询案例
8.1 多表关系
一对多(多对一): 实现:在多的一方建立外键,指向一的一方的主键
多对多: 实现:建立第三张中间表,中间表至少包含2个外键,分别关联2方主键
一对一: 实现:在任意一方加上外键,关联另一方的主键,并且设置外键为唯一的(unique)。 经常做单表的拆分
8.2 多表查询
-- 笛卡尔积: 两个集合A,B所有的组合情况 A*B --> 在进行多表查询时,需要消除无效的笛卡尔积
select * from emp, dept where emp.dept_id = dept.id;
-- 多表查询分类:
-- 1.连接查询:
-- 1.1 内连接: 相当于查询A,B交集部分数据
-- 1。2 外连接:
-- 1.2.1 左外连接: 查询左表所有的数据,以及两张表交集部分数据
-- 1.2.2 右外连接: 查询右表所有数据,以及两张表交集部分数据
-- 1.3 自连接:当前表与自身的连接查询,自连接必须使用表别名
-- 1.4 联合查询: 把2次或多次查询的结果进行合并
-- 2.子查询: sql中嵌套select语句,称为嵌套查询,又称子查询
8.3 内连接:
相当于查询A,B两张表的交集数据
-- 隐式内连接: select 字段列表 from 表1, 表2 where 条件...;
-- 显示内连接: select 字段列表 from 表1 [inner] join 表2 on 连接条件...;
select emp.name, dept.name from emp, dept where emp.dept_id = dept.id; -- 隐式内连接: 查询每一个员工的姓名, 及关联的部门的名称
select e.name, d.name from emp e, dept d where e.dept_id = d.id;
select e.name, d.name from emp e inner join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id; -- 显式内连接
8.4 外连接
8.4,1 左外连接
相当于查询表1(左表)的所有数据,包含表1和表2交集部分的数据 ** 用的多些
-- 查询emp表所有的数据, 和对应的部门信息
select e.*, d.name from emp e left join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id;
select e.*, d.name from emp e left outer join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id; -- outer关键字可以省略
8.4,2 右外连接
相当于查询表2(右表)的所有数据,包含表1和表2交集部分的数据 ** 右外可以转换为左外连接
-- 查询dept表所有的数据, 和对应员工信息
select d.*, e.name from emp e right join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id; -- outer关键字可以省略
8.5 自连接
可以是内连接查询,也可以是外连接查询。
-- 查询员工及所属领导的名字 - 内连接 只查询表a,b交集的部分
select e.name, e1.name from emp e, emp e1 where e.manage_id = e1.id;
-- 查询所有所有员工 emp及其领导名字 emp, 如果员工没有领导,也需要查询出来 -- 外连接
select e.name as '员工姓名', e1.name as '领导名字' from emp e left join emp e1 on e.manage_id = e1.id;
8.6 联合查询
union, union all 就是把多次查询的结果合并起来,形成一个新的查询结果集 A+B 形成all,
union all 直接将查询的结果进行合并
union 将查询结果合并后再进行去重处理
-- 对于联合查询,多张表的列数必须保持一致,字段类型也需要保持一致
select 字段列表 from 表A...
union[all]
select 字段列表 from 表B...
-- 将薪资低于5000的员工, 和年龄大于50岁的员工全部查询出来
select * from emp where salary < 5000
union all
select * from emp where age > 50;
8.7 子查询:
sql中嵌套select语句,称为嵌套查询,又称子查询
子查询外部的语句可以是insert/uodate/delete/select 的任何一个
根据子查询结果不同,分为:
①. 标量子查询: 子查询的结果为单个值
②. 列子查询: 子查询的结果为一列(可以是多行)
③. 行子查询: 子查询结果为一行
④. 表子查询: 子查询结果为多行多列
根据子查询位置,分为: WHERE之后, FROM之后,SELECT之后
8.7.1 标量子查询:
子查询返回的结果是单个值 (数字,字符串,日期等),最简单的形式,这种子查询称为标量子查询
常用的操作符: = <> > >= < <=
①查询’销售部‘所有员工信息
select * from emp where dept_id = (select id from dept where name = '销售部');
②查询'方东白'入职之后的员工信息
select * from emp where entrydate > (select entrydate from emp where name = '方东白');
8.7.2 列子查询:
子查询返回的结果是一列(可以是多行)一列多行
常用的操作符: IN , NOT IN , ANY , SOME , ALL
IN 在指定的集合范围之内, 多选一
NOT IN 不在指定的集合范围之内
ANY 子查询返回列表中,有任意一个满足即可
SOME 与ANY等同,使用SOME的地方都可以使用ANY
ALL 子查询返回列表的所有值都必须满足
①: 查询'销售部','市场部'的所有员工 (1列多行)
select * from emp where dept_id in (select id from dept where name in ('销售部', '市场部'));
②: 查询比'财务部'所有人工资都高的员工信息
第一步: 查询所有 ’财务部‘ 员工的工资
select salary from emp where dept_id = (select id from dept where name = '财务部');
第二步: 比财务部所有人工资都高的员工信息
select * from emp where salary > all(select salary from emp where dept_id = (select id from dept where name = '财务部’));
③:查询比 ‘研发部’其中任意一人工资高的员工信息
select * from emp where salary > any(select salary from emp where dept_id = (select id from dept where name = '研发部'));
select * from emp where salary > some(select salary from emp where dept_id = (select id from dept where name = '研发部'));
8.7.3 行子查询:
子查询结果为一行,(可以是多列) 一行多列
常用的操作符: = , <> , IN , NOT IN
①:查询与 '张无忌'的薪资及直属领导相同的员工信息
-- 第一步: 查询‘张无忌’的薪资及直属领导 (字段1: ‘张无忌的薪资’ 字段2: 直属领导)
select salary,manage_id from emp where name = '张无忌';
-- 第二步:
select * from emp where (salary, manage_id) = (select salary,manage_id from emp where name = '张无忌')
8.7.4 表子查询:
子查询返回的结果是多行多列
常用的操作符: IN
①: 查询与 ‘张无忌’,‘宋元桥’的职位和薪资相同的员工信息
select job, salary from emp where name = ‘张无忌’ or name = ‘宋元桥’; //多行
select * from emp where (job, salary) in (select job, salary from emp where name = ‘张无忌’ or name = ‘宋元桥’);
②: 查询入职日期是 ‘2024-12-10’之后的员工信息,及其部门信息
select * from emp where entrydate > ‘2024-12-10’; – 把这个查询结果作为一张表
select e., d. from (select * from emp where entrydate > ‘2024-12-10’) e left join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id;
8.8: 多表查询练习:
①; 查询员工的 姓名,年龄,职位,部门信息 (隐式内连接)
select e.name, e.age, e.job, d.* from emp e , dept d where e.dept_id = d.id;
②: 查询年龄小于30岁的员工的姓名,年龄,职位 部门信息(显式内连接)
select e.name, e.age, e.job, d.* from emp e inner join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id where e.age < 30
③:查询拥有员工的部门id,部门名称 (内连接: 查询的是两张表交集的部分)
select distinct d.id, d.name from emp e , dept d where e.dept_id = d.id;
④:查询所有年龄大于40岁的员工,及其归属的部门名称; 如果员工没有分配部门,也需要查询出来。
select e.*, d.name from emp e left join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id where e.age > 40;
⑤:查询所有员工的工资等级
select e.*, s.grade, s.losal, s.hisal from emp e, salgrade s where e.salary >= s.losal and e.salary <= s.hisal;
select e.*, s.grade, s.losal, s.hisal from emp e, salgrade s where e.salary between s.losal and s.hisal;
⑥:查询 '研发部' 所有员工的信息及工资等级
select e.*, s.grade from emp e, salgrade s, dept d where e,dept_id = d.id and (e.salary between s.losal and s.hisal) and d.name = '研发部';
⑦:查询 '研发部' 员工的平均工资
select avg(e.salary) from emp e, dept d where e.dept_id = d.id and d.name = '研发部';
⑧:查询工资比‘灭绝’高的员工信息;-- 子查询
select e.* from emp e where e.salary > (select e1.salary from emp e1 where e1.name = '灭绝');
⑨:查询比平均工资高的员工信息
select e.* from emp e where e.salary > (select avg(e1.salary) from emp e1);
⑩:查询低于本部门平均工资的员工信息
select e.* from emp e where e.salary < (select avg(e1.salary) from emp e1 where e.dept_id = e1.dept_id);
11: 查询所有的部门信息,并统计部门的员工人数
select d.id, d.name, (select count(*) from emp e where e.dept_id = d.id) as ‘人数’ from dept d;
12: 查询所有学生的选课情况,展示学生名称,学号,课程名称 多对多 表 student, course, student_course 中间表
select s.name,s.no,c.name from student s,student_course sc,course c where s.id = sc.student_id and c.id = sc.course_id;
9 事务
事务简介, 事务操作, 事务四大特性, 并发事务问题, 事务隔离级别
9.1. 事务:
是一组操作的集合,他是不可分割的工作单位,事务会把所有的操作作为一个整体一起向系统提交或撤销操作请求,即这些操作:要么同时成功,要么同时失效
9.2. 操作示例: 张三向李四转账1000元
select * from account where name = '张三'
update account set money = money -1000 where name = '张三';
update account set money = money + 1000 where name = '李四';
select @@autocommit; -- 1:自动提交 0:手动提交 mysql支持,oracle不支持
-- 方式一: 手动提交事务
set @@autocommit = 0; -- 设置会话为手动提交
commit; -- 提交事务
rollback; -- 回滚事务
-- 方式二: 显示开启事务
start transaction 或 begin -- 开启事务
--- do things
commit; -- 提交事务
rollback; -- 回滚事务
9.3 事务四大特性ACID***:
原子性, 一致性, 隔离性, 持久性
①: 原子性: Atommicity 事务是不可分割的最小操作单元,要么全部成功,要么全部失败。
②: 一致性: Consistency 事务完成时,必须使所有的数据都保持一致状态
③: 隔离性: Isolation 数据库系统提供的隔离机制,保证事务在不受外部并发操作影响的独立环境中运行。
④: 持久性: Durability 事务一旦提交或回滚,它对数据库中的数据的改变是永久的。
9.4.并发事务引发的问题: 脏读, 不可重复读, 幻读
脏读:一个事务A读到另一个事务B还没有提交的数据。
不可重复读: 一个事务A先后读取同一条记录,但两次读取的数据不同,称之为不可重复读。
幻读: (前后多次读取,数据总量不一致)一个事务按照条件查询数据时,没有对应的数据行, 但是在插入数据时,又发现这行数据已经存在,好像出现了幻读。
9.5 事务的隔离级别:
√ 存在,有 X 不存在 TODO:这一块4,5重新梳理下, 后续锁完结后再来总结
①: Read uncommitted : 脏读 √(存在) 不可重复读 √(存在) 幻读 √(存在)
②: Read committed: (Oracle默认隔离级别) 脏读 x(不存在) 不可重复读 √(存在) 幻读 √(存在)
③: Repeatable Read(mysql默认隔离级别) 脏读 x(不存在) 不可重复读 X(不存在) 幻读 √(存在,MYSQL采用MVCC机制解决了幻读的问题,MYSQL不存在幻读,意味着mysql查询两次查询结果相同)
④: Serializable: 脏读 x(不存在) 不可重复读 X(不存在) 幻读 X(不存在)
查询事务的隔离级别
select @@transaction_isolation;
设置事务的隔离级别
set [session|grobal] transaction isolation level [read uncommited | read commited | repeatable read | serializable]
-事务的隔离级别越高,数据越安全,但是性能越低。 反之易之- 权衡之
进阶篇: 存储引擎,索引,SQL优化,视图/存储过程/触发器, 锁, InnoDB引擎, MYSQL管理
10. 存储引擎
10.1 mysql体系结构
10.1.1 Mysql系统结构图
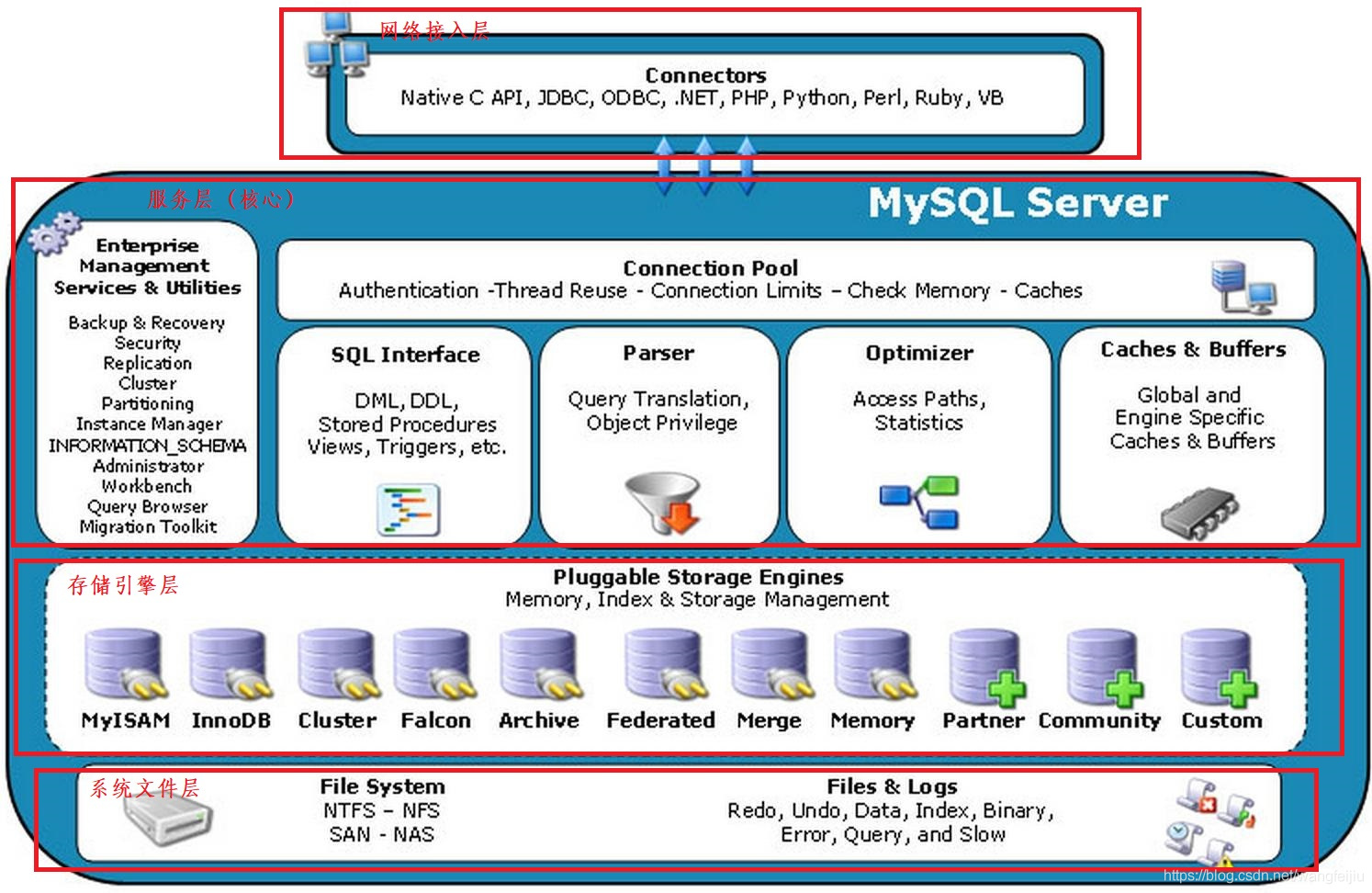
由上至下,我们可以MySQL的体系构架划分为:1.网络接入层 2.服务层 3.存储引擎层 4.文件系统层
网络接入层
提供了应用程序接入MySQL服务的接口。客户端与服务端建立连接,客户端发送SQL到服务端。








 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 3万+
3万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










