版权声明
笔记出自《Spring 开发指南》一书。
Spring 初探
前面我们简单介绍了 Spring 的基本组件和功能,现在我们来看一个简单示例:
- Person接口
Person接口定义了一个 say 的方法,在其不同的实现中实现了各自的 say 逻辑。1 /** 2 * @author X 3 */ 4 public interface Person { 5 6 public void say(); 7 }
- Person接口的两个实现
1 /** 2 * @author X 3 */ 4 public class Man implements Person { 5 6 private String word; 7 8 public String getWord() { 9 return word; 10 } 11 12 public void setWord(String word) { 13 System.out.println("执行了Set"); 14 this.word = word; 15 } 16 17 @Override 18 public void say() { 19 System.out.println("一个男人委屈的说:" + word); 20 } 21 }
1 /** 2 * @author X 3 */ 4 public class Woman implements Person { 5 6 private String word; 7 8 public String getWord() { 9 return word; 10 } 11 12 public void setWord(String word) { 13 this.word = word; 14 } 15 16 @Override 17 public void say() { 18 System.out.println("一个女人委屈的说:" + word); 19 } 20 }
- Spring配置文件(bean.xml)
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> 5 6 <bean id="TheAction" class="Man"> 7 <property name="word"> 8 <value>一百块钱都不给我还打我</value> 9 </property> 10 </bean> 11 </beans>
- 调用代码
1 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 2 import org.springframework.context.support.FileSystemXmlApplicationContext; 3 4 /** 5 * @author X 6 */ 7 public class Run { 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 10 ApplicationContext ac = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("D:\\Study\\study-spring\\src\\main\\resources\\bean.xml"); 11 12 Person action = (Person) ac.getBean("TheAction"); 13 action.say(); 14 } 15 }
运行结果如下图所示:
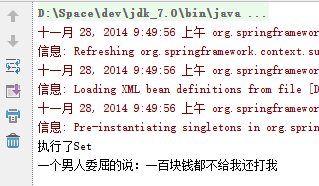
怎么样,是不是很简单?通过这个简单的例子,我们可以看到,我们在实例化Person的时候,根本无需知道它是如何实现的。在编码中,我们只需要去关心接口就可以了,而无需关心它的创建过程,因为这件事 Spring 已经帮我们做掉了。如果你想了解更多,推荐你去了解控制反转(IOC)和依赖注入(DI)的概念。























 3838
3838

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








