前面总结中分别使用了单纯的jdbc以及jdbc配合数据库连接池的方式进行了简单的数据库查询操作,从代码编写的复杂度以及性能两个方面来看使用数据库连接池都好于用单纯的jdbc。另外,在上述两种方式中我们也看到了很多的重复代码,比如获取connection、获取statement,关闭connection、关闭statement等,这些代码在我们每一次的数据库操作中都是重复的,是否有更好的屏蔽这种重复操作的方式呢?这篇文章给出答案。
通用的操作流程如下:
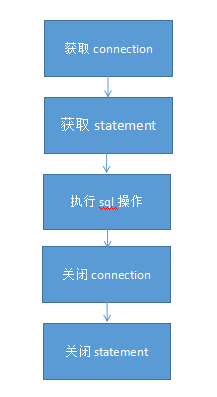
在流程中只有执行sql在每次数据库操作中是不一样的,其他的步骤都是相同的,那就需要解决这个问题,而这个问题与模板设计模式所解决的问题非常相似。模板设计模式的定义:模板方法模式:在一个方法中定义一个算法的骨架,而将一些步骤延迟到子类中。模板方法使得子类可以在不改变算法结构的情况下,重新定义算法中的某些步骤。而spring提供了相关实现JdbcTemplate,下面代码示例如何使用:
一、spring配置文件:spring-context.xml
二、jdbctemplate的配置文件:spring-context-jdbctemplate.xml
三、具体实现的service类:JdbcTemplateService
packagecom.test.database.jdbctemplate;importorg.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;importorg.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;importorg.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Servicepublic classJdbcTemplateService {
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;public voidtestJdbcTemplate() {
String sql= "select * from user";
System.out.println(jdbcTemplate.queryForList(sql));
}
}
四、测试类:JdbcTemplateMain.java
packagecom.test;importorg.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;importorg.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;importcom.test.database.jdbctemplate.JdbcTemplateService;public classJdbcTemplateMain {public static voidmain(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context= new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-context.xml","spring-context-jdbctemplate.xml");
context.getBean(JdbcTemplateService.class).testJdbcTemplate();
}
}
五、执行结果为(数据库有两条记录):
[{id=1, name=tim, password=tim}, {id=2, name=park, password=park}]
另外:配置文件中配置的数据源(dataSource)也可以是一个数据库连接池。
*************************************************************************************
下面分析一下JdbcTemplate是如何完成数据库操作的:
jdbcTemplate.queryForList(sql)
跳到JdbcTemplate类中:
下一步:
@Overridepublic List> queryForList(String sql) throwsDataAccessException {returnquery(sql, getColumnMapRowMapper());
}
下一步:
@Overridepublic List query(String sql, RowMapper rowMapper) throwsDataAccessException {return result(query(sql, new RowMapperResultSetExtractor<>(rowMapper)));
}
下一步(进入query方法):
@Override
@Nullablepublic T query(final String sql, final ResultSetExtractor rse) throwsDataAccessException {
Assert.notNull(sql,"SQL must not be null");
Assert.notNull(rse,"ResultSetExtractor must not be null");if(logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Executing SQL query [" + sql + "]");
}/*** Callback to execute the query.*/
class QueryStatementCallback implements StatementCallback, SqlProvider {
@Override
@Nullablepublic T doInStatement(Statement stmt) throwsSQLException {
ResultSet rs= null;try{
rs=stmt.executeQuery(sql);returnrse.extractData(rs);
}finally{
JdbcUtils.closeResultSet(rs);
}
}
@OverridepublicString getSql() {returnsql;
}
}return execute(newQueryStatementCallback());
}
下一步:
@Override
@Nullablepublic T execute(StatementCallback action) throwsDataAccessException {
Assert.notNull(action,"Callback object must not be null");
Connection con=DataSourceUtils.getConnection(obtainDataSource()); //获取connection(算法骨架)
Statement stmt= null;try{
stmt=con.createStatement(); //获取statement(算法骨架)
applyStatementSettings(stmt);
T result=action.doInStatement(stmt); //执行具体的操作(延迟到子类的操作)
handleWarnings(stmt);returnresult;
}catch(SQLException ex) {//Release Connection early, to avoid potential connection pool deadlock//in the case when the exception translator hasn't been initialized yet.
String sql =getSql(action);
JdbcUtils.closeStatement(stmt);
stmt= null;
DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, getDataSource());
con= null;throw translateException("StatementCallback", sql, ex);
}finally{
JdbcUtils.closeStatement(stmt);//关闭statement(算法骨架)
DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, getDataSource());//关闭connection(算法骨架)
}
}
通过上述代码分析可以看出,spring的JdbcTemplate为我们实现了模板流程和方法(即算法骨架),我们需要做的就是配置好JdbcTemplate的dataSource,并且将JdbcTemplate纳入spring的管理,然后编写具体的数据库访问逻辑就可以了。
一是为我们省了繁琐的通用流程,像获取关闭connection、statment;
二是为我们提供了非常丰富且优雅的api进行sql操作。







 本文介绍如何使用Spring的JdbcTemplate简化数据库操作流程,避免重复代码,提高开发效率。通过实例展示了JdbcTemplate的基本配置及使用方法。
本文介绍如何使用Spring的JdbcTemplate简化数据库操作流程,避免重复代码,提高开发效率。通过实例展示了JdbcTemplate的基本配置及使用方法。
















 26
26

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








