一.LINQ介绍
所有的所有LINQ查询操作由三个不同的操作组成:
1.获取数据源
2.创建查询
3.执行查询
下图显示了完整的查询操作。在LINQ中,查询的执行与查询本身不同;换句话说,仅通过创建查询变量是不能检索到任何数据。
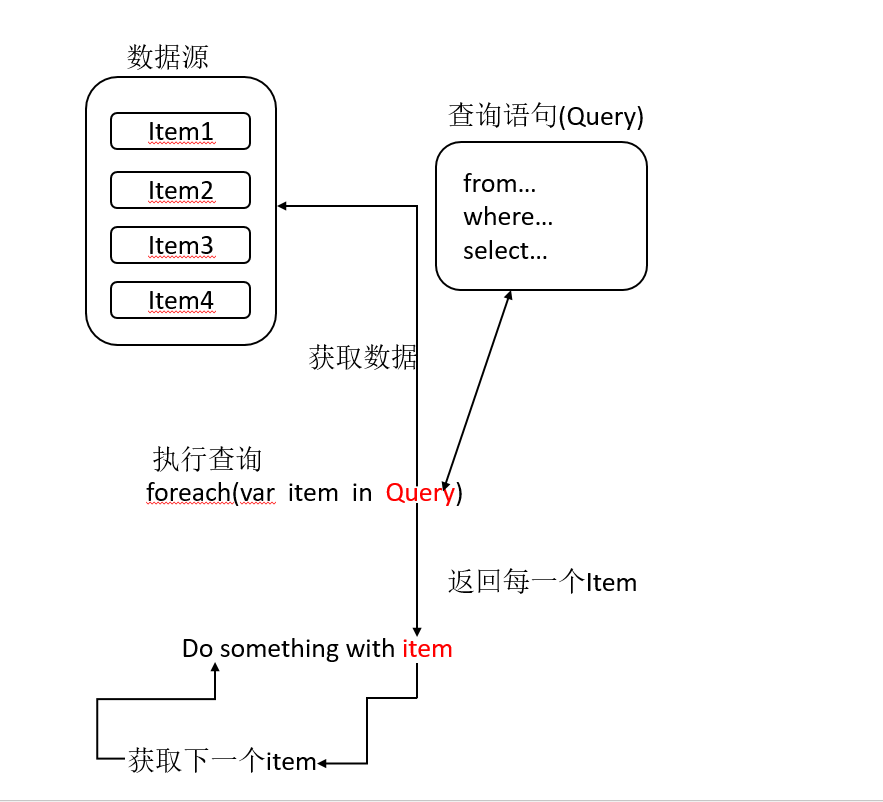
下面是一个使用LINQ语句对集合对象进行查询的实例:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace MyLinq { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { List<int> intList = new List<int>(); //创建数据源 for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { intList.Add(i); } //创建查询 var queryResults = from item in intList where item % 2 == 0 && item > 2 select item; //执行查询 foreach(var item in queryResults) { Console.Write(item + ","); } Console.ReadKey(); } } }
from....in:子句指定数据源;where:子句应用删选器;select:子句指定返回的元素类型
二.LINQ查询方法
(1).Select()方法
Select()方法使用的时候需要传递一个委托实例
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace MyLinq { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { List<int> intList = new List<int>(); //创建数据源 for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { intList.Add(i); } var list = intList.Select(item => item * 2); foreach(var item in list) { Console.Write(item + " "); } Console.ReadKey(); } } }
(2).删选数据:Where()方法
Where()方法使用的时候要传递一个委托示例,但该实例是一个判断条件,因此返回的类型必须是bool类型
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace MyLinq { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { List<int> intList = new List<int>(); //创建数据源 for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { intList.Add(i); } var list = intList.Where(item => item % 2 == 0).Select(item => item * 2); foreach(var item in list) { Console.Write(item + " "); } Console.ReadKey(); } } }
(3).排序数据:OrderBy()
OrderBy()里面的参数要求传递一个排序的字段,默认为升序,如果想要降序,可以使用Ordery Descending
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace MyLinq { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { List<int> intList = new List<int>() { 1,5,3,6,4,10,16,15 }; var list = intList.Where(item => item % 2 == 0).Select(item => item).OrderBy(item => item); foreach(var item in list) { Console.Write(item + " "); } Console.ReadKey(); } } }
(4).分组数据:Group()
Group()里面的参数要求传递一个分组的字段
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace MyLinq { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { string[] names = { "张三", "张勇", "王五", "李四", "刘闯", "刘丽", "王理", "李媛" , "李文静"}; var list = names.Where(item => item.Length == 2).Select(item => item).GroupBy(item => item.Substring(0, 1)); foreach(var groupItem in list) { Console.WriteLine("---------------------"); Console.WriteLine("分组字段:{0}", groupItem.Key); foreach (var item in groupItem) { Console.WriteLine(item); } } Console.ReadKey(); } } }

以上定义查询后,查询并没有立即执行,而是知道需要遍历结果时才被真正执行,这种方式称为“延迟执行”
使用“聚合扩展方法”返回单一结果,强制查询立即执行
下例所示:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace MyLinq { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int[] nums = { 1, 12, 32, 4, 20, 9 }; int nLength = nums.Where(item => item % 2 == 0).Select(i => i).Count(); Console.WriteLine("长度:{0}", nLength); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
三.关于数据源
(1).如果数据源是泛型类型,则编译器可以自动推断出范围变量的类型。
(2).如果数据源是非泛型类型,如ArrayList,则必须显示指定范围变量的数据类型
下例所示:
using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace MyLinq { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { ArrayList Arraylist = new ArrayList(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { Arraylist.Add(i); } var list = from int item in Arraylist where item % 2 == 0 select item; foreach(var item in list) { Console.Write(item + " "); } Console.ReadKey(); } } }
如果数据源中的元素还包含子数据源,如果要查询子数据源中的元素,则需要使用from子句。
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace MyLinq { public class Student { public string name { get; set; } public int age { get; set; } public List<int> ScoreList { get; set; } } }
using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace MyLinq { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { var studentList = new List<Student>(){ new Student(){name="张三", age=18, ScoreList = new List<int>(){60,80,70}}, new Student(){name="李四", age=24, ScoreList = new List<int>(){75,95,68}}, new Student(){name="王五", age=19, ScoreList = new List<int>(){62,98,69}} }; //查询类里集合中的数据 var queryResult = from stu in studentList from score in stu.ScoreList where score >= 80 select score; foreach(var item in queryResult) { Console.WriteLine("80分以上的有{0}", item); } Console.ReadKey(); } } }
若LINQ查询表达式中包含两个或两个以上独立的数据源时,可以使用多个from子句查询所有数据源中的数据
using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace MyLinq { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { var studentList1 = new List<Student>() { new Student(){name="张三", age=18, ScoreList = new List<int>(){60,80,70}}, new Student(){name="李四", age=24, ScoreList = new List<int>(){75,95,68}}, new Student(){name="王五", age=19, ScoreList = new List<int>(){62,98,69}} }; var studentList2 = new List<Student>() { new Student(){name="张琪", age=23, ScoreList = new List<int>(){68,82,98}}, new Student(){name="李云", age=18, ScoreList = new List<int>(){62,89,70}}, new Student(){name="刘三", age=25, ScoreList = new List<int>(){65,60,83}} }; var queryResult = from stu1 in studentList1 where stu1.age > 20 from stu2 in studentList2 where stu2.age > 23 select new { stu1, stu2 }; foreach(var item in queryResult) { Console.WriteLine("年龄大于20的有{0}", item.stu1.age); Console.WriteLine("年龄大于23的有{0}", item.stu2.age); } Console.ReadKey(); } } }
四.LINQ的高级查询
Max/Min求最大值,最小值;Average返回集合的平均值;Sum返回集合的总数。
using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace MyLinq { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { List<int> list = new List<int>(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { list.Add(i); } var Max = (from s in list select s).Max(); var Min = (from s in list select s).Min(); var Avgage = (from s in list select s).Average(); var Sum = (from s in list select s).Sum(); Console.WriteLine("最大值:{0},最小值:{1},平均值:{2},和:{3}", Max, Min, Avgage, Sum); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
集合类查询Distinct()去掉集合中的重复项
using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace MyLinq { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { List<int> list = new List<int>() { 1,2,2,2,3,5,5,8,8,9 }; var query = list.Distinct(); foreach(var item in query) { Console.Write(item + " "); } Console.ReadKey(); } } }























 739
739

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








