1.继承条件下的构造方法调用
package parent;
class Grandparent
{
public Grandparent()
{
System.out.println("GrandParent Created.");
}
public Grandparent(String string)
{
System.out.println("GrandParent Created.String:" + string);
}
}
class Parent extends Grandparent
{
public Parent()
{
//super("Hello.Grandparent.");
System.out.println("Parent Created");
//super("Hello.Grandparent.");
}
}
class Child extends Parent
{
public Child()
{
System.out.println("Child Created");
}
}
public class TestInherits
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Child c = new Child();
}
}

结论:通过super调用基类构造方法,必须是子类构造方法中第一个语句。
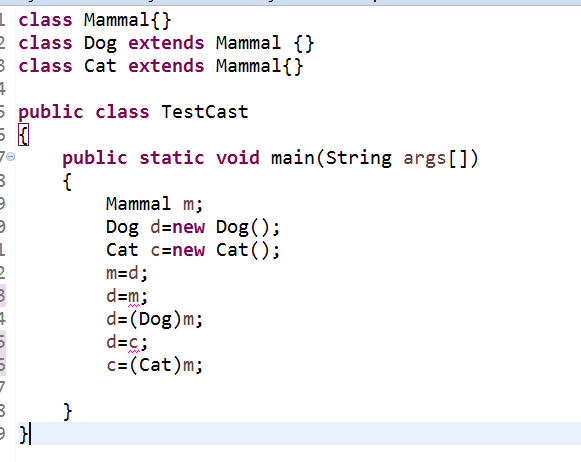
2.下列语句哪一个将引起编译错误?为什么?哪一个会引起运行时错误?为什么?
d=m,d=c运行时将会报错。因为m是父类对象,d是子类对象。将父类对象转化成子类对象,必须进行强制转换。而d和c是两个互不相干的类对象,不能直接赋值,所以会运行错误。
3. 左边的程序运行结果是什么? 你如何解释会得到这样的输出? 计算机是不会出错的,之所以得 到这样的运行结果也是有原因的, 那么从这些运行结果中,你能总 结出Java的哪些语法特性?public class ParentChildTest { public static void main(String[] args) Parent parent=new Parent();
parent.printValue();
Child child=new Child();
child.printValue();
parent=child;
parent.printValue();
parent.myValue++;
parent.printValue();
((Child)parent).myValue++;
parent.printValue();
}
}
class Parent{
public int myValue=100;
public void printValue() {
System.out.println("Parent.printValue(),myValue="+myValue);
}
}
class Child extends Parent{
public int myValue=200;
public void printValue() {
System.out.println("Child.printValue(),myValue="+myValue);
}
}

结论:
1. 子类对象可以直接赋值给父类的对象而父类对象必须进行强制转换才可以赋值给子类的对象。
2.子类对父类访问时能覆盖父类中的变量,被覆盖后无论对父类变量进行什么操作,最后都会输出子类的变量。




 本文探讨了Java中继承条件下构造方法的调用规则,分析了子类构造方法中super关键字的使用,并讨论了父类与子类对象之间的赋值及类型转换问题。此外,还通过一个具体的例子说明了子类对象对父类变量覆盖的现象。
本文探讨了Java中继承条件下构造方法的调用规则,分析了子类构造方法中super关键字的使用,并讨论了父类与子类对象之间的赋值及类型转换问题。此外,还通过一个具体的例子说明了子类对象对父类变量覆盖的现象。
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








