List方法举例:
1 package com.zhuoyue.rq; 2 3 import java.util.LinkedList; 4 import java.util.List; 5 6 public class ListTest { 7 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 List l1 = new LinkedList(); 10 for(int i=0;i<=5;i++){ 11 l1.add("a"+i); 12 } 13 System.out.println(l1); 14 l1.add(3,"a100");//在第3个位置,插入,其他元素后移 15 System.out.println(l1); 16 l1.set(6,"a200");//把第6个位置设置为a200,覆盖第6个位置的元素 17 System.out.println(l1); 18 System.out.println((String)l1.get(2)+" ");//0,1,2 第2个 19 System.out.println(l1.indexOf("a3"));//4 20 l1.remove(1); 21 System.out.println(l1); 22 } 23 24 }
执行结果:

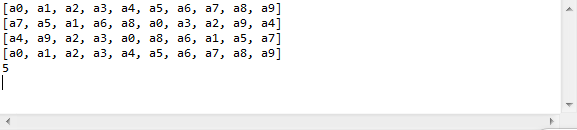
举个栗子:
1 package com.zhuoyue.rq; 2 3 import java.util.Collections; 4 import java.util.LinkedList; 5 import java.util.List; 6 7 public class ListTest2 { 8 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 List l1 = new LinkedList(); 11 for(int i=0;i<=9;i++){ 12 l1.add("a"+i); 13 } 14 System.out.println(l1); 15 Collections.shuffle(l1);//随机排序 16 System.out.println(l1); 17 Collections.reverse(l1);//逆序 18 System.out.println(l1); 19 Collections.sort(l1);//排序 20 System.out.println(l1); 21 System.out.println(Collections.binarySearch(l1, "a5"));//折半查找 22 } 23 24 }
运行结果:
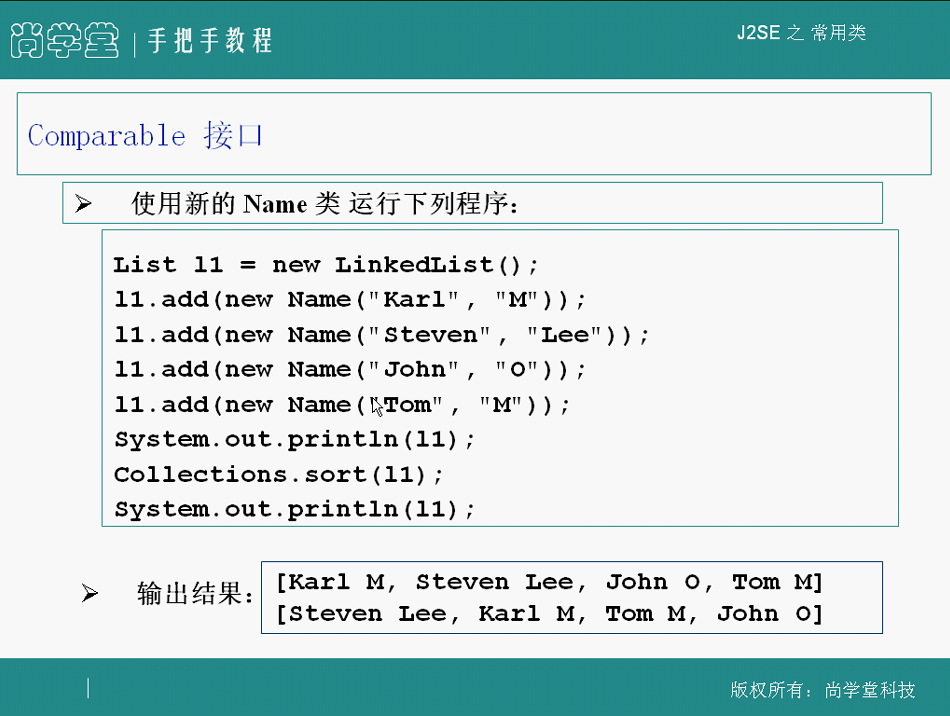
Comparable接口

举个栗子:
1 import java.util.*; 2 3 public class BasicContainer { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 Collection c = new HashSet(); 6 c.add("hello"); 7 c.add(new Name("f1","l1")); 8 c.add(new Integer(100)); 9 c.remove("hello"); 10 c.remove(new Integer(100)); 11 System.out.println 12 (c.remove(new Name("f1","l1"))); 13 System.out.println(c); 14 } 15 16 17 } 18 19 class Name implements Comparable { 20 private String firstName,lastName; 21 public Name(String firstName, String lastName) { 22 this.firstName = firstName; this.lastName = lastName; 23 } 24 public String getFirstName() { return firstName; } 25 public String getLastName() { return lastName; } 26 public String toString() { return firstName + " " + lastName; } 27 28 public boolean equals(Object obj) { 29 if (obj instanceof Name) { 30 Name name = (Name) obj; 31 return (firstName.equals(name.firstName)) 32 && (lastName.equals(name.lastName)); 33 } 34 return super.equals(obj); 35 } 36 public int hashCode() { 37 return firstName.hashCode(); 38 } 39 40 41 42 public int compareTo(Object o) { 43 Name n = (Name)o; 44 int lastCmp = 45 lastName.compareTo(n.lastName); 46 return 47 (lastCmp!=0 ? lastCmp : 48 firstName.compareTo(n.firstName)); 49 } 50 51 }
数据结构的选择:
Array读快改慢
Linked读慢改快
hash两者之间
Map接口
键值
实现类有hashmap和treemap
键不能重复(equals)
Map方法举例:
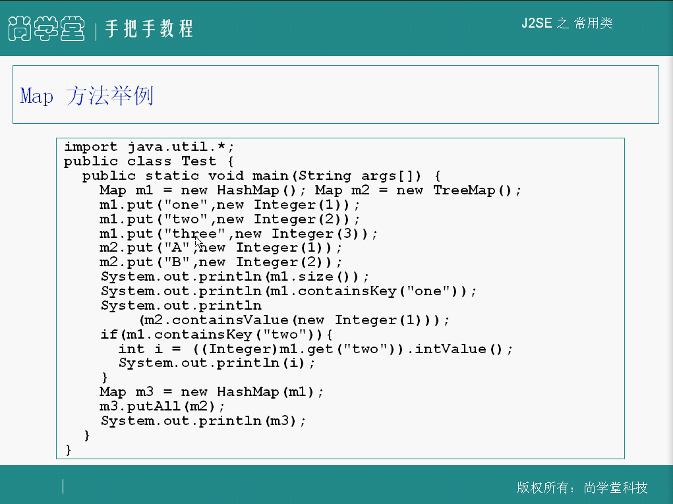
假如原来位置有值,put返回原来位置的值,把新的值加进去




 本文通过实例展示了Java中List接口的使用方法,包括添加、删除、获取、排序、随机排序、逆序等操作,并介绍了Comparable接口和数据结构选择的重要性。此外,还探讨了Map接口的应用场景和实现类,以及如何进行数据存储与检索。
本文通过实例展示了Java中List接口的使用方法,包括添加、删除、获取、排序、随机排序、逆序等操作,并介绍了Comparable接口和数据结构选择的重要性。此外,还探讨了Map接口的应用场景和实现类,以及如何进行数据存储与检索。
















 2900
2900

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








