springboot启动时,会自动识别出当前环境是否是web环境还是非web环境。

默认的web环境的context(DEFAULT_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS):org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext
默认的非web环境的context(DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS):org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
以下代码为springboot启动类springApplication创建context代码:ConfigurableApplicationContext org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.createApplicationContext():
/**
* Strategy method used to create the {@link ApplicationContext}. By default this
* method will respect any explicitly set application context or application context
* class before falling back to a suitable default.
* @return the application context (not yet refreshed)
* @see #setApplicationContextClass(Class)
*/
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
switch (this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
case REACTIVE:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
default:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS);
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Unable create a default ApplicationContext, "
+ "please specify an ApplicationContextClass",
ex);
}
}
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
那么我们来详细看下默认的web环境的AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext的具体实现:
public class AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext extends ServletWebServerApplicationContext implements AnnotationConfigRegistry
发现AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext继承了org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.ServletWebServerApplicationContext,
我们看AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext的代码,发现并没有和webServer(tomcat,jetty....)相关的代码。那么我们继续来看下父类ServletWebServerApplicationContext的实现:
ServletWebServerApplicationContext:发现这个类是boot包下的,继承了GenericWebApplicationContext是spring-web这个jar包,推断springboot嵌入webServer的逻辑很有可能是在这个ServletWebServerApplicationContext中
类结构:public class ServletWebServerApplicationContext extends GenericWebApplicationContext implements ConfigurableWebServerApplicationContext
我们终于在org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.ServletWebServerApplicationContext看到了和webServer相关的代码:
@Override
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
try {
createWebServer();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex);
}
}@Override
protected void finishRefresh() {
super.finishRefresh();
WebServer webServer = startWebServer();
if (webServer != null) {
publishEvent(new ServletWebServerInitializedEvent(webServer, this));
}
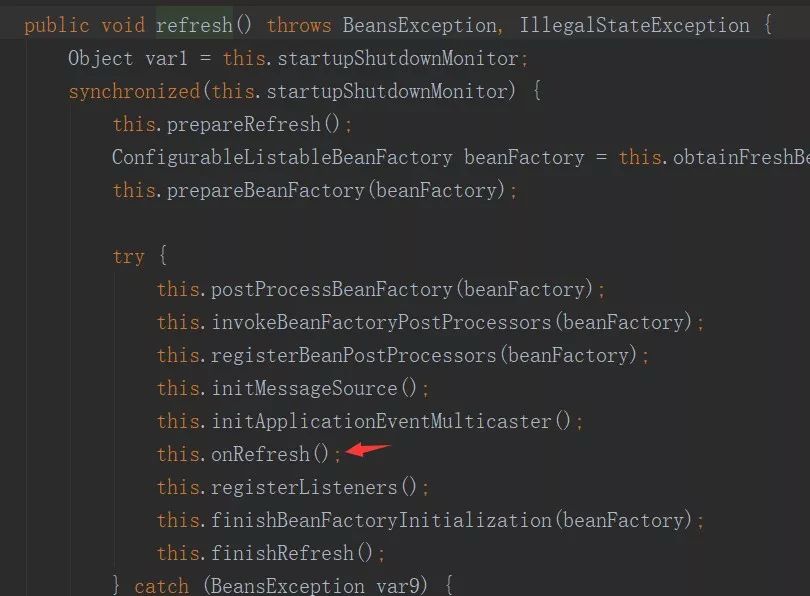
}其中onRefresh方法会在void org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.refresh() 中会在context注册BeanFactoryPostProcessor、执行BeanFactoryPostProcessor、注册BeanPostProcessor之后调用,
而finishRefresh方法会在void org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.finishRefresh()中会在context完成各种初始化(初始化bean)后被调用到,从而在context启动完成后,启动WebServer(tomcat、jetty)...
接下来我们看下创建WebServer和启动WebServer的逻辑:
private void createWebServer() {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) {
ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory();
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer());
}
else if (servletContext != null) {
try {
getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext);
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot initialize servlet context",
ex);
}
}
initPropertySources();
}private WebServer startWebServer() {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
if (webServer != null) {
webServer.start();
}
return webServer;
}






 本文解析了SpringBoot如何根据当前环境自动选择合适的上下文,重点介绍了web环境下AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext的作用及其实现细节,包括WebServer的创建与启动过程。
本文解析了SpringBoot如何根据当前环境自动选择合适的上下文,重点介绍了web环境下AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext的作用及其实现细节,包括WebServer的创建与启动过程。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








