Windows Azure Storage allows application developers to store their data in the cloud, so the application can access its data from anywhere at any time, store any amount of data and for any length of time, and be confident that the data is durable and will not be lost. Windows Azure Storage provides a rich set of data abstractions:
· Windows Azure Blob – provides storage for large data items.
· Windows Azure Table – provides structured storage for maintaining service state.
· Windows Azure Queue – provides asynchronous work dispatch to enable service communication.
To use Windows Azure Storage a user needs to create a storage account. This is done via the Windows Azure portal web interface. The user will receive a 256-bit secret key once the account is created. This secret key is then used to authenticate user requests to the storage system. Specifically, a HMAC SHA256 signature for the request is created using this secret key. The signature is passed with each request to authenticate the user requests by verifying the HMAC signature.
Windows Azure Blob Data Modal
The figure below depicts the namespace of Windows Azure Blob.
· Storage Account – All access to Windows Azure Storage is done through a storage account.
o This is the highest level of the namespace for accessing blobs
o An account can have many Blob Containers
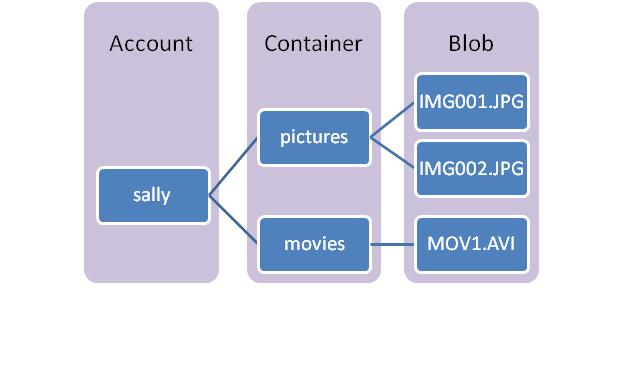
- Blob Container – A container provides a grouping of a set of blobs. The container name is scoped by the account.
o Sharing policies are set at the container level. Currently "Public READ" and "Private" are supported. When a container is "Public READ", all its contents can be read by anyone without requiring authentication. When a container is "Private", only the owner of the corresponding account can access the blobs in that container with authenticated access.
o Containers can also have metadata associated with them. Metadata is in the form of <name, value> pairs, and they are up to 8KB in size per container.
o The ability to list all of the blobs within the container is also provided.
· Blob – Blobs are stored in and scoped by Blob Containers. Each blob can be up to 50GB. A blob has a unique string name within the container. Blobs can have metadata associated with them, which are <name, value> pairs, and they are up to 8KB in size per container. The blob metadata can be gotten and set separately from the blob data bits.




 本文介绍了Windows Azure存储服务,包括Blob、Table和Queue三种主要的数据抽象方式。详细阐述了如何创建存储账户并使用256位密钥进行身份验证的过程。此外,还深入解析了Blob数据模型,包括存储账户、Blob容器及Blob等概念。
本文介绍了Windows Azure存储服务,包括Blob、Table和Queue三种主要的数据抽象方式。详细阐述了如何创建存储账户并使用256位密钥进行身份验证的过程。此外,还深入解析了Blob数据模型,包括存储账户、Blob容器及Blob等概念。
















 7
7

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








