题目:
Given a binary tree containing digits from 0-9 only, each root-to-leaf path could represent a number.
An example is the root-to-leaf path 1->2->3 which represents the number 123.
Find the total sum of all root-to-leaf numbers.
For example,
1 / \ 2 3
The root-to-leaf path 1->2 represents the number 12.
The root-to-leaf path 1->3 represents the number 13.
Return the sum = 12 + 13 = 25.
思路:
刷题刷到现在了,做这种题已经有点感觉了,之所以拿这道题目出来写到博客上是因为这题比较典型,而且自己用了半小时就ac了,应该是用了最快的算法了,思路非常清晰:先序遍历,用一个容器记录遍历到的节点,遍历到叶子节点时计算此条路径的数字,然后加到result中,result是作为一个引用参数包含在每一次递归中的。
这里尤其要注意一点:最后那句path.pop_back();千万别漏也别放错地方,其实只要把程序如何递归的想想清楚就自然不会写错。
代码:
/**
* Definition for binary tree
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int sumNumbers(TreeNode *root) {
int result=0;
sumNumbers2(root, result);
return result;
}
void sumNumbers2(TreeNode *root, int &result)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
return;
}
path.push_back(root->val);
if(root->left==NULL && root->right==NULL)
{
int sum=0;
for(vector<int>::iterator it=path.begin();it!=path.end();it++)
{
sum=sum*10+*it;
}
result+=sum;
}
if(root->left!=NULL)
{
sumNumbers2(root->left, result);
}
if(root->right!=NULL)
{
sumNumbers2(root->right, result);
}
path.pop_back();
}
private:
vector<int> path;
};
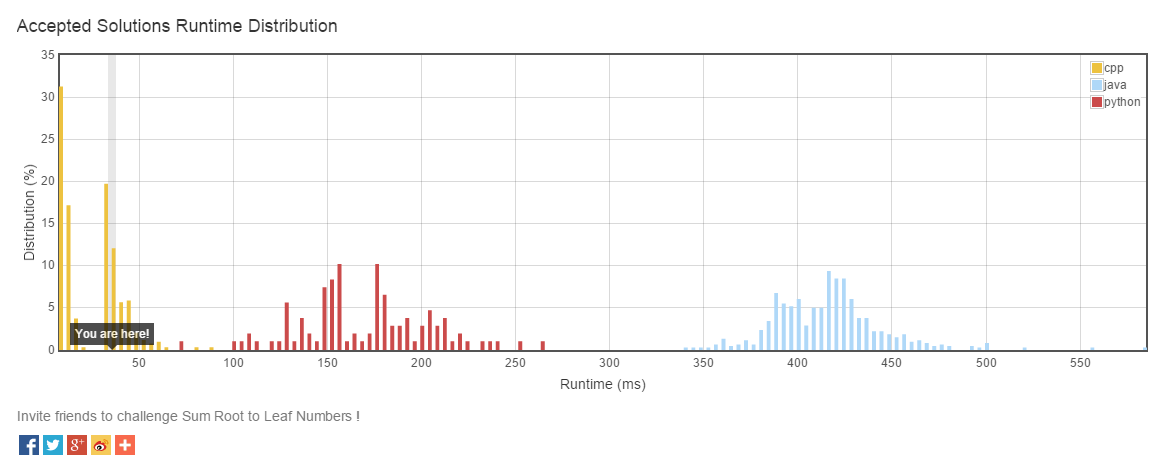
效率截图(有一半是归功于c++的功劳):
本博客内容与代码均为作者Jarvis原创,如若转载请注明。



 本文介绍了一种解决二叉树路径之和问题的有效方法。通过先序遍历的方式,利用一个容器记录遍历过程中的节点值,在到达叶子节点时计算路径上的数值总和。
本文介绍了一种解决二叉树路径之和问题的有效方法。通过先序遍历的方式,利用一个容器记录遍历过程中的节点值,在到达叶子节点时计算路径上的数值总和。
















 253
253

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








